It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Sign Up for newsletter!
Subscribe to get the latest eBook!
Hotline


 2
2
 4,042
4,042
 0
0
 1
1
 2
2
 10,202
10,202
 0
0
 1
1
 2
2
 10,053
10,053
 0
0
 1
1
 2
2
 10,039
10,039
 0
0
 1
1
 2
2
 9,940
9,940
 0
0
 1
1



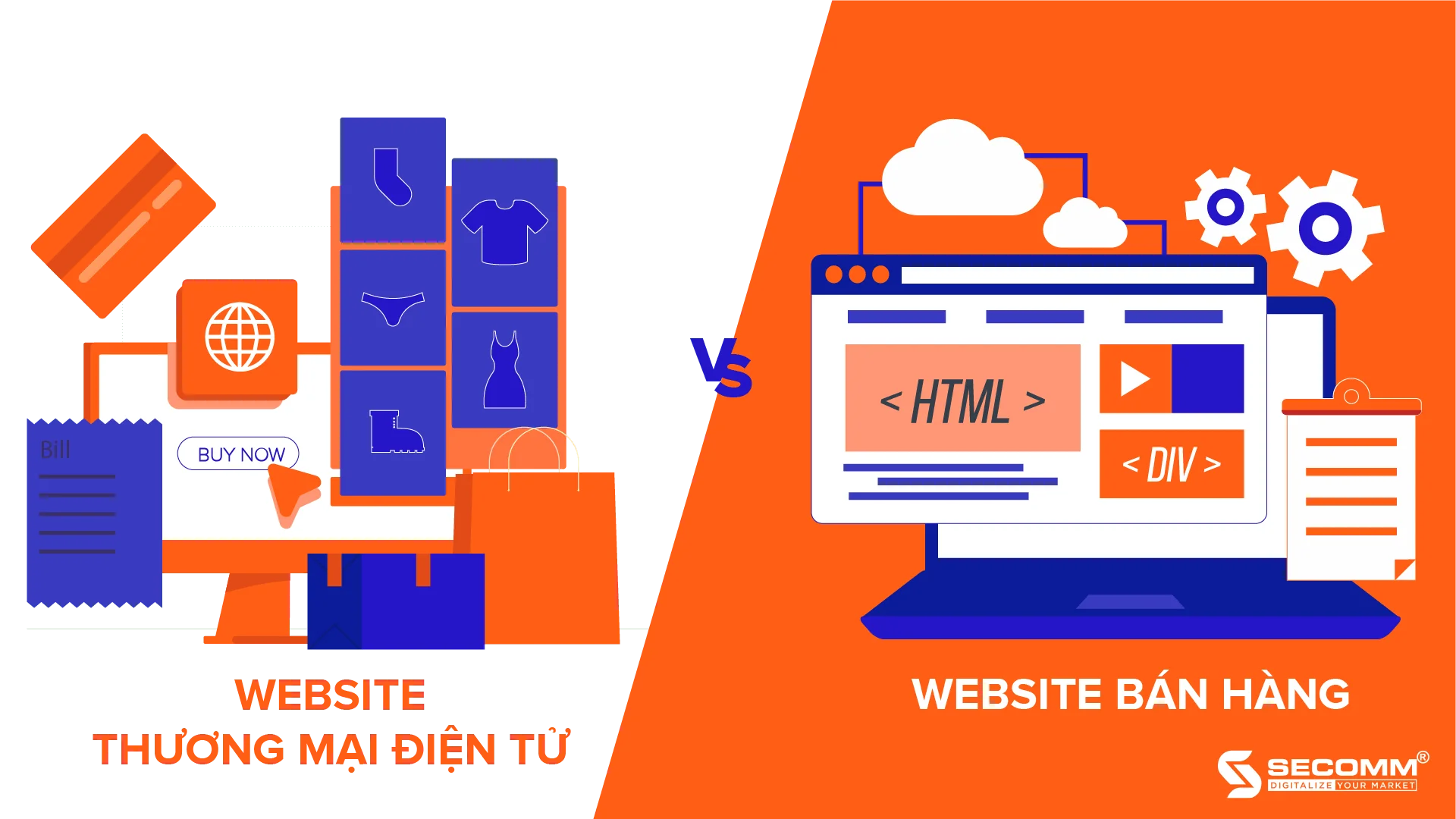
Ecommerce websites and online shopping websites both serve the purpose of buying and selling products and services online for businesses.
So:
An e-commerce website is established to serve the entire process of selling goods or providing services, from providing information and introducing the business, products or services, to supporting payment and post-purchase services. In particular, the payment feature on e-commerce websites is executed through multiple steps and follows certain standards. On the other hand, shopping websites mainly provide information about the store, business, or the products and services offered.

In terms of scale, e-commerce websites typically have a diverse range of product categories and services. In contrast, shopping websites usually only deal with a specific set of products or areas, so the scale is generally small to medium.

To present a variety of products, and services to customers, and support businesses in managing their online business systems, e-commerce websites need a complex back-end operating system (data access layer) with integrated functions such as customer management, product category management, analysis and reporting, SEO support, Ecommerce Marketing, Omni-channel (ecommerce platforms such as Shopee, Lazada, Tiki, Sendo; social networks such as Facebook, Zalo, Tiktok, Linkedin, and individual e-commerce websites…) online payment, and shipping services. In contrast to e-commerce websites, shopping websites primarily introduce businesses and products, so they do not require the integration of many supporting features.

The interface of ecommerce websites is usually focused on and designed meticulously with a standardized UI, UX. Not only eye-catching, professional, and impressive, the interface of ecommerce websites also needs to demonstrate the complex features underlying the system and provide an optimal online shopping experience for users. Shopping websites have a simple interface and operational functions because they focus on only one type of product or specific area.

With a professional interface and a complex feature system, the investment cost for designing e-commerce websites is generally higher than for shopping websites. Especially for websites with a diverse feature set, the costs can be even higher. Regarding shopping websites, the development cost is usually lower as they are developed from a simple platform and sometimes do not require much specialized knowledge.

In summary, shopping websites are suitable for businesses that deal with a few products, services, or a specific industry group, do not require many complex features, and need to save website construction costs.
On the other hand, e-commerce websites are suitable for businesses with a diverse range of products and services, have the need to develop an ecommerce system for long-term business and budget savings, have specific growth goals, and have the financial capacity to enter the ecommerce market.
 2
2
 3,987
3,987
 0
0
 1
1
A website is a powerful tool for supporting ecommerce (Electronic Commerce) business, serving as a bridge between businesses and customers in the online shopping market, facilitating the entire process of buying and selling goods, and boosting sales. Therefore, building an ecommerce website is crucial for the ecommerce business of a company, requiring not only serious investment but also a long-term strategy.
However, there are still many ecommerce websites facing certain issues that need to be addressed promptly! Here are some common problems:
To evaluate the speed of a website, tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, WebPageTest, Pingdom Speed Test, Uptrends, etc., can be used.
Scores range from 0 to 100, where 0-49 indicates relatively low speed, 50-89 indicates average speed that needs improvement, and 90-100 indicates excellent speed.
Slow page load speed affects user experience, conversion rates, customer retention, and SEO ranking.
Causes:
Solutions:
Issues with graphic design, colour schemes, inconsistent images and fonts, lack of brand representation, and non-optimal website structure affect the professionalism of the interface.
Consequences:
Causes:
Solution:
Poorly structured product categories and incomplete product information negatively impact the user experience.
Issues:
Consequences:
Solutions:
Websites should support customer search, and provide convenient and quick shopping processes.
Issues:
Consequences:
Causes:
Solutions:
Failure to link sales channels (social media, ecommerce platforms, ecommerce websites) with internal business systems like CRM, and ERP for synchronization can lead to misinformation and management difficulties.
Issues:
Consequences:
Causes:
Solution:
 2
2
 4,656
4,656
 0
0
 1
1
When deploying an ecommerce website, Magento is the top choice of platform that businesses are aiming for, including global giants like Nike, ASUS, HP, and Burger King, as well as leading Vietnamese enterprises such as Canifa, CellphoneS, Trung Nguyen, and CGV Vietnam.
With outstanding advantages ranging from a diverse ecosystem and flexible customisation capabilities to absolute security, Magento is considered the ‘ultimate boss’ among ecommerce website development platforms today.
So, what are the superior points of Magento?
Magento possesses all the features for a complete ecommerce website:
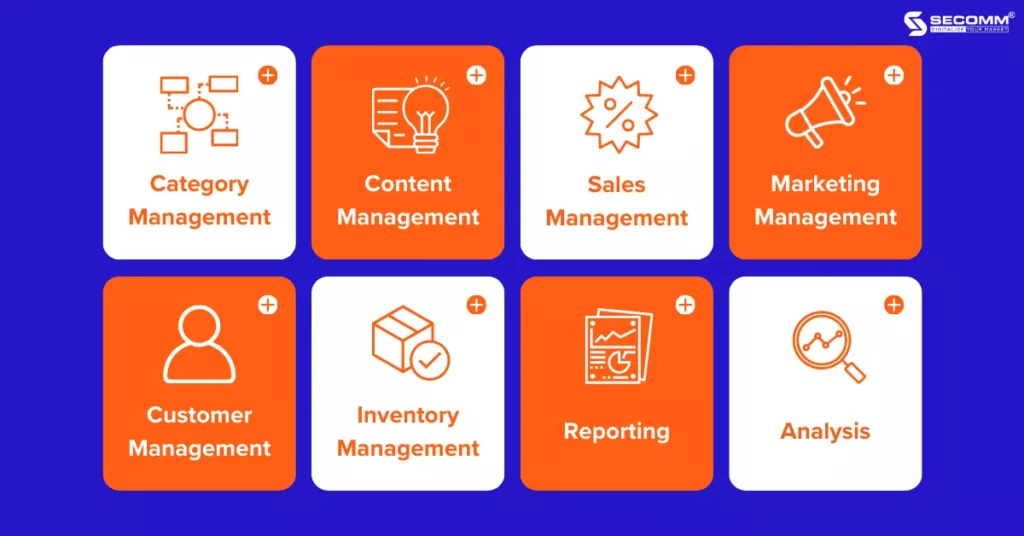
In addition to the basic features of a complete ecommerce website, Magento also owns a diverse system of extensions with many advanced functions in themes, products, marketing, optimal payment solutions, shipping, etc. to meet every operational need and ensure sustainable development of ecommerce for businesses.
When building an ecommerce website, Magento also supports businesses to integrate and link third-party services for efficient ecommerce website operation, such as:
Furthermore, Magento also has a global technical support community, including many rich experts and professional developers to meet all the requirements of businesses.
The Magento ecommerce website platform possesses all the advantages of open-source software with flexible customisation capabilities to operate the ecommerce website more effectively.

High security is also a superior advantage of Magento compared to other ecommerce website platforms, helping businesses minimise potential risks from data systems and transaction processes on the system.
Some outstanding points of Magento’s security features include:

With the advantages of having all ecommerce website functions, from basic to advanced, high customisation capabilities, and high security, Magento is the top choice for businesses when deploying an ecommerce website system. However, issues related to costs, time, and the requirement for a highly specialised technical team make it challenging for many businesses to implement an ecommerce website system with Magento.
Contact SECOMM now for FREE CONSULTATION SUPPORT!
 2
2
 4,055
4,055
 0
0
 1
1
The recent Covid-19 pandemic has influenced a shift in the purchasing behaviour of consumers, including businesses in the manufacturing and wholesale markets of B2B. It has prompted businesses to gradually transition from traditional business models to Business-to-Business (B2B) ecommerce.
B2B ecommerce involves online business transactions between two enterprises. According to “The Ultimate B2B Ecommerce Guide: Tradition is out. Digital is in,” published by DHL Express, it demonstrates the significant potential of the B2B ecommerce market, projecting a growth of over 70% by 2027, equivalent to 20.9 trillion USD.
Why should businesses implement B2B ecommerce now?
A structured product catalogue interface, making product searches easier. Adding/removing products from the cart and automatically calculating the total cost makes order control more convenient. Features like keyword search, quick product filtering, fast cart access, and speedy checkout facilitate the online shopping process for customers.
Traditionally, B2B customers faced barriers in the invoicing process and traditional payment methods. Nowadays, payments in B2B ecommerce occur more quickly. Businesses can easily set up electronic invoices for data management. Customers have various payment options: Cash, Bank Transfer, Internet Banking, E-wallets, Installments, or Regular Payments. The payment process takes place on the phone or computer with an internet connection.
Ecommerce websites support online shopping consultation with features like Live Chat (direct communication with customers) and Chatbox (answering frequently asked questions without the need for a consultant).
Simplified registration process, only requiring online form registration (information collection and customer shopping needs) and the creation of electronic contracts for transaction signing.
In B2B ecommerce, detailed information on product prices and pricing policy changes is always updated on the website.
Order processing speed is faster thanks to:
Sales processes are automated through:
Production costs are reduced by producing according to customer orders instead of mass production. Additionally, it saves costs for premises, paperwork, printing, etc.
Improved post-sales services:
Building a return/exchange policy:
Regarding the personnel system:
Ecommerce B2B websites operate 24/7 with almost no staff, optimizing personnel costs. Additionally, the B2B ecommerce system supports businesses in assigning tasks and managing the progress of employees.
What data is exploited?
What can be done with this data?
Reporting:
Support business analysis and forecasting based on the collected data. Determine how factors are influenced by various elements.
Implement personalized experiences: Personalized emails, and product recommendations.
Improve revenue based on the received reports and analysis:
Plan long-term business development strategies. Introduce improvements to new products and associated services (payment, shipping, etc.).
In summary, B2B ecommerce contributes to improving business models, boosting sales, and expanding the sales network for enterprises. However, implementing B2B ecommerce is still new to many B2B business owners, and they may not know where to start and how to improve the ecommerce system!
As an expert in providing comprehensive ecommerce solutions, SECOMM supports B2B enterprises with:
Contact SECOMM now for FREE CONSULTATION SUPPORT!
 2
2
 7,415
7,415
 0
0
 1
1
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) ecommerce is online transactions between businesses and consumers.
B2C ecommerce is considered a potential market for Vietnamese businesses at present. According to the 2020 Ecommerce White Paper, B2C ecommerce in Vietnam reached 11.8 billion USD, ranking 3rd in the ASEAN region, with a 41% increase in new participants, the highest in the region.
This type of ecommerce is currently popular with a global scale of 4,280 billion USD in 2020. Examples include the B2C websites of Mobile World (Top 5 with 16,606,700 visits), Bach Hoa Xanh (Top 9 with 5,440,000 visits), and FPT Shop (Top 10 with 4,213,300 visits).
Why do businesses need to implement B2C ecommerce?
Changes in consumer shopping habits have influenced the B2C ecommerce market. Customers tend to spend on brands in the online market rather than shopping and experiencing directly at physical stores. Therefore, implementing B2C ecommerce helps not only to position the brand in the market but also to maximize revenue and profit for businesses.
Effective Ecommerce Marketing campaigns help businesses reach more potential customers. On popular social media platforms (Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, Zalo), businesses can reach customers through advertising tools and directly interact with customers, supporting the brand’s presence in the subconscious of customers. Additionally, customer search habits for product information help businesses that have implemented SEO and SEM attract a large amount of traffic to their ecommerce websites, increasing the conversion rate of orders.
Establishing an additional online sales channel helps businesses maximize revenue. Unlike physical stores, ecommerce websites operate 24/7, supporting customers in shopping at any time. They also provide features to facilitate the online shopping process for consumers, such as quick search, product comparison, fast cart, recommended products, and quick payment. This speeds up the online shopping process, improves order conversion rate, and boosts business sales.
Moreover, in 2020, businesses that implemented B2C ecommerce demonstrated its importance when social distancing due to Covid-19 occurred. B2C businesses with ecommerce maintained their business activities compared to traditional businesses.
With the nature of unlimited time and location for shopping, online stores help businesses solve cost-related problems more effectively.
In the current era of “Big Data,” data plays a crucial role… When deploying their ecommerce systems, businesses can easily:
Examine scenarios that data has shown regarding developments in the B2C ecommerce market, thereby devising more suitable business strategies.
Upgrade B2C ecommerce systems to adapt to market changes. Introduce innovations in new products and accompanying services (payment, shipping…).
When a business successfully transitions to the B2C ecommerce business model, issues related to sales, marketing, and operations are improved.
Automate the sales process:
Order processing speed is faster:
Improve Marketing campaigns:
Improve Customer Support:
Personalize the user experience at each stage through:
Build better return/exchange policies:
After understanding the importance of B2C ecommerce for business development, the next important thing businesses need to do is learn about effective and flexible methods to deploy this system.
With more than 9 YEARS OF EXPERIENCE providing comprehensive ecommerce solutions for many businesses in various countries, SECOMM provides solutions such as:
Contact SECOMM now for FREE CONSULTATION SUPPORT!
 2
2
 7,282
7,282
 0
0
 1
1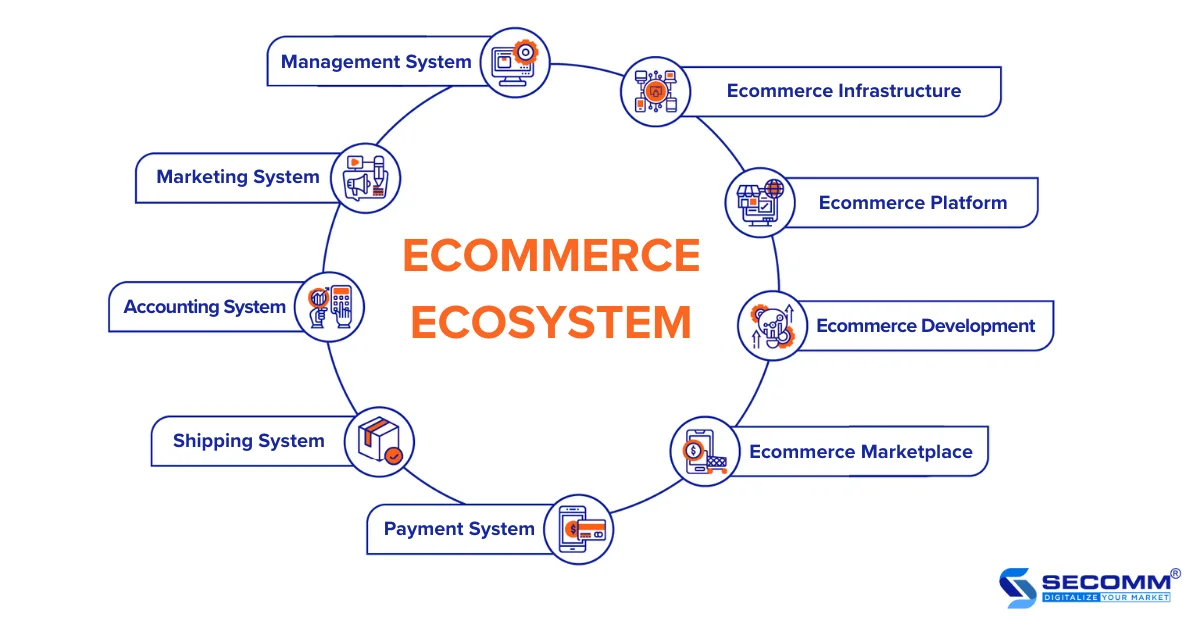
The ecommerce (Electronic Commerce) ecosystem is an open space that facilitates all interactions, connecting human factors, social elements, and information technology platforms with applications and services to provide value and efficiently operate components within the ecosystem. So, what are the components of the ecommerce ecosystem?
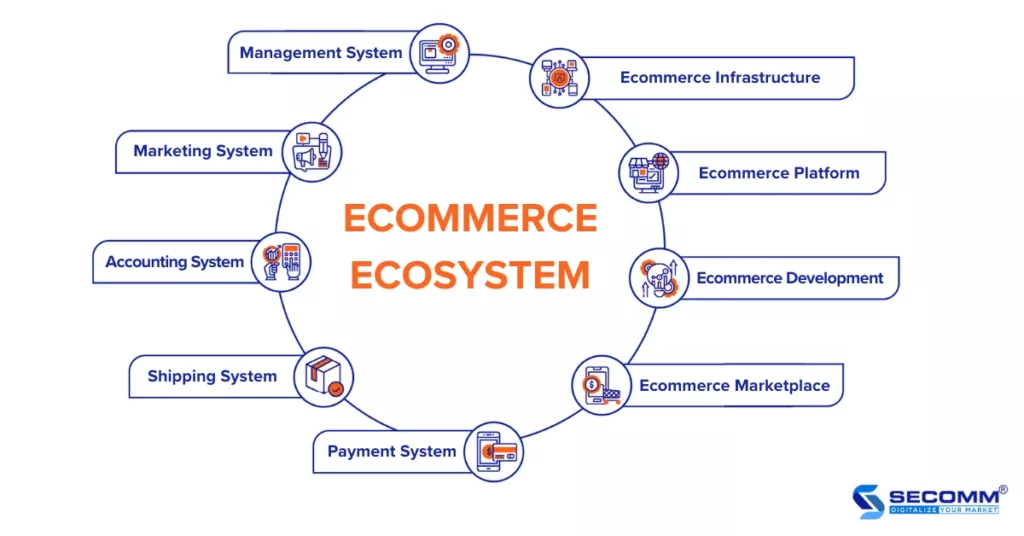
The system includes hardware (servers and devices), software (services/tools for management, and analysis), network systems, and physical facilities that form the foundation for the remaining components, ensuring smooth and efficient ecommerce processes.
Software applications are used to build and manage all activities within the system. Currently, businesses often use platforms such as Magento, Shopify, BigCommerce, WooCommerce, Haravan, and Wix to create ecommerce websites.
Provides services and solutions for developing websites, systems, and ecommerce processes. Some popular ecommerce solution providers in Vietnam include SECOMM, SmartOSC, Isobar, etc.
Provides an environment and all the services supporting ecommerce, allowing easy buying and selling between multiple sellers and buyers. Popular ecommerce marketplaces in Vietnam include Shopee, Lazada, Tiki, Sendo, etc.
Includes networks, systems, and devices processing all transactions within ecommerce. In addition to common payment methods such as cash, card payments (domestic cards, Visa, Mastercard, etc.), payment gateways (OnePay, PayPal, etc.), and e-wallets (Momo, ZaloPay, etc.) are developing in Vietnam.
The shipping system includes all processes for managing, distributing goods from warehouses, packaging, and delivering to customers. Popular shipping service providers in Vietnam include Giao Hàng Tiết Kiệm, Giao Hàng Nhanh, ViettelPost, J&T, Ahamove, etc.
Supports businesses in managing data related to invoices, sales revenue, and all financial flows in ecommerce activities. The emergence of e-invoicing software such as E-Invoice, MISA meInvoice, FPT.eInvoice, etc., has greatly supported accounting processes.
Marketing activities support effective brand and product development, reaching and personalizing customer experiences through strategies, channels, and supporting tools.
Uses resource management and operational process management software to enhance seamlessness and efficiency for the entire ecommerce system. Commonly used management systems include ERP, CRM, IMS, POS, OFM, etc.
In general, the components of the ecom ecosystem operate through a system of mechanisms, policies, and consistent laws to form a secure electronic data exchange system, ensuring the rights and responsibilities of businesses and consumers.
To achieve outstanding and sustainable growth, besides optimizing opportunities, businesses need to build a complete for themselves, creating a platform to enhance interactions between businesses, the market, and users more robustly. However, most Vietnamese businesses still face many challenges in building their ecommerce business plans. The majority of businesses have not correctly identified the necessary and appropriate components for their business models, leading to issues related to deployment time and budget constraints.
 2
2
 7,772
7,772
 0
0
 2
2
Frequent monitoring of metrics in business allows a deeper understanding of customers and quantifies important aspects of the business. Particularly in ecommerce (Electronic Commerce), measuring these indices is even more crucial as they assist businesses in assessing existing risks and opportunities in the market.
Indicates how much profit is generated for every dollar of revenue.
Formula: Gross Profit Ratio (%) = Gross Profit / Revenue
The value of goods sold or consumed during a specific period.
Formula: Cost of Goods Sold = Beginning Inventory + Additional Purchases During the Period – Ending Inventory
The average amount a customer spends when shopping on an ecommerce website.
Formula: Average Order Value = Revenue / Number of Orders
Average revenue based on the conversion rate each time a customer visits an ecommerce website.
Formula: Revenue Per Click = Revenue / Number of Visits
The value a customer contributes to a company over their entire lifetime.
Formula: Customer Lifetime Value = (Transaction 1 + Transaction 2 + Transaction 3 + …Transaction n) x Average Profit Margin
Indicates the average number of times a customer purchases within a specific period.
Formula: Purchase Frequency = Total Orders / Total Customers
Measures the time between consecutive purchases by a customer.
Formula: Time Between Purchases = Purchase Frequency / 365
Measures the number of customers who added items to their cart but did not complete the purchase.
Formula: Cart Abandonment Rate = 1 – (Completed Transactions / Carts with Products) x 100
The cost associated with persuading consumers to purchase a company’s products or services.
Formula: Cost of Acquiring Customer = Total Cost / Number of New Customers
Indicates the likelihood of customers returning to make a second or subsequent purchase.
Formula: Repeat Purchase Rate = Number of Repeat Purchases / Total Number of Purchases
Refers to the total number of visits to an ecommerce website.
Identifies the primary sources directing traffic to your website.
Indicates the average time a visitor spends on the website.
The average time users spend in a single session.
Formula: Total Session Duration / Number of Sessions
Measures the level of content engagement, indicating how deeply users explore information on the website.
Formula: Pages per Visit = Number of Pages Viewed / Visits
The percentage of single-page visits where visitors leave without clicking on any other content.
Formula: Bounce Rate = Total Bounces in a Period / Total Visits in that Period
The rate at which customers view and click on a business’s advertisements.
Formula: Click Through Rate = Number of Clicks / Number of Impressions
Indicates the number of people who interacted with a company’s content through various ecommerce channels such as the business’s ecommerce website/app, ecommerce platforms, Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, etc.
Formula: Social Media Engagement = Number of Interactions / Number of Followers
The Internet marketing model is where businesses pay a fee each time their ads are clicked.
Formula: Pay-Per-Click Cost = Advertising Cost / Number of Clicks
Measures the ratio of potential customers who become actual customers by making a purchase.
Formula: Conversion Rate = Number of Conversions / Total Ad Interactions
 2
2
 12,068
12,068
 0
0
 1
1
Payment services play a crucial role in ecommerce. Diversifying payment methods can provide a more complete shopping experience for consumers, maximise revenue, and enhance the brand for businesses.
Here are some payment methods in ecommerce:

COD is a payment method where the buyer pays the delivery person directly upon receiving the goods. Buyers don’t have to pay in advance when placing an order, and if the products are not satisfactory, they have the right to refuse and return the items.

A bank transfer involves transferring money from the buyer’s bank account to the seller’s bank account to pay for products or services. Modern bank transfer methods, such as Internet Banking and Mobile Banking are replacing traditional ATM transfers.

Online payment gateways connect banks, buyers, and sellers, with the ultimate goal of allowing sellers to receive funds immediately after completing online transactions. These gateways accept domestic debit cards, credit cards, and ATM cards. Popular gateways in Vietnam include VNPay, ZaloPay, Payoo, Paypal, OnePay, etc.

E-wallets are online payment accounts used for various online transactions. Payments through e-wallets are made by linking the account to a bank account, depositing money into the wallet, and then making simple and convenient payments for linked services. Some popular e-wallets in Vietnam include Momo, ZaloPay, etc.

Payment using scratch cards allows users to pay or top up their electronic accounts by purchasing mobile phone card codes from mobile network providers such as Viettel, Mobifone, Vinaphone, etc. However, this payment method is usually only applicable to specific ecommerce platforms and websites.

Brand-specific cards/wallets are payment methods designed by brands or businesses that allow users to make payments within the brand’s or business’s system. Examples include Shopee’s wallet, Lazada’s eM wallet, Starbucks’ card, VinGroup’s VinID, etc.

E-vouchers are online discount vouchers/codes provided by e-commerce businesses such as Shopee, Lazada, Tiki, Luxstay, etc. Customers can use them flexibly and conveniently to choose products and services and make payments using e-vouchers.
The most popular payment method in ecommerce today is COD. However, due to the “digital transformation” nature of the ecommerce market, electronic payment methods are developing and becoming a new trend in payment services.
In 2020 alone, the revenue from the electronic payment market reached 8,904 million USD, a growth of 14.2% compared to 2019 (according to the Landscape 2020 report). Additionally, developing brand-specific cards/wallets for businesses is a potential method for the ecommerce website payment services.
 2
2
 14,961
14,961
 0
0
 1
1
Branding plays a crucial role for businesses, especially in the e-commerce market. An effectively built brand in the e-commerce market helps customers recognize and favor the brand, leading to a tendency to shop on e-commerce websites and become loyal customers in the long run. Building a brand on an e-commerce website is the key to sustainable growth for businesses in this market.
Here are 10 prominent trends in building brands on e-commerce websites applied during the current ‘new normal’ era!
One of the most important tasks for any business during development is to establish a unique style for the brand, especially on e-commerce websites. …Creating an impression in the consumer’s mind helps customers distinguish the brand’s products from competitors. Simultaneously, establishing a unique style creates consistency across all products/services that the e-commerce website provides.
Mobile World Investment Corporation (MWG) has designed a logo and layout with characteristic imagery and uniformity across all e-commerce websites of its brand chain, such as The Gioi Di Dong, Dien May Xanh, Bach Hoa Xanh, Nha Thuoc An Khang. This helps customers of one of the four brands to recall the other brands within MWG.
Brand storytelling is a method to attract customer attention to a brand through the brand’s origin story and promoting the brand’s mission and vision. Sharing brand stories on e-commerce websites helps businesses create a connection to customers’ awareness.
With the goal of creating a brand image through storytelling, the ‘Coolmate Story’ section on the e-commerce website is built based on its name ‘Coolmate,’ with ‘cool’ symbolizing the cool, dynamic appearance of men and ‘mate’ symbolizing the brand’s mission – to be a companion in men’s fashion. Building a story about a fashion brand for men has made Coolmate’s e-commerce website a popular online shopping destination for young male customers in Vietnam.
The trend of building a “made-in” Vietnam brand is not unfamiliar to customers, from supermarkets with the motto “Vietnamese people use Vietnamese products” to the branding method of “Proudly Vietnamese Brand” appearing on e-commerce websites of Vietnamese brands such as Vinfast, Gumac, Highlands Coffee, etc. … Eliciting pride in the Vietnamese nation and calling for support from customers.
The branding strategies of Biti’s, especially for the Biti’s Hunter product line, are always closely associated with the “made-in-Vietnam” message. When launching the online store https://bitis.com.vn, Bitis also subtly incorporates national elements into every corner of the website, such as images, product information, banners, and blog posts.
Brand positioning associated with community benefits, such as supporting charities, donations, non-profit sales, or becoming a brand that encourages support… Building a brand through charitable activities helps enhance the company’s image in the eyes of consumers, promoting online shopping support on the brand’s e-commerce website.
Vinamilk is always a pioneer in social responsibility activities. Vinamilk has established several community funds to support activities to improve nutritional knowledge, healthcare, and improve clean living environments for surrounding communities, such as the School Milk Program (since 2006), the Vietnam Tall Milk Fund, the 1 Million Green Trees Fund for Vietnam. These messages are consistently conveyed on the company’s website.
By designing the brand or product lines displayed on e-commerce websites in line with the environmental protection trend, brands can increase public and potential customer sentiment.
Cocoon, a cosmetics brand from Vietnam, has successfully built the “Eco-Friendly” brand image on the current e-commerce market. The “Eco-Friendly” element of Cocoon is immediately shown in the website’s title tag as 100% vegetarian cosmetics. The content on the website consistently emphasizes the brand’s direction of environmentally friendly cosmetics, sourced from natural ingredients, not tested on animals, and certified by international organizations. Thanks to this, Cocoon has successfully positioned the “Eco-Friendly” brand in the hearts of Vietnamese beauty and nature lovers.
This is a new trend that helps brands maintain their values but adapt their business direction to fit the new normal period, such as:
F&B shifting to cloud kitchens, Travel companies offering touchless and virtual tours…
Changing business models have breathed new life into brands, creating a transformation for the brand. This stimulates curiosity about the brand’s changes among customers.
National Geographic – U.S. National Geographic Society has developed a virtual tour of Vietnam’s Son Doong Cave on its website, combining augmented reality (AR) virtual reality (VR) technology. This achievement not only contributes to the attractiveness of Son Doong Cave but also enhances the brand position for National Geographic, becoming a case study for many famous travel websites about virtual tours.
Consumers today are becoming more discerning and will not easily accept low-quality products on the e-commerce market.
Building a brand that focuses on a few high-quality products on the e-commerce website can make customers loyal to the brand and enhance the brand’s reputation.
3 Sach Food, a brand that focuses on providing clean, chemical-free, non-stimulant, and preservative-free products, has successfully attracted a group of customers interested in the quality of food. Thanks to the focus on product quality, 3 Sach Food has successfully attracted the attention of customers interested in food quality.
Content contributes to developing the relationship between the brand and customers.
Building content with the potential to spread among customer groups will help the brand establish a faster image in the eyes of consumers.
With the goal of building viral content, CellphoneS focuses on updating dramas, hot news, reaction videos, etc., to attract the attention of the youth on the blog website and cleverly embeds technology products, encouraging shopping activities.
To connect emotionally with customers, businesses need to speak their language.
Responding to customers in the language they use for communication will help them react more quickly to brand marketing campaigns and contribute to leaving a more positive impression after brand-building efforts.
Durex, dubbed the ‘content saint’ in the marketing world, always impresses people with its ability to creatively create content using customer language even on the e-commerce website. Applying customer language not only helps the brand increase sales growth but also becomes a companion in every ‘love affair’ of customers.
Brand positioning through digital brand experiences, integrating automation, AI, and virtual reality VR, is considered a new trend for ecommerce businesses. Increasing touchpoints for the brand on e-commerce websites through enhancing the customer experience.
Fitin provides a completely new furniture shopping solution for customers on the e-commerce website and mobile app by integrating 3D technology: VR, AR, Homestyler. Thanks to this, customers not only experience new, professional shopping but also contribute to affirming the position of the Fitin brand in the furniture industry in the eyes of consumers.
Doing ecommerce business in Vietnam is undoubtedly a long-term game for any business entering this market. To develop sustainably, building a brand on e-commerce websites is a prerequisite that cannot be ignored. However, building a brand on eCommerce websites is still a relatively new story for many businesses in Vietnam.
To inquire about free consultation on eCommerce solutions, please contact SECOMM for expert advice.
 2
2
 5,702
5,702
 0
0
 1
1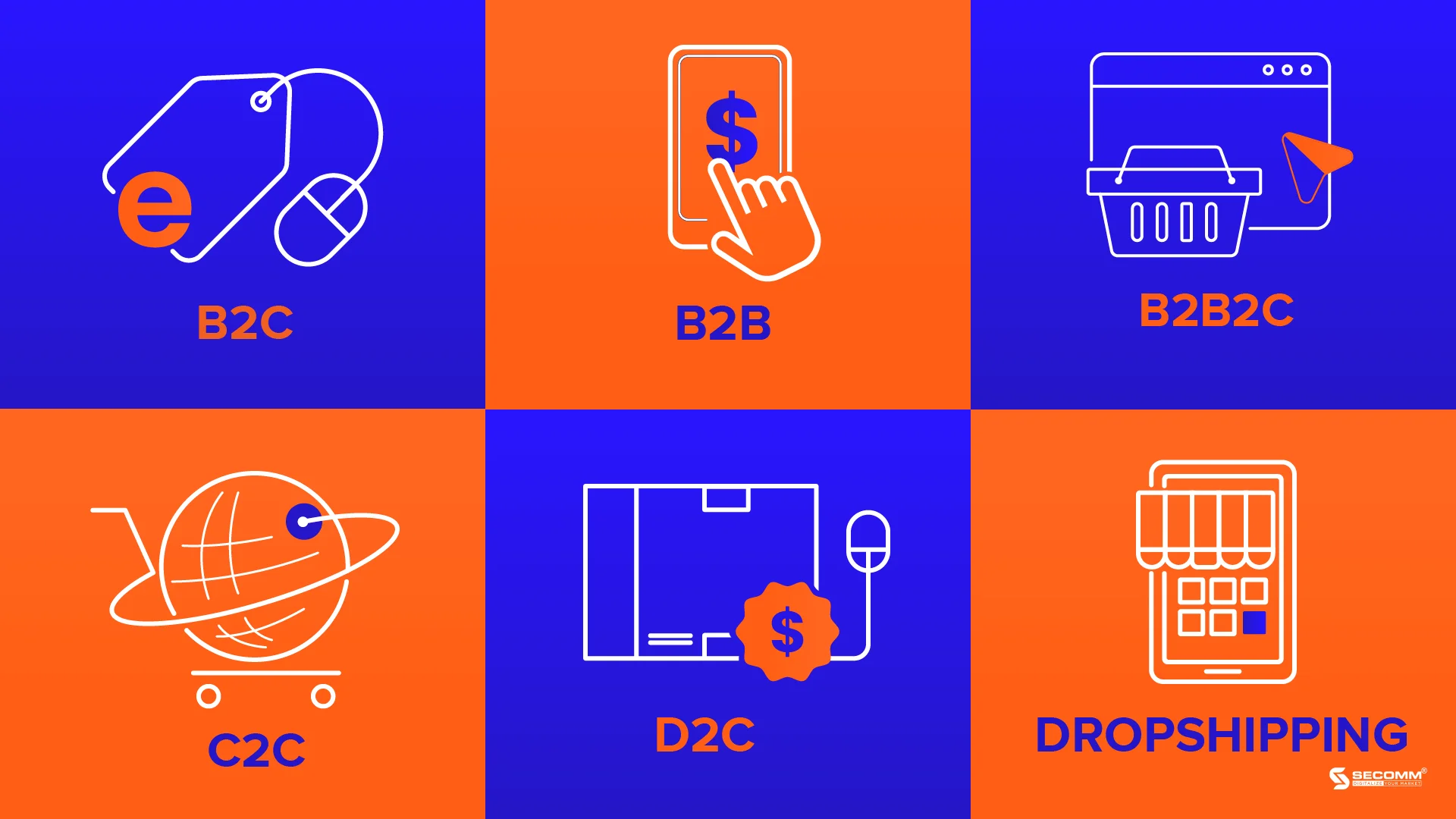
The Vietnamese e-commerce market is highly diverse, featuring a variety of models that cater to large and small businesses, individual sellers, and consumers alike. In the context of rapid digitalization, e-commerce business models have evolved in many directions to meet the needs of both consumers and enterprises. They can be summarized into six main types:
B2C (Business To Customer) involves transactions between businesses and customers. This is also the most popular model in the Vietnamese market.
The Gioi Di Dong is the number 1 retail model in Vietnam for electronic devices such as phones, laptops, tablets, and accessories.
B2B (Business To Business) involves commerce between two businesses.
TELIO is the first B2B e-commerce platform in Vietnam, connecting small-scale traditional retailers with brands and wholesalers on a centralized platform. By aggregating needs, Telio can provide small retailers with more choices, better prices, and more efficient backend support through economies of scale.
B2B2C (Business To Business To Customer) is a collaborative business model between two businesses (B2B) to create and deliver products, services to end consumers (B2C).
Shopee is the most popular e-commerce platform in Vietnam. Shopee Vietnam initially operated as a C2C model, acting as an intermediary in the buying and selling process between individuals. However, Shopee Vietnam has now evolved into a B2B2C model by providing many services and utilities to support the shopping process for both businesses and consumers.
C2C (Consumer To Consumer) is a form of business between two individuals, not businesses.
Chotot is a C2C e-commerce website supporting individuals in buying and selling real estate, cars, recruiting, used electronics, pets, and home services.
D2C (Direct to Customer) is a form of providing products directly from businesses to customers, bypassing intermediary distribution steps.
Lavender specializes in directly supplying premium bed sheets for homes and hotels in the e-commerce market without relying on any distributors.
Dropshipping is a business model that allows online stores to operate without storing inventory, owning products, and shipping products to customers.
Selly is an e-commerce platform that supports business sellers without the need for capital, or inventory storage and takes care of shipping to consumers.
To inquire about free consultation on ecommerce solutions, please contact SECOMM for expert advice.
 2
2
 13,321
13,321
 0
0
 1
1
To gain a competitive advantage in the Ecommerce market, businesses need a detailed strategy outlining the transition stages and implementation measures for each stage. Determining an Ecommerce business strategy helps provide a comprehensive view of the market, business products, and brand development potential. Below is an Ecommerce business strategy for businesses to reference and guide their operations.

Transition the traditional business model to online business on popular social media platforms. This stage allows businesses to test the viability of their products in the online market. Conducting business on social media helps save costs, increases reach, and enhances interaction with customers.
Support Platforms: Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, Zalo.
Business Process on Social Media:
Officially join the Ecommerce game by establishing an online store on Ecommerce Marketplace. Utilize existing customer groups on these platforms and leverage support utilities to improve customer services, such as payment services, delivery services, and marketing services.
Support Platforms: Shopee, Lazada, Tiki, Sendo.
Business Process on Ecommerce Marketplaces:
Build a website to position the brand in the online market, utilize search tools to reach a larger potential customer base, and provide business and product information.
Popular Platforms: Wix, Weebly, Spacesquare.
Website Building Process:
Designing an Ecommerce website helps businesses expand their online sales channels, connect with more customers, and increase brand coverage in the market. Having a proprietary Ecommerce system allows easier data exploitation and reduces dependency on data from other Ecommerce platforms.
Support Platforms: Sapo, Haravan, Shopify, WordPress, Magento, Bigcommerce, Woocommerce.
Basic E-commerce System Building Process:
Developing an in-depth Ecommerce system helps maximize Ecommerce revenue, allows easy system upgrades and customization based on specific needs, and introduces new features to enhance the customer experience.
Platforms: Magento, Bigcommerce, Woocommerce.
In-Depth E-commerce System Building Process:
Implementing Omni-channel helps synchronize all sales channels for easier data management and maximizes Ecommerce business efficiency. Omni-channel creates a seamless experience for customers, allowing businesses to sell through multiple channels and increase conversion rates.
When implementing Omni-channel, businesses can use service providers like ETP Group, NEF, Goell, or choose a centralized system like Magento, ERP.
Omni-channel Implementation Process:
The journey from Social Commerce to Omni-channel is a common strategy for businesses entering the E-commerce market. However, E-commerce has become increasingly popular in all industries, whether Low-involvement or High-involvement. Many businesses deploy social media channels, Ecommerce platforms, and proprietary E-commerce systems early on to shorten the conversion time, keep up with market trends, and meet the diverse needs of customers.
Depending on the overall business strategy and current situation, each business needs to plan the most suitable development roadmap!
Contact SECOMM for free consulting!
 2
2
 12,393
12,393
 0
0
 1
1
As consumer shopping trends shift from offline to online, owning an ecommerce website (EC) is almost a prerequisite for successful business operations. Despite its importance, many businesses are still unsure where to start to build an effective EC website.
Here is a step-by-step journey to building an EC website from basic to advanced for businesses to refer to!
When entering the ecommerce market, businesses often build a basic-level ecommerce website to minimize time and budget for website development and gradually adapt to market changes.

Businesses can use free website-building tools with ready-made interfaces and features to create a website through simple drag-and-drop operations, without investing too much time and budget in website development and programming. Some popular platforms include Sapo, Haravan, Nhanh.web.
Advantages
Reasonable initial deployment costs with a contract based on usage time.
Disadvantages
Businesses use ready-made templates on the platform and customize them to fit the brand image, industry, and consumer preferences. The chosen platforms offer basic features, and businesses only need to select suitable functions and set them up on the website.
According to Government Decree 52/2013/ND-CP, individuals or organizations that own ecommerce websites for selling goods must notify or register with the Ministry of Industry and Trade on the Ecommerce Management Information Portal.
After using a basic ecommerce website for some time, businesses gradually realize the need to develop an independent, in-depth, and uniquely designed ecommerce website to promote a sustainable ecommerce journey.
Developing a specialized ecommerce website requires both experience and substantial investment in costs and time. However, this is a cost-effective solution for long-term business plans and a suitable transition for a separate and comprehensive ecommerce system.

At this stage, businesses can choose specialized e-commerce platforms like WooCommerce, BigCommerce, Magento, which are scalable and customizable to maximize the requirements of:
However, implementing a specialized e-commerce website may face some difficulties:
When building an ecommerce website on specialized platforms, as it requires time, costs, and high expertise, businesses often collaborate with service providers for ecommerce website development. Afterward, businesses can build an in-house team or continue working with the provider to maintain website operations.
Some service providers for deploying specialized ecommerce systems include SECOMM, SmartOSC, Co-well Asia, Isobar, Magenest.
During project deployment based on the agreed solution with the development provider, all factors related to the quality and effectiveness of the website need to be optimized and tested before handover. Especially crucial functions include:
To maintain seamless online-to-offline business operations, the website needs continuous maintenance, care, and updates.
Implement activities to increase sales operations on the website and stimulate online sales.
The journey from building a basic to an advanced ecommerce website helps businesses adapt to market changes over time.
 2
2
 4,601
4,601
 0
0
 1
1
Ecommerce website has been a companion for businesses facing COVID-19 challenges in 2020-2021. Efficient utilization of ecommerce (EC) not only helps businesses adapt to changing user and market dynamics but also enables them to seize opportunities and excel in the fiercely competitive landscape. Some successful standalone EC websites include thegioididong.com, bachhoaxanh.com, and fptshop.com.vn.
What is the formula for the success of these businesses?
This success hinges on the ability to have a broad vision and a strategic approach at the management level. Building a dedicated EC website is not just about establishing offline stores; it involves developing and optimizing an EC system that aligns with the business, brand, and users. Building a successful brand website offers various benefits, from brand positioning, cost savings, maximizing revenue to owning all data and controlling the game.
A dedicated EC website serves as a medium to convey the brand image and connects businesses with customers in the online market. By owning a dedicated EC website, businesses can easily convey messages, establish specialized marketing campaigns, provide accurate information, and promote the brand to get closer to customers.

Operating on a website, businesses are not limited by time and space. Business transactions can occur 24/7, regardless of location. Actively updating and upgrading the system’s features based on user characteristics, business needs, and industry specifics ensures an optimal user experience and facilitates a more convenient and faster purchasing process.

In addition to enabling direct access and sales to customers, eliminating intermediary costs, establishing an online store (brand.com) is an optimal solution for minimizing various expenses such as rent, personnel, and equipment. Moreover, the automated business process with E-Payment, E-Logistic, E-Invoice functions on the website helps save costs related to personnel and paperwork.

Building a dedicated EC website means owning a unique “playing field,” reducing dependence on data from EC platforms, social media, or other business systems. With this data, businesses can conduct in-depth data analysis, make business predictions, and develop appropriate directions for the business.
With these superior benefits of deploying a standalone EC website, many businesses have quickly embarked on building an online store for their brand. However, to truly own a successful website that meets specific requirements, similar to Vinamilk, Thế giới di động, Canifa, businesses need a suitable strategy and significant time and investment.
With extensive experience in building numerous standalone ecommerce websites for businesses across various sectors, SECOMM fully understands the challenges encountered during the e-commerce deployment process that businesses are facing.
Contact SECOMM to receive consultation on building your own ecommerce website!
 2
2
 3,419
3,419
 0
0
 1
1
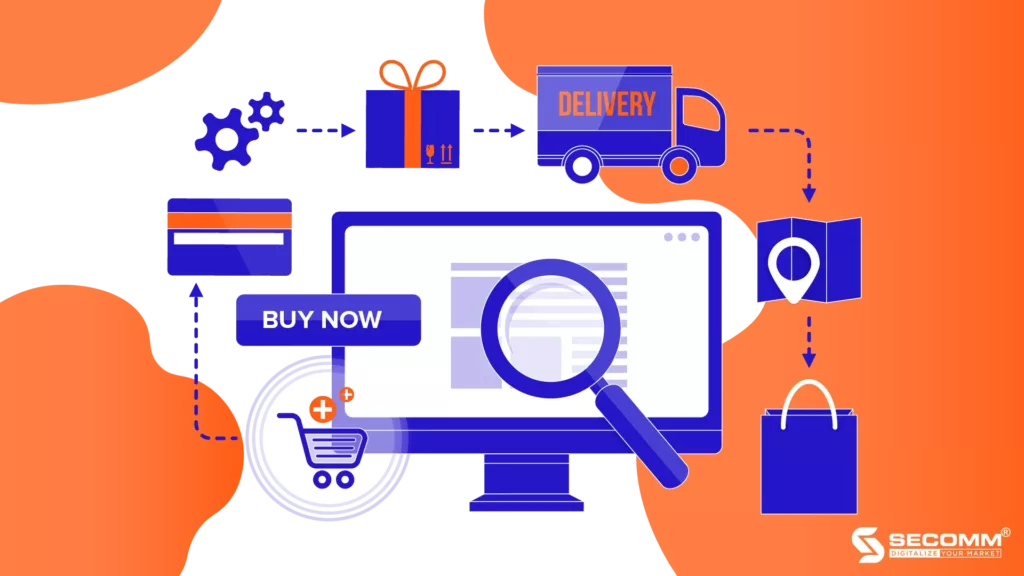
In the rapidly evolving landscape of today’s economy, where opportunities and competition are just a mouse click away, the effective implementation of E-commerce (EC) is a non-negotiable for businesses, regardless of their involvement in low or high-involvement industries. This comprehensive guide outlines the crucial steps that Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) can take to deploy and manage EC strategies successfully, ensuring a competitive edge in the digital marketplace.
The initial phase involves meticulous planning and selecting an EC business model that aligns with the overall development direction of the business. SMEs have three primary models to consider:
Building a robust EC strategy is a cornerstone for SMEs. Leveraging the 5W1H method provides a structured approach to strategic planning:
The focus of this step is on determining purchasing channels and ensuring a seamless customer experience:
Once the EC system is operational, the emphasis shifts to maintaining and enhancing the system for optimal performance:
Improving post-purchase services is essential for customer satisfaction and increased conversion rates:
The implementation of EC is a critical endeavor for SMEs, representing a transformative journey that, when executed effectively, can lead to sustainable growth and increased market share. However, navigating the complexities of the EC landscape requires a strategic approach and a wise investment of time and resources.

 6
6
 5,797
5,797
 0
0
 2
2
OVER 50 YEARS OF GLOBAL E-COMMERCE JOURNEY (1969 – 2020)
In 1969, Dr. John R. Goltz, Jeffrey Wilkins, and electrical engineering students founded CompuServe – a service that provided an information-sharing portal through the Internet and email network connections.
Michael Aldrich pioneered the first EC system by connecting a television and a computer for transaction processing via telephone lines, enabling a secure information system to be opened and shared externally. This innovation laid the foundation for the development of modern EC systems.
Initially a store supporting the resale of used computers, Boston Computer Exchange became one of the earliest models for today’s EC companies.
Charles M. Stack established the brand Book Stacks Unlimited as the world’s first online book store. Initially using a dial-up bulletin board format, the company later transitioned to the Internet to create an online book trading market.
Jeff Bezos founded Amazon initially as a book-selling business but later expanded its business model to include various products by incorporating new technologies such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence. Amazon ushered in a new era for the EC industry by integrating Internet technology into its business strategy.
Confinity (the predecessor of PayPal) was founded by Max Levchin, Peter Thiel, Luke Nosek, and Ken Howery. In 2000, eBay acquired Confinity and renamed it PayPal, the world’s largest online payment gateway. PayPal addressed many limitations of traditional payment methods, making the buying and payment process more convenient and laying the foundation for EC development.
Alibaba officially entered the EC market, successfully raising $25 million in capital. By 2001, the company became profitable and led the EC platform under the B2B, C2C, and B2C business models. In 2020, Alibaba contributed $12.2 billion to global EC revenue.
Google introduced Google AdWords, the world’s first online advertising tool. This tool supported businesses in marketing their products on Google’s search network, boosting sales for EC companies at that time.
After unsuccessful attempts to build an e-commerce website selling snowboarding equipment on various platforms, Tobias Lütke and Scott Lake founded Shopify – the first platform supporting the development of EC websites worldwide. This platform enables users to easily create online stores without requiring extensive technical knowledge.
The National Retail Federation (USA) coined the term “Cyber Monday” to describe the first Monday after Black Friday, initiating the online shopping season between Thanksgiving and Christmas. This event marked economists’ interest in the global retail market.
Developed by Roy Rubin and Yoav Kutner in 2007, Magento is an open-source platform written based on the Zend Framework and PHP programming language, specifically designed to build complex EC websites. Magento, known for its multitasking capability, high performance, flexible customization, and easy scalability, has become the top choice for enterprises with 200,000 partners and 2.5 million downloads worldwide.
Multinational corporations using Magento to build sophisticated EC systems include Samsung, Nike, Coca-Cola, Asus, HP, Lenovo, Canon, Sigma, Olympus, Port, Pox, Nestle, BevMo, Burger King, and millions of small and medium-sized EC sites globally.
With the ambition to dominate the EC market, Facebook, a tech giant, continuously introduced new features on Facebook Marketplace, Instagram, and WhatsApp, and collaborated with various EC platforms (Shopify, OpenCart, BigCommerce, WooCommerce, and Magento). This made giants like Amazon, Lazada, and Shopee wary, demonstrating the strong allure of the EC market.
The global EC industry set a new revenue record of $2.352 trillion in 2017, a 25% increase from 2016 (according to eMarketer – a US market research company). Cyber Monday alone surpassed $6.5 billion in online sales. Economists predict that EC will be the world’s focal industry by 2025.
2020 marked a significant turning point for the global EC industry. The impact of COVID-19 accelerated the construction of EC systems to meet consumer demands promptly. Currently, EC is not only present on platforms like Amazon, Shopee, and Lazada but also brands are starting to build their own EC websites. Additionally, EC spans various sectors from fast-moving consumer goods (fashion, food, technology) to service sectors (travel, finance, education, furniture, and real estate).
According to the “Southeast Asia Internet Economy 2020” report by Google & Temasek, consumers tend to spend more time shopping online than before COVID-19 (increased from 3.7 hours/day to 4.7 hours/day). Global B2C EC revenue increased from $1.948 trillion to $4.280 trillion, doubling Statista.com’s forecast of $2.238 trillion.
COVID-19 has brought positive effects on the global rise of the EC industry and opened up new opportunities for the Vietnamese economy.
 2
2
 5,910
5,910
 0
0
 1
1Subscribe to get the latest eBook!
Hotline