8 Steps To Start a Sustainable ECommerce Business








For businesses that are just entering the market, the term “eCommerce” is often recognized through eCommerce marketplaces. Most managers are often unsure of where to start, including which systems to use, which eCommerce platform to choose for development, and what steps to take next.
Therefore, in this article, SECOMM will share comprehensive information from basics to advanced levels to kickstart eCommerce business in Vietnam.
1. Learn about eCommerce business
According to Decree No. 52/2013/ND-CP on eCommerce: “eCommerce activities involve conducting all or part of the commercial process through electronic means connected to the Internet, mobile telecommunications networks, or other open networks.”
In simpler terms, eCommerce business is the activity of buying and selling goods or services online.

2. Popular eCommerce models
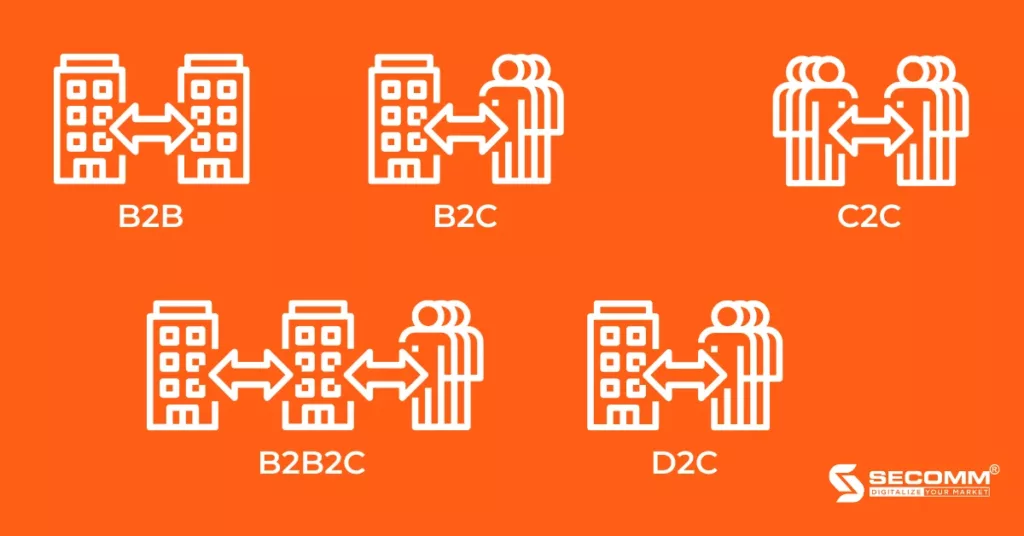
B2C
B2C (Business to Customer) involves transactions between businesses and customers. This is also the most common model in the Vietnamese market.
Example: Thế Giới Di Động is the number one retail model in Vietnam’s eCommerce market for devices such as phones, laptops, tablets, and accessories.
- Website: https://www.thegioididong.com/
- Monthly traffic: 62.23 million
- Website ranking: #19 (Vietnam), #758 (Global)
B2B
B2B (Business to Business) involves commercial transactions between two businesses.
Example: TELIO is Vietnam’s first B2B eCommerce platform, facilitating the connection between small-scale traditional retailers and brands by aggregating demand, providing more choices, better prices, and more efficient logistics support.

- Website: https://www.telio.vn/
- Monthly traffic: 5 million
- Website ranking: #112,909 (Vietnam), #6,105,937 (Global)
B2B2C
B2B2C (Business to Business to Customer) is a business model that involves collaboration between two businesses (B2B) to create and deliver products or services to end consumers (B2C).
Example: Shopee is the most popular eCommerce platform in Vietnam. Shopee Vietnam initially operated under a C2C model, serving as an intermediary in the buying and selling process between individuals. However, Shopee Vietnam has evolved into a B2B2C hybrid model by offering various services and conveniences to support the shopping process for both businesses and consumers.
- Website: https://shopee.vn/
- Monthly traffic: 105.5 million
- Website ranking: #6 (Vietnam), #295 (Global)
C2C
C2C (Consumer to Consumer) is a form of business where transactions occur directly between two individuals rather than involving businesses.
Example: Chợ Tốt is an eCommerce website that facilitates transactions between individual sellers and buyers for items such as real estate, cars, job postings, used electronics, pets, and various home services.

- Website: https://www.chotot.com/
- Monthly traffic: 13.19 million
- Website ranking: #54 (Vietnam), #2,980 (Global)
D2C
D2C (Direct to Customer) is a business model that delivers products directly from the business to the customer, bypassing intermediary distribution channels.
Example: Coolmate is a men’s fashion startup established in 2019. Within just 2 years of operation, the brand raised a rapid $500,000 in funding for Sharktank.

- Website: https://www.coolmate.me/
- Monthly traffic: 1.204 million
- Website ranking: #861 (Vietnam), #46,051 (Global)
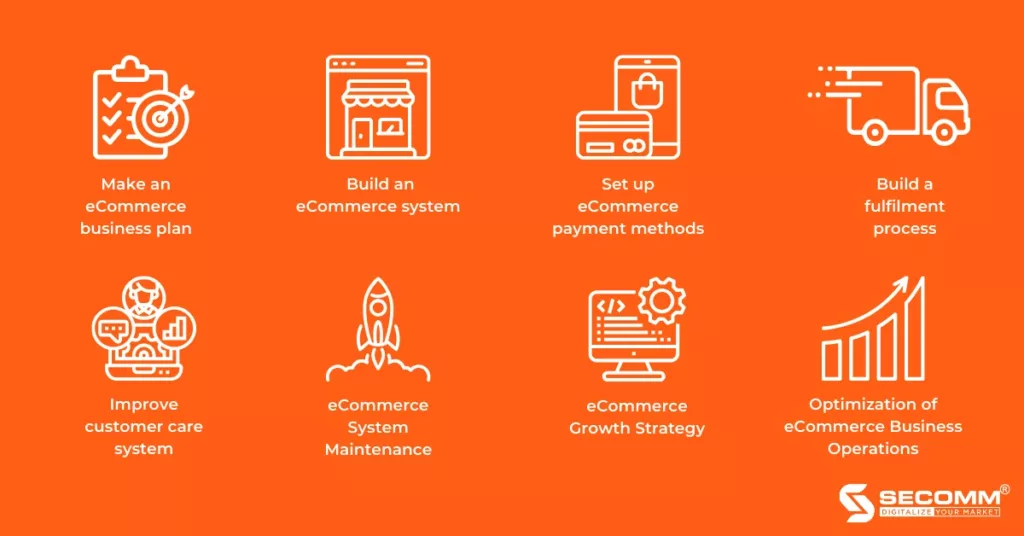
3. Steps to start a sustainable eCommerce business
Step 1. Make an eCommerce business plan
When starting to plan a business, the first step that managers should take is market research to understand the overall market situation, details about competitors, trends, and consumer behaviour. Some free and reputable sources businesses can refer to include the White Paper on eCommerce in Vietnam by IDEA, the e-Conomy SEA report by Google & Temasek, the eCommerce Index report by Vecom, etc.
After conducting market research, the next thing businesses should pay attention to is defining objectives, such as adding sales channels to increase revenue, positioning the brand in the eCommerce market, supporting marketing campaigns, enhancing user experience and interaction, etc.
Following market research and goal setting, businesses should also budget and plan the implementation timeline for each stage of eCommerce operations. Depending on the goals and strategies, each business will set budgets and timelines for the most effective eCommerce operations.
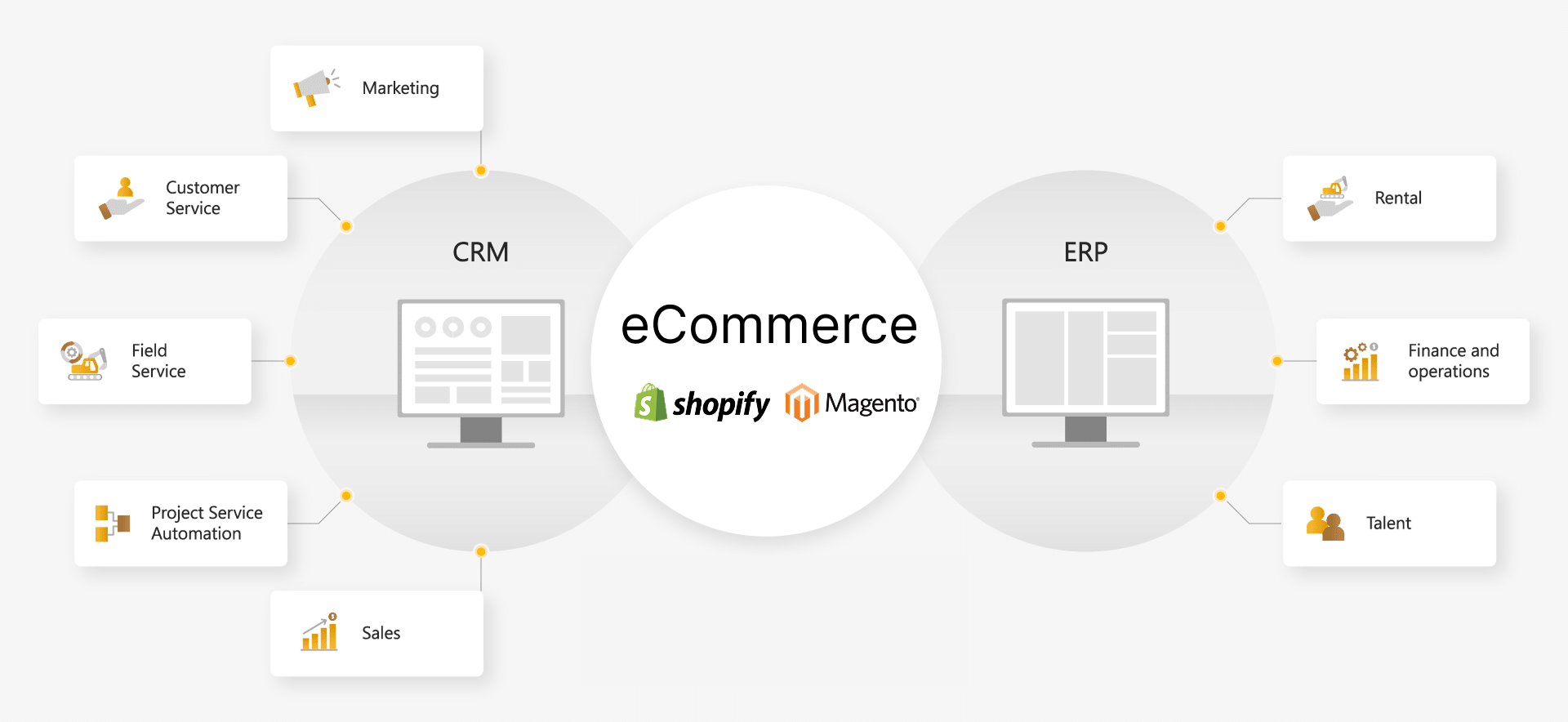
Step 2. Build an eCommerce system
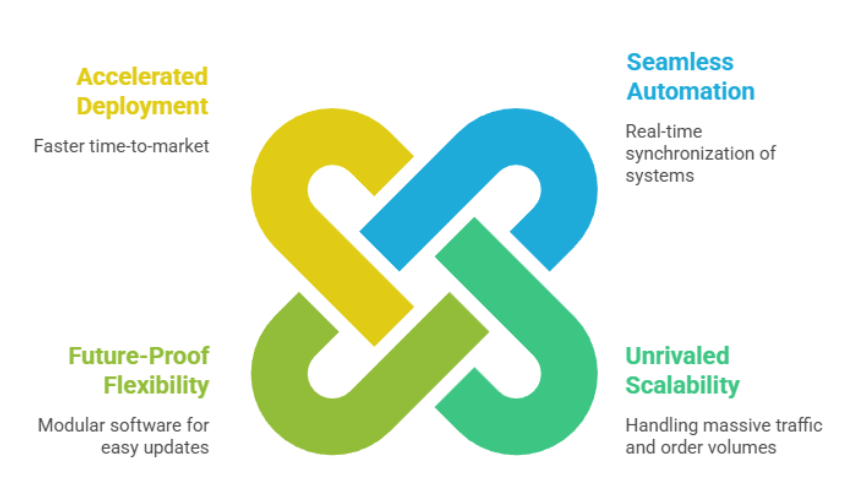
Next, businesses need to choose an eCommerce platform to build a system that aligns with the brand’s scale and strategy. The components of an eCommerce system typically include a website and an eCommerce website application.
There are two main types of platforms nowadays: SaaS (Software as a Service) and Open Source.
For Open Source platforms:
- Advantages: Full ownership of source code and data, the ability to build advanced features, flexible customization, easy integration, and scalability.
- Disadvantages: High initial development costs and specialized expertise required, often requiring experienced professionals for implementation.
- Popular Open Source platforms: Magento, WooCommerce, OpenCart, PrestaShop, etc.
- Target users: Suitable for businesses looking for a long-term investment, aiming to save costs in the future.
For SaaS platforms:
- Advantages: User-friendly, many pre-built interfaces and features, low initial costs.
- Disadvantages: Increasing usage fees over time, limited customization and scalability, and challenging integration with external tools.
- Popular SaaS platforms: Haravan, Shopify Plus, BigCommerce, Squarespace, Wix, etc.
- Target users: Suitable for businesses needing a simple website with minimal customization.
Once the eCommerce platform is selected, businesses have two options for resources to build the website: building an in-house team or using services from developers.
For building an in-house team, businesses need to recruit and train IT and eCommerce professionals with expertise and experience on the chosen platform. This process may take time and budget to build a suitable team but provides better control over resources, allowing adjustments or developments according to specific requirements.
For collaborating with development firms, businesses should seek developers based on criteria such as deep experience in eCommerce, an experienced team, a clear process, quick handling and support, and commitments to warranty and maintenance. This approach helps businesses gain professional expertise, enhance experience, and develop a suitable website.
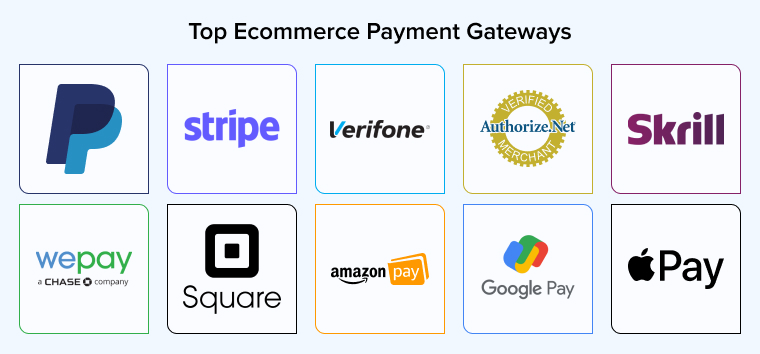
Step 3. Set up eCommerce payment methods
In the eCommerce market, there are various payment methods, with Cash on Delivery (COD) being the most common. However, due to the rise of “cashless” payment trends amid the Covid-19 pandemic, electronic payment methods are gaining more prominence.
Some payment methods chosen by eCommerce businesses include:
- Bank Transfer: Transferring money from the buyer’s bank account to the seller’s bank account to pay for products or services. Internet Banking and Mobile Banking are gradually replacing traditional ATM transfers.
- Online Payment Gateways: Systems connecting banks, buyers, and sellers, allowing the seller to receive funds immediately when online transactions are completed. Some popular gateways in Vietnam such as VNPay, ZaloPay, Payoo, Paypal, Onepay, etc.
- E-wallets: Payment through e-wallets involves linking a bank account, depositing money into the wallet, and making simple and convenient payments for linked services. Some popular E-wallets in Vietnam such as Momo, ZaloPay, VNPay.
- Scratch Cards: Allowing users to pay or top up their electronic accounts by purchasing scratch cards from mobile network providers such as Viettel, Mobifone, Vinaphone, etc. However, this payment method is often limited to certain eCommerce platforms and specific websites.
- Brand-Specific Cards/Wallets: Payment methods designed and allowed for use within the system of a specific brand or business. Some popular wallets such as Shopee Wallet, Lazada’s eM Wallet, Starbucks Card, VinID by VinGroup.
- E-vouchers: Also known as online discount vouchers/codes provided by eCommerce businesses like Shopee, Lazada, Tiki, etc.
Step 4. Build a fulfilment process
Usually, a fulfilment process includes the following steps: Importing goods or manufacturing → Shipping to warehouse/distribution centre → Warehousing → Processing goods upon request (Shipping, invoicing, packaging, labelling) → Delivery → Handling post-sale requests (Returns, refunds, exchanges).
Therefore, a comprehensive eCommerce system needs to build or integrate functionalities such as eLogistics, blockchain, QR codes, etc., to automate the shipping process, track orders, and thereby enhance the quality of delivery to end consumers.
Step 5. Improve customer care system
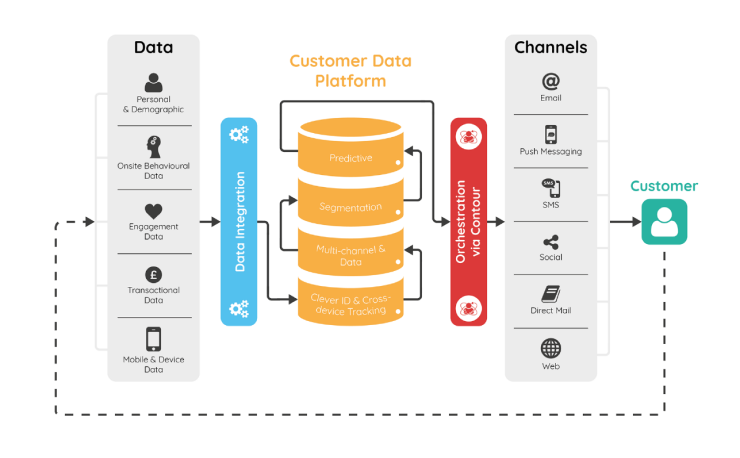
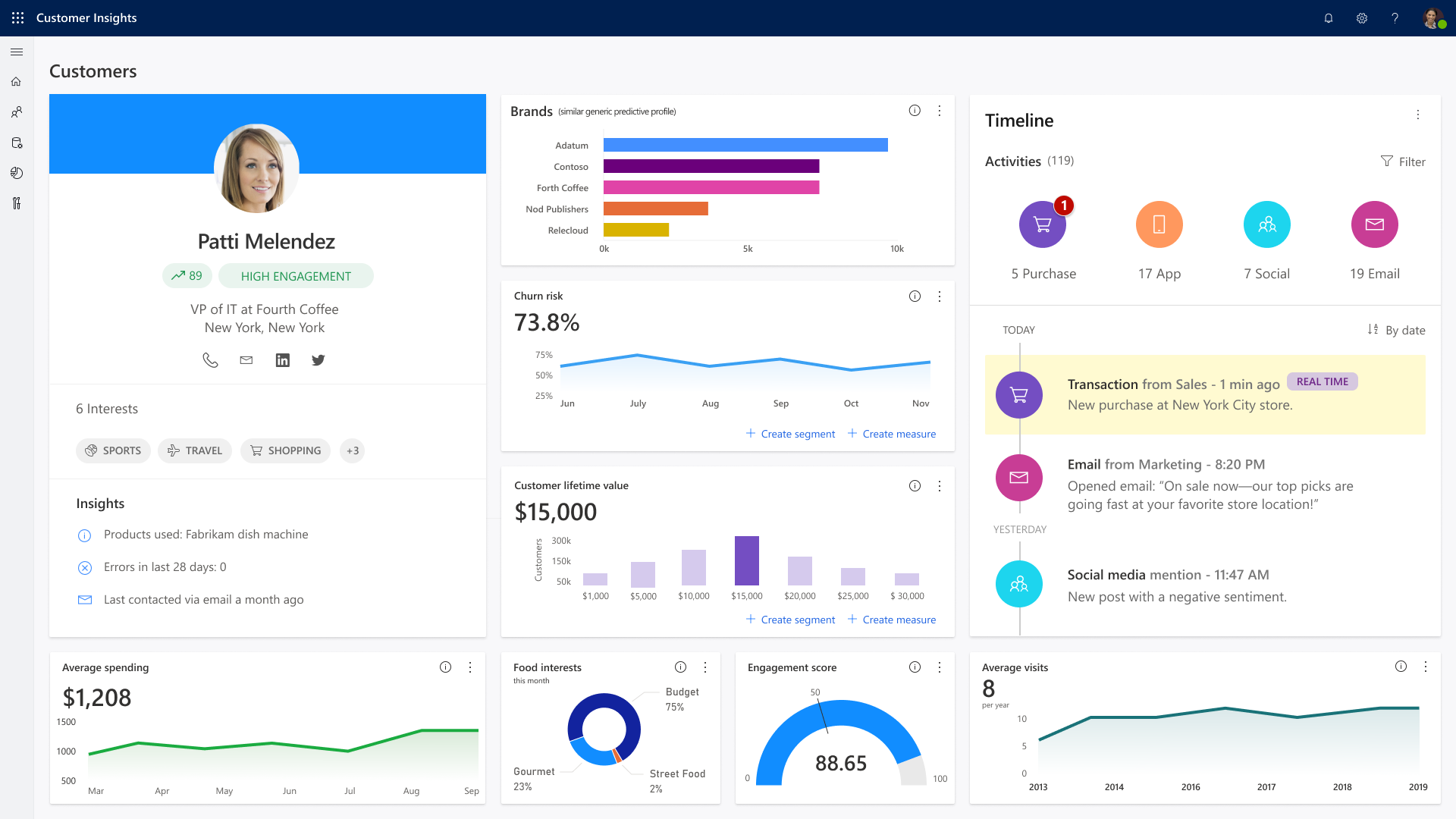
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is an essential component in the operation of eCommerce businesses. Building and continuously improving the CRM system, as well as implementing a multi-channel customer care centre, helps expedite the processing of complaints, returns, and refunds. Additionally, a CRM system assists businesses in gaining insights into customer needs, facilitating the establishment of interactions between the brand and its customers.
Step 6: eCommerce System Maintenance
Maintaining the eCommerce system 24/7, continually updating and upgrading it helps businesses promptly address arising issues, achieve sustainable sales growth, and adapt quickly to the ever-changing market. Simultaneously, continuous monitoring and maintaining eCommerce operations aim to prevent risks from hackers, data breaches, etc.
Step 7: eCommerce Growth Strategy
One of the crucial strategies in current eCommerce operations is omnichannel selling. By following customers’ “footprints” across eCommerce platforms (Shopee, Lazada, Tiki, Sendo), social media (Facebook, TikTok, Instagram, Zalo), websites, and eCommerce apps, this strategy centralizes customer data, reaches diverse shopping behaviours, and optimizes personalized experiences in the eCommerce system. Additionally, various eCommerce marketing campaigns are being developed, such as Affiliate Marketing, Shoppertainment, SEO, Email Marketing, etc. This strategy optimizes brand visibility and boosts online sales.
Step 8: Optimization of eCommerce Business Operations
Building reporting functions to exploit the efficiency of data, including reports on Sales, Marketing, Customers, Inventory, and Operational Performance, to improve and enhance business efficiency. Integrating analytical tools such as Google Analytics, Facebook Pixels, Microsoft Power BI, etc., supports tracking and measuring system performance to provide detailed reports on business results in eCommerce.
In summary, conducting eCommerce based on the above 8 steps is not an easy task for business managers. To stay competitive in the eCommerce race, various factors come into play, including financial strength, human resources, the general economic situation, changes in consumer behaviour, etc. Therefore, managers need to be cautious when making critical decisions to bring business efficiency.
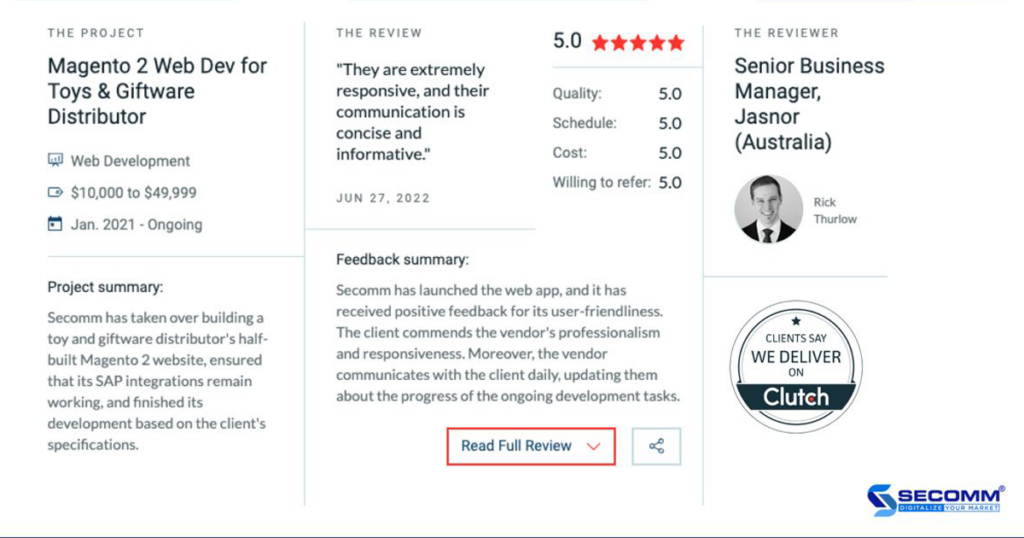
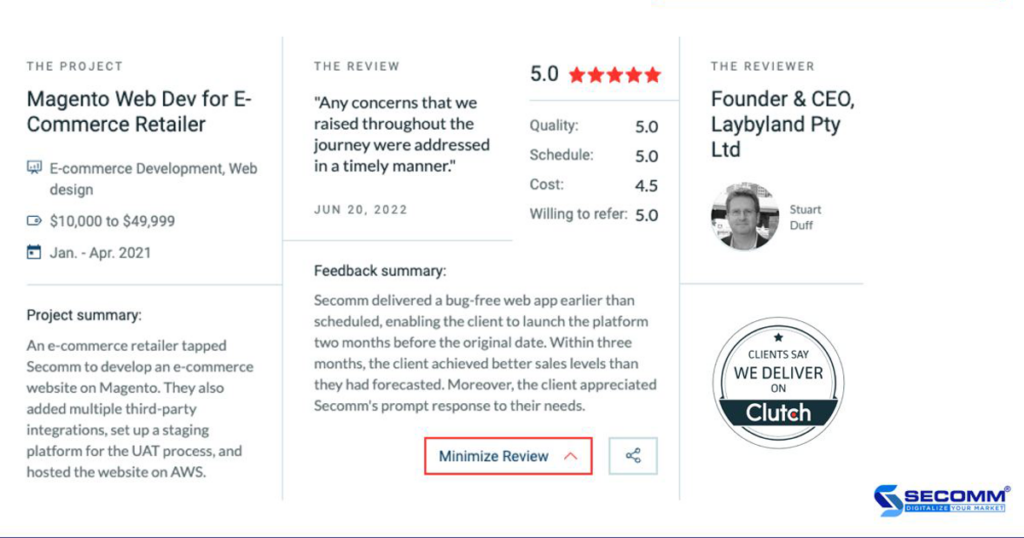
With over 9 years of experience in designing complex eCommerce systems for companies like Annam Gourmet, Laybyland, and Jasnor, SECOMM understands the challenges businesses face in researching and efficiently implementing eCommerce.
Contact SECOMM now for free consultation on detailed eCommerce system development solutions!
























































Comment (0)