It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Sign Up for newsletter!
Subscribe to get the latest eBook!
Hotline


 113
113
 6,482
6,482
 1
1
 40
40
 2
2
 13,502
13,502
 0
0
 1
1
 2
2
 13,426
13,426
 0
0
 1
1
 2
2
 13,390
13,390
 0
0
 1
1
 4
4
 13,318
13,318
 0
0
 2
2




Today, with the growing demand for flexible and scalable eCommerce system development, large-sized businesses turn their attention to solutions like Headless, Microservices, and Composable Commerce. The Composable approach will allow you to integrate independent components to tailor and enhance the eCommerce experience.
Knowing this insight, Shopify has unveiled the Commerce Components solution, offering you — as a large-sized business — the most straightforward approach to deploying Composable Commerce.
Learn more: What is Composable Commerce?
Commerce Components is an innovative tech stack designed for large businesses. Rather than introducing new features, the company has transformed its infrastructure into modular components that can be combined to build and customize adaptable eCommerce websites. This means you can select components based on your deployment needs and seamlessly integrate them into your existing tech stack using flexible and unlimited API connections, ensuring a smooth customer experience across all devices.
“We’ve always approached innovation by anticipating what retailers need and then providing those solutions,” said Harley Finkelstein, president of Shopify. “Commerce Components opens our infrastructure so enterprise retailers don’t have to waste time, engineering power and money building critical foundations it has already perfected, and instead frees them up to customize, differentiate and scale”
The solution offers six main categories including over 30 components, allowing you to build a tailored solution that aligns with your needs.


Although both ‘Plus’ and Components are enterprise eCommerce solutions, they differ in several aspects:
If you don’t prefer to deploy pre-packaged eCommerce platforms. Composable architecture is the ideal choice. It allows you to select and purchase components based on your needs, integrate them into your existing systems, and customize them.
With its modular architecture, the tech stack provides unlimited API connections, meaning there is no limit to the number of components and add-ons that you can use to build your tech stack.
Moreover, since components are entirely independent, you can add, remove, and modify components without affecting the entire system.
Commerce Components employs a pricing model structured around the level and quantity of components used. This means you only pay for the components you require. Furthermore, as you acquire and utilize more components, you’ll benefit from increasingly significant discounts.
Additionally, the annual payment structure of Components helps you facilitate precise cost predictions.
Since its inception, the platform has proudly highlighted the trust and adoption of its solution by major global businesses. Notable among these are Glossier, JB Hi-Fi, Coty, Steve Madden, Spanx, and Staples.

Leading U.S. toy brand Mattel is one of the first enterprises to successfully implement this technology solution. Sven Gerjets, Mattel’s CTO, said in a statement.
“We first worked with Shopify on a project called Mattel Creations, a platform for creators to reimagine the most iconic toys in the world. Creations empowered Mattel to move quickly, meet our customers where they are, and most importantly leverage its infrastructure to scale globally. It was hugely successful, and we’re excited to transform our brand offerings using Commerce Components.”
The trust placed by Mattel and other industry leaders forms a solid basis for expecting the ongoing success of this new solution, extending its impact not only within the U.S. market but also on a global scale.
Final Thoughts
In the past, large businesses often favored open-source platforms like Magento or Salesforce due to their customizable and flexible expansion capabilities. However, in today’s landscape, SaaS platforms, particularly Shopify, offer innovative solutions for developing Composable or Headless Commerce.
In 2021, the company launched the Hydrogen + Oxygen solution to enhance Headless Commerce development. Continuing this trend into early 2023, they once again surprise the industry with Commerce Components, designed for deploying Composable Commerce.
This move highlights its commitment to anticipating and responding to customer needs, earning the trust of large enterprises in the face of competitive rivals.
Reach out or call the SECOMM hotline at 028 7108 9908 for a more in-depth understanding of Commerce Components by Shopify and to explore the implementation of Headless Commerce or Composable Commerce.
 2
2
 11,592
11,592
 0
0
 1
1
In today’s eCommerce landscape, it isn’t just open-source platforms that can meet the complex development and customization needs of large-scale enterprises, but SaaS platforms are also steadily rising with significant improvements. Among them, two SaaS platforms designed specifically for large enterprises are Shopify Plus and BigCommerce Enterprise.
However, these two platforms have many key differences. This article aims to clarify the pros and cons of each platform and compare the differences between the two platforms to help you — as a business leader — make well-informed decisions.
Learn more: Shopify vs BigCommerce: Which platform is right for you?
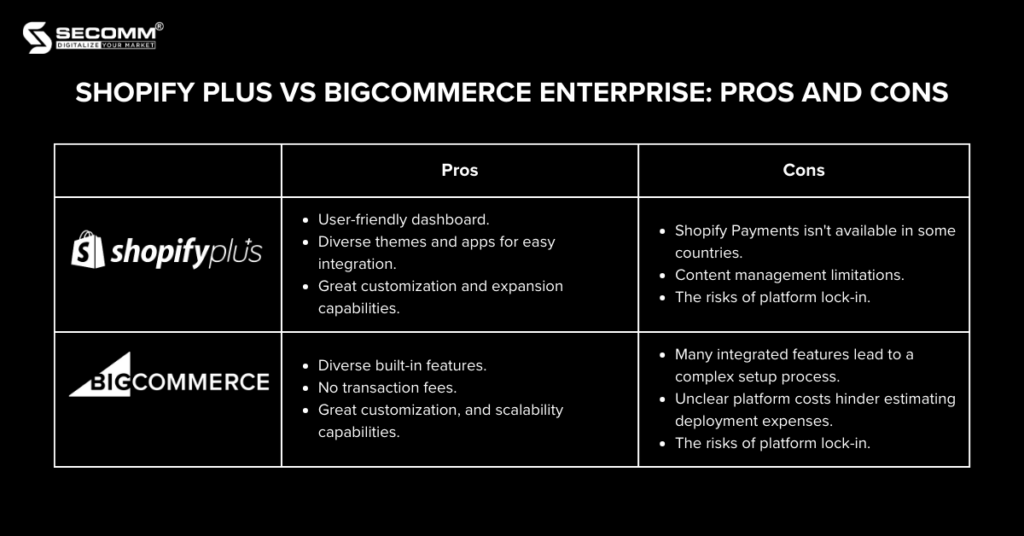
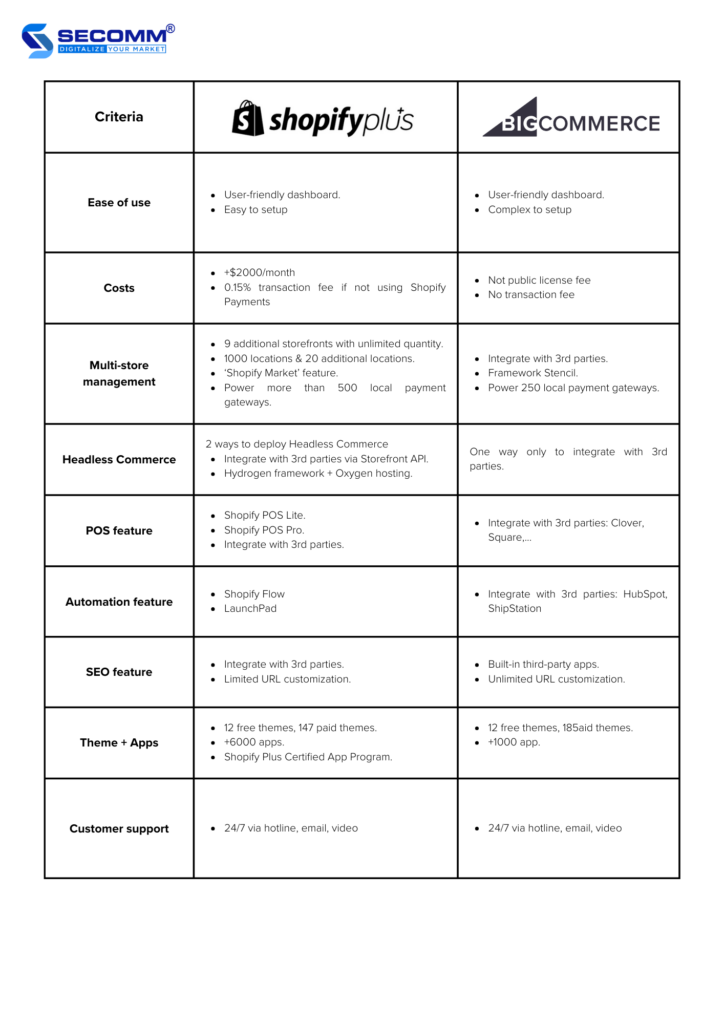
Both platforms are recognized for their user-friendliness compared to open-source platforms. Their intuitive dashboard and user-friendly navigation, along with features like drag-and-drop editing, extensive documentation, and 24/7 support, make them accessible for users of varying technical expertise.
However, Shopify, known for its inherent user-friendly design, ensures that users, whether using the Plus version or the regular ones, can easily explore and set up their eCommerce website with efficiency.
Both these two premium solution platforms — which are Shopify Plus and BigCommerce Enterprise — cater to the deployment needs of large enterprises, these platforms offer advanced features and technologies that require some learning.
For example, the ‘Plus’ users need to grasp the Liquid template language, while those opting for the ‘Enterprise’ may benefit from understanding the Google Cloud Platform for optimizing website performance.
BigCommerce, renowned for its built-in features, continues this trend with the ‘Enterprise’ version. Some features may suit specific businesses but might be unnecessary for others. While BigCommerce allows flexibility for customizing and configuring these advanced features, it can introduce complexity and intricacy into the setup process.
Similarly to other premium solutions on SaaS platforms, the license fee will depend on the deployment requirements and the current scale of the business. BigCommerce doesn’t disclose the fee publicly, requiring businesses to directly contact the platform for tailored consultation and pricing.
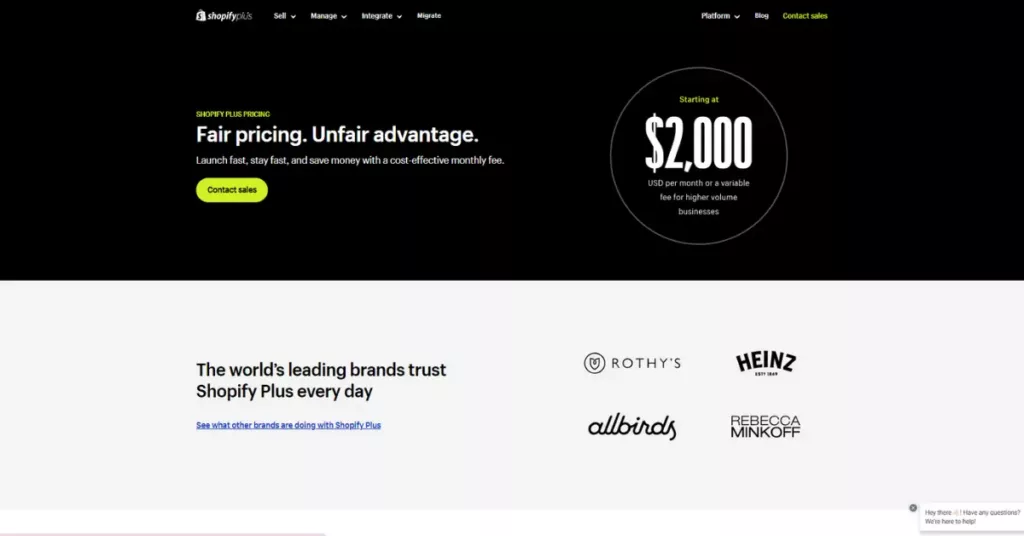
On the other hand, Shopify Plus has a license fee starting at $2000 per month. Once you reach a monthly revenue threshold of $800,000, the platform fee becomes revenue-based, amounting to 0.25% of monthly revenue, capped at $40,000 per month or $480,000 per year.
Considering transaction fees is also important. While BigCommerce doesn’t charge transaction fees, Shopify Plus charges a 0.15% transaction fee for not using Shopify Payments.
To estimate deployment costs effectively, you should partner with development agencies and engage in detailed consultations with BigCommerce or Shopify for comprehensive guidance.
For large enterprises, the multi-store management feature is crucial and a primary consideration when selecting an eCommerce platform to sell globally. To engage in sales across various markets worldwide, your eCommerce website needs to be crafted to suit the preferences of each target audience in different markets.
This involves addressing issues related to language conversion, currency units, and payment methods with flexibility. Moreover, stores should be administered efficiently in a centralized manner rather than separately.
Shopify Plus allows you to create up to 9 additional storefronts alongside the main storefront at 1000 different inventory locations and 20 additional inventory locations. All these storefronts can be centrally managed through a single dashboard.
Plus, the Shopify Market feature will help you select the markets you want to sell in. The system will then automatically convert and manage multiple languages, currency units, shipping options, and payment methods based on the user’s IP address. Currently, Shopify Plus supports a range of local payment gateways, and you can refer to the provided list.
BigCommerce Enterprise doesn’t provide many solutions or features for global selling. Instead, it allows you to deploy multiple stores within the platform and then integrate with 3rd-party PIM solutions to manage data across these stores.
Another option is to leverage the BigCommerce Stencil framework to tailor content language for each local market. Also, the Enterprise version supports multi-currency payments through more than 250 local payment gateways.
The demand for adopting Headless eCommerce is on the rise, especially among large enterprises seeking to deliver a seamless and optimized experience for their customers. Both Shopify Plus and BigCommerce Enterprise offer effective solutions for going Headless.
BigCommerce Enterprise allows you to integrate with various frameworks (Next.js, Gatsby.js, Nuxt.js), APIs (REST, GraphQL), and your preferred or previously used tools.
When using Shopify Plus, there are three approaches. You can use the Storefront API to connect and develop with your preferred frameworks, hosting solutions, and tools. Or, you can leverage Shopify Hydrogen framework and Oxygen hosting to facilitate a headless eCommerce website flexibly.
Just like their regular pricing plans, both the ‘Enterprise’ and the ‘Plus’ include Point of Sale (POS) features for eCommerce transactions, catering to both online and offline stores, as well as Omnichannel operations.
POS can be configured on various devices like mobile devices (tablets, smartphones), and other hardware like cash registers and barcode scanners.
BigCommerce Enterprise offers smooth integration with third-party POS systems like Square, Vend, Clover, and Heartland Retail. It’s good for those who already using POS software from these third-party providers.
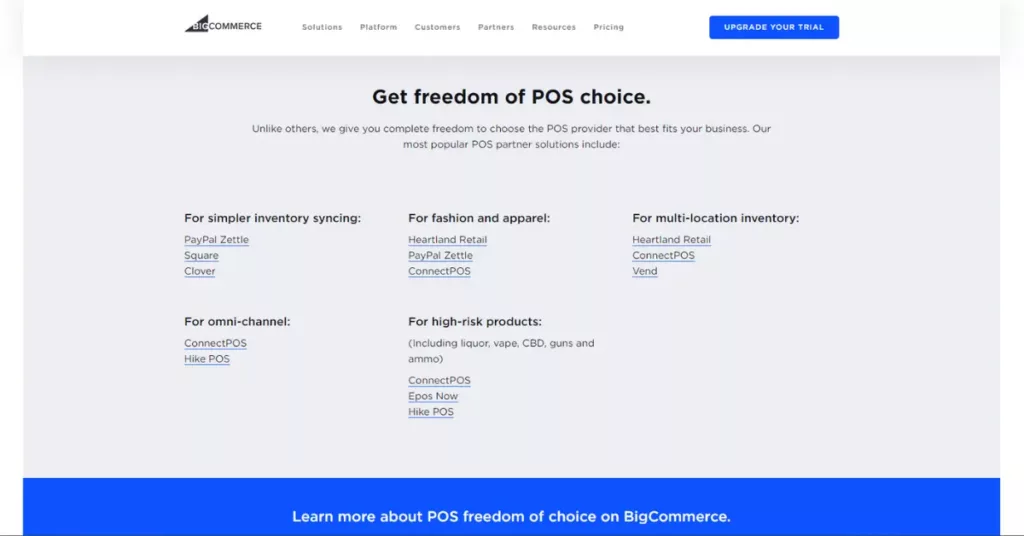
For Shopify Plus, beyond the option to integrate with third-party POS systems like BigCommerce Enterprise (Clover, Square, Zend), Shopify offers its own Shopify POS solution, available in two plans:
Both ‘Plus’ and ‘Enterprise’ offer tools and solutions to help you automate your eCommerce website operations.
Shopify Plus offers an exclusive solution, Shopify Flow, and LaunchPad, allowing you to automate routine tasks and set up automated workflows for tasks like email marketing campaigns or new product launches.
On the other hand, BigCommerce Enterprise takes a different automation approach which enables you to smoothly integrate with 3rd-party apps. Some of them are HubSpot, Avalara, ShipStation, etc.
SEO plays a crucial role in improving the search visibility of an eCommerce site and attracting potential customers. Both platforms offer features to enhance SEO efforts.
The ‘Plus’ stands out for its user-friendly interface and an integrated app ecosystem that can enhance SEO, incorporating tools such as Google Search Console and Analytics. However, it comes with limitations in URL control and customization.
The ‘Enterprise’, on the other hand, provides more versatile SEO capabilities, including complete control over URLs and integration with applications like Google Search Console and Analytics. It makes the process more intricate compared to Shopify Plus, involving additional setup operations.
Shopify Plus offers businesses approximately 12 free themes and 147 paid themes, with prices ranging from $150 to $380 per theme. On the other hand, BigCommerce Enterprise provides around 12 free themes and 185 paid themes, with prices ranging from $150 to $400 per theme.
Both platforms offer a wide range of visually appealing and mobile-friendly theme options. While the ‘Enterprise’ themes are characterized by elegant, tidy, and modern designs with highly customizable features, the ‘Plus’ themes can meet higher requirements for user experience, making navigation easier.
To facilitate efficient eCommerce deployment, the two provide vast app stores and extensions, tailored for ‘Plus’ and ‘Enterprise’ businesses. While both platforms offer free versions, access to comprehensive features requires a modest monthly fee.
Shopify Plus boasts over 6,000 apps and extensions, while BigCommerce Enterprise has around 1,000. This can be explained by Shopify’s widespread popularity among businesses and developers globally, providing them with ample documentation and resources for app and extension development, including the Shopify Plus Certified App Program.
For businesses that are ready to deploy the ‘Plus’ or the ‘Enterprise’ solutions, the demand for technical support and efficient eCommerce website operations is significant.
Both platforms receive high praise for their customer service. They offer 24/7 support via hotline, email, and video available in multiple languages. However, if you need specialized and complex technical support, Shopify Plus may be the preferable choice.
Final Thoughts
In the competitive business landscape, selecting the right platform for launching an eCommerce website is an important decision. Both Shopify Plus and BigCommerce Enterprise offer distinct advantages and cater to various business models.
Regardless of the platform chosen, you should prioritize the development and delivery of an exceptional shopping experience for your customers. eCommerce platforms serve as tools, and the ultimate key to success lies in an effective deployment strategy and great collaboration with a proficient team.
With extensive experience helping numerous businesses deploy diverse eCommerce development projects on both Shopify Plus and BigCommerce Enterprise, SECOMM boasts a team of seasoned experts capable of collaborating to create exceptional eCommerce experiences and help you enhance your brand positioning.
Reach out or directly call the hotline at 028 7108 9908 to explore how SECOMM can contribute to optimizing the potential of Shopify Plus and BigCommerce Enterprise for enduring your business success.
 2
2
 7,534
7,534
 0
0
 1
1
Baby eCommerce is a promising market experiencing a steady annual growth rate (CAGR 2023-2027) of 9.86%, projected to reach a market value of approximately USD 129.40 billion by 2027.
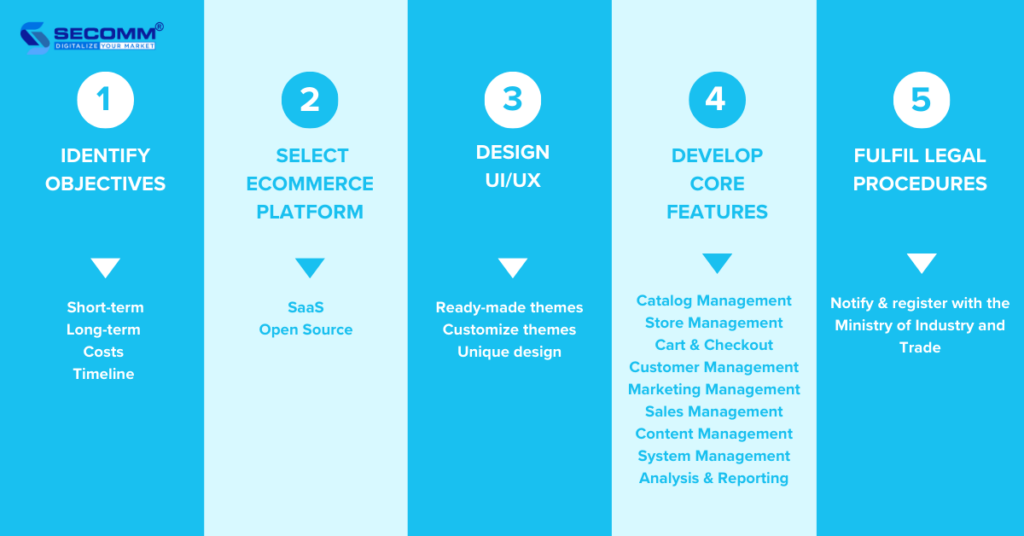
To tap into this market, you’ll need to develop a professional and efficient eCommerce website. Here are 10 steps to create an eCommerce website tailored for maternity and baby products.
The first step is to identify your business goals and prioritize them, forming a plan tailored to develop an effective Baby eCommerce website.
Concerning long-term goals, you may focus on objectives like establishing a strong brand presence, reaching potential customers, and enhancing the efficiency of both online and offline operations.
For short-term goals, businesses can give priority to activities like monitoring, analyzing customer behavior, assessing the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, and boosting revenue.
When it comes to timeline, you can decide to deploy quickly to enter the market or proceed gradually to test and adapt to this eCommerce world.
As for the budget, it depends on your business strategy and financial capacity for this Baby eCommerce development project.
Currently, there are two types of eCommerce platforms to help you build your first Baby website: SaaS (Software as a Service) and Open-Source platform.
Some popular SaaS eCommerce platforms include Shopify, BigCommerce, Squarespace, and Wix.
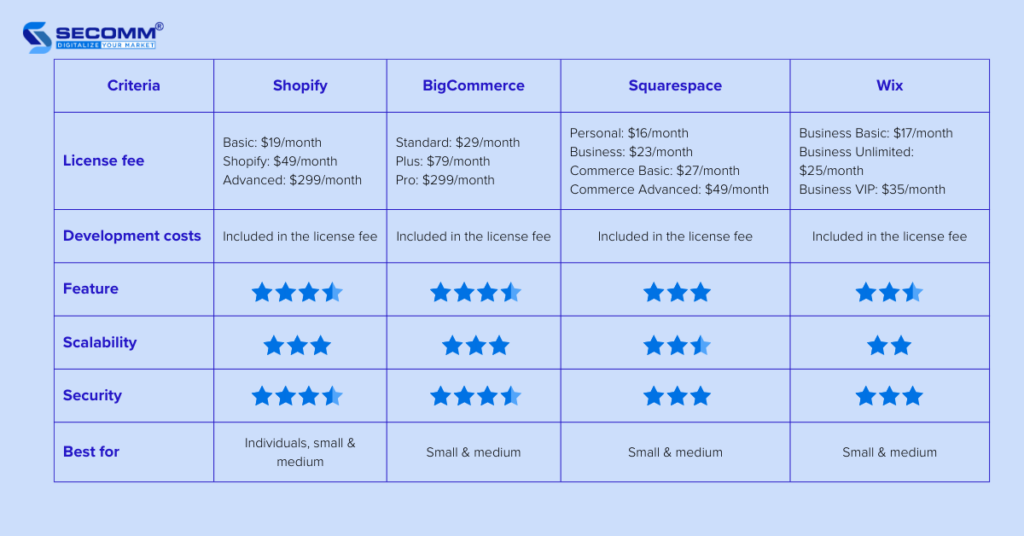
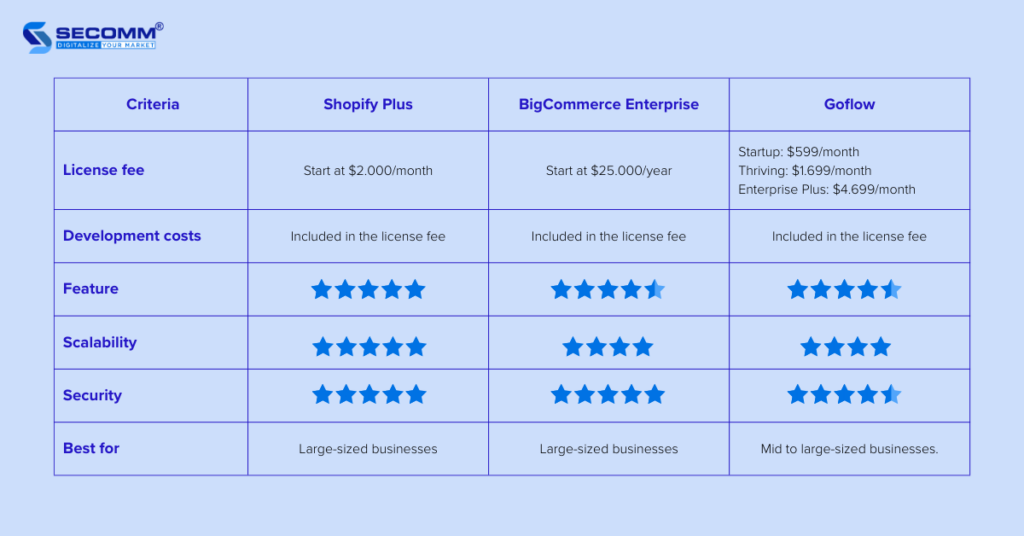
In addition, there are premium versions of these SaaS platforms such as Shopify Plus, BigCommerce Enterprise, and Goflow.
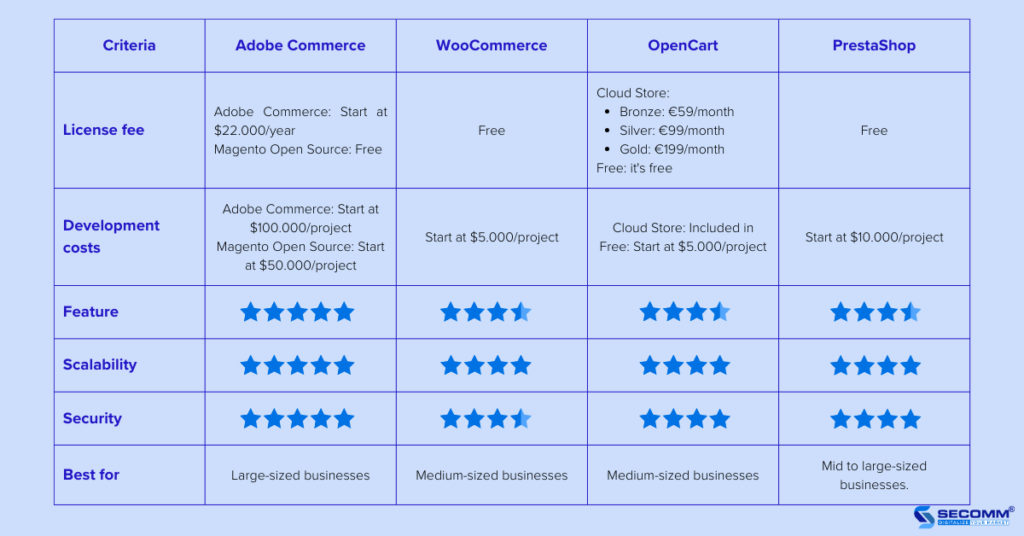
Some open-source platforms are widely used: Adobe Commerce (Magento), WooCommerce, OpenCart, and PrestaShop.
Typically, some new businesses choose basic SaaS platforms to save time and budget in the initial phase of the Baby eCommerce website development. After a while, they may switch to a premium SaaS or an open-source platform to develop their baby websites more advanced.
In another case, some businesses opt for open-source platforms to build a basic eCommerce website and then gradually upgrade the system over time to minimize the need for platform switching in later phases.
Typically, most eCommerce businesses decide to initially partner with a professional development agency and gradually build their in-house team.
For establishing an in-house team, you’ll need to recruit and train IT and eCommerce professionals for expertise on the chosen platform. It’ll take you significant time and budget but allow you to have full control over your resources. You can develop and adjust your Baby eCommerce website according to your needs and wants.

When it comes to partnering with an agency, here are some criteria you need to evaluate:
Partnering with a professional development agency gains you specialized eCommerce knowledge, enhances your technical skills, and above all, you’ll facilitate the eCommerce website exactly what you need, tailoring it to the unique features of the maternity and baby industry.
When it comes to UI/UX design, it’s important to showcase the brand image, products, user guide, etc. There are three popular ways to make your design:
Some essential features that a Baby eCommerce website should have include
Some advanced features for the baby eCommerce industry:

After developing features and ensuring a successful testing and website launch, you’ll need to complete the legal procedures associated with eCommerce operations.
According to Decree 52/2013/ND-CP by the Government of Vietnam, any individual or organization owning an eCommerce website for sales is required to notify or register with the Ministry of Industry and Trade through the online public service portal of the Ministry of Industry and Trade.
Note: Websites that operate beyond the specified period or fail to register/notify the authorized management agency within the designated timeframe may be subject to administrative penalties as per regulations.
When QC/testing your eCommerce website, you can leverage either the Waterfall or Agile model to test the entire system.
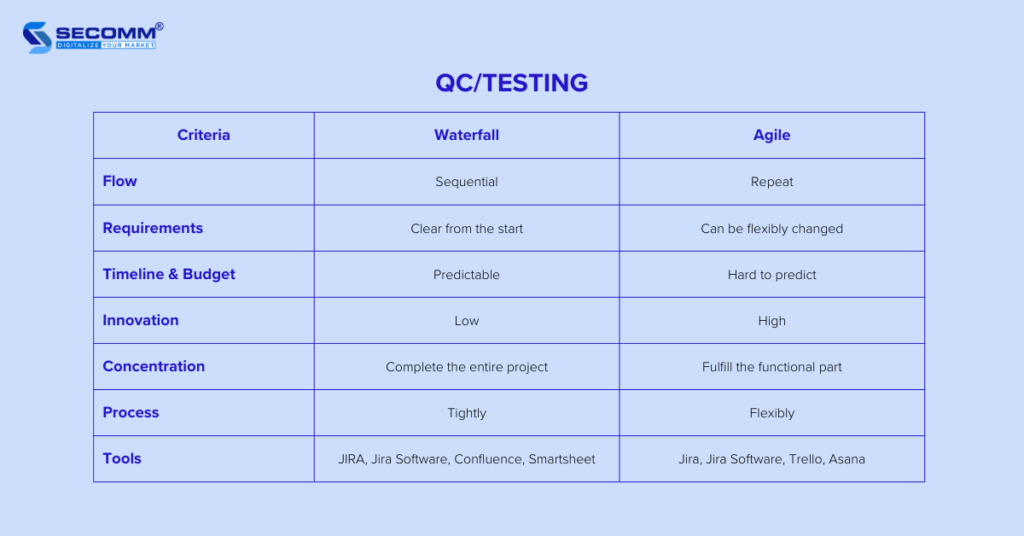
Using these models helps you review and test your entire eCommerce system, functions, and features within a specified timeframe, ensuring optimal order processing speed and overall website stability. In case of any issues, your in-house team or development partner will help you to address them before officially going live.
When the QC/testing process is done, your baby eCommerce website is ready to launch. To ensure a smooth go-live process, here are three steps you should prepare:

Running a baby website is an ongoing effort aimed at ensuring the steady and effective functioning of the system. This involves various activities, including:
Furthermore, you should regularly maintain, update, and upgrade the website system to achieve sustainable growth, adapting quickly to shifts in the eCommerce world or the maternity and baby products market.

After a period of operation, you should shift your focus toward eCommerce marketing strategies or Omnichannel to expand your online presence in the market of maternity and baby products
businesses should redirect their focus toward implementing eCommerce marketing strategies or embracing Omnichannel approaches to expand their online presence in the market of mother and baby products.
Implementing Omnichannel involves setting up a seamless sales, marketing, and management system across channels such as the website, social media platforms (Facebook, Instagram, Zalo, TikTok Shop), and online marketplaces (Shopee, Tiki, Lazada, Sendo) to optimize the customer experience and boost business efficiency.
Developing a comprehensive marketing strategy, centered around key eCommerce marketing channels like Content Marketing, SEO/SEM, Email Marketing, and Affiliate Marketing, becomes crucial for achieving rapid sales growth.
The Bottom Line
In general, the journey of building a baby eCommerce website for the Vietnamese market isn’t an easy task. It requires you to invest a significant amount of time and budget in researching the most fitting strategies tailored to each phase of your eCommerce development.
Understanding the difficulties and challenges that businesses may encounter when building a baby eCommerce website, SECOMM is ready to provide free consultation on detailed eCommerce solutions.
Reach out or call the SECOMM hotline at 028 7108 9908 to get started!
 2
2
 6,508
6,508
 0
0
 1
1
Since the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, the pharmaceutical industry has proven the potential of transitioning from offline to online pharmacy. In the United States, the number of remote health consultations surged by 2,600% in March 2020 (during the peak of COVID-19 in the U.S.) compared to the same month in 2019. According to Statista, the global pharmaceutical eCommerce sector is projected to reach 32 billion USD by the end of 2023.
Several brands have successfully embraced eCommerce early on, achieving unexpected successes. Examples include Apollo Pharmacy (India), FPT Long Châu (Vietnam), CVS Health (USA), and Droga Raia (Brazil). The common thread among these brands lies in their comprehensive eCommerce platforms, catering to the shopping needs of customers for healthcare, pharmaceutical, and medical products.
With nearly 10 years of experience in the eCommerce sector, SECOMM has outlined the journey of building pharmaceutical eCommerce websites for the Vietnamese market.
The first thing to do is identify and prioritize goals to plan the pharmacy eCommerce website development for each phase.
In the long run, businesses can consider goals like branding, generating potential customers, and optimizing online and offline operations.
For short-term goals, businesses should prioritize objectives like monitoring and analyzing customer behavior, evaluating marketing campaigns, and revenue growth.
In the first phase, businesses can decide to deploy quickly to enter the market or proceed gradually to test and adapt to this eCommerce world.
There are two types of platforms to help businesses facilitate pharmacy eCommerce websites: SaaS (Software as a Service) and open source.
Some popular SaaS eCommerce platforms include

Some outstanding open-source eCommerce platforms include

Typically, new eCommerce businesses will choose SaaS platforms to save time and budget in the initial phase of building a basic eCommerce website or an online pharmacy. Then, businesses will re-platform to an open-source platform to develop more advanced eCommerce systems.
However, some businesses decide to build their eCommerce websites in the basic phase on an open-source platform and then upgrade the system over time to remove the re-platforming step in the later phase.
When designing the interface, businesses need to meet basic criteria such as UI/UX standards, showcasing the brand’s characteristics, maintaining consistent product presentation, providing sufficient user guidance, etc.
When it comes to UI/UX design, it’s important to showcase the brand image, products, user guide, etc.
There are three ways to design UI/UX:
In this phase, businesses often choose ready-made themes to minimize costs, but some financially robust businesses may opt for the other two methods to better position their brand.
In the basic development phase, businesses should prioritize developing core features for an online pharmacy.
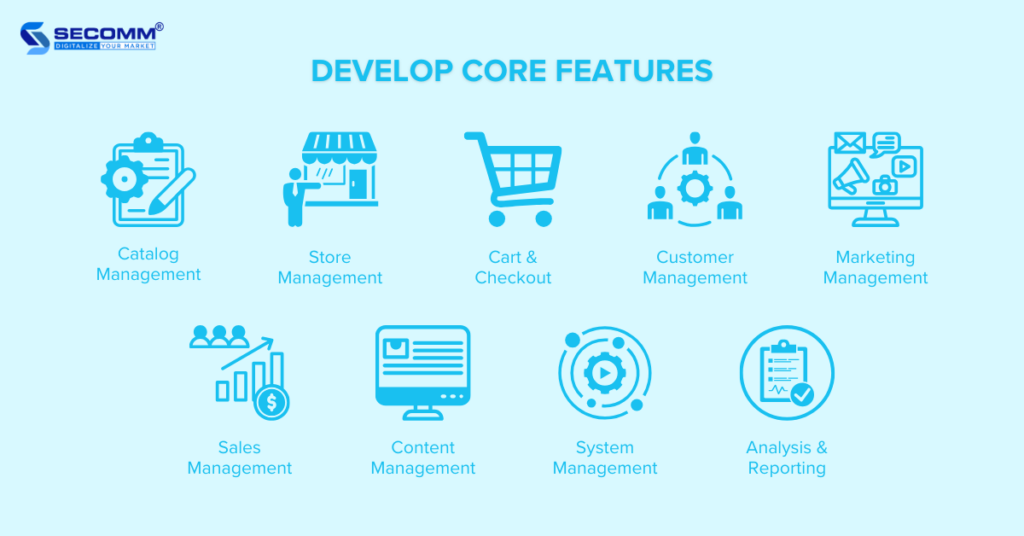
Some essential features that a pharmacy eCommerce website should have include
After developing features and ensuring a successful testing and website launch, businesses are obligated to complete the legal procedures associated with eCommerce operations.
According to Decree 52/2013/ND-CP by the Government of Vietnam, any individual or organization owning an e-commerce website for sales is required to notify or register with the Ministry of Industry and Trade through the online public service portal of the Ministry of Industry and Trade.
Note: Websites that operate beyond the specified period or fail to register/notify the authorized management agency within the designated timeframe may be subject to administrative penalties as per regulations.
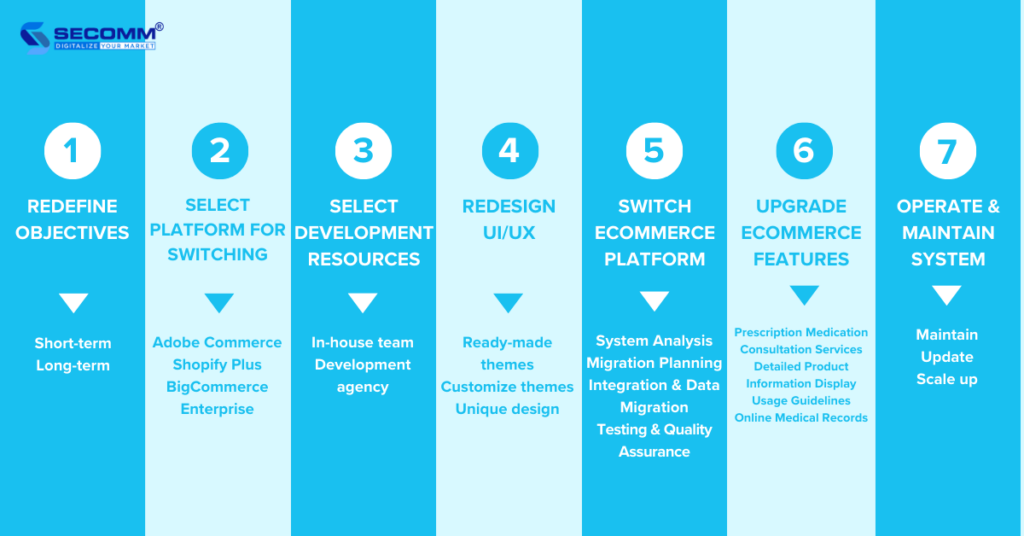
In the process of business development and amidst significant market changes, it’s important to realign goals to suit the evolving landscape. This time for business leaders to redefine objectives regarding the overall strategy, timeline, and budget for investing in the pharmacy eCommerce website.
During this phase, businesses often focus on short-term and long-term goals related to expanding the online pharmacy
For long-term goals, businesses may consider goals such as expanding market segments, establishing a loyalty program, and cultivating shopping habits for healthcare products, pharmaceuticals, and medical equipment.
For long-term goals, businesses may prioritize goals related to tapping into new potential customers, revenue growth, and supporting eCommerce marketing strategies such as livestreaming, gamification, affiliate marketing, and influencer marketing.
When SaaS platforms can’t support businesses to expand the system anymore, re-platforming to another robust platform is a top choice. Platforms like Adobe Commerce, Shopify Plus, and BigCommerce Enterprise can help businesses facilitate a deeply custom pharmacy eCommerce website.

When re-platforming, businesses have challenges such as switching costs, time to train personnel, and data loss throughout the platform migration process.
To build a high-complexity online pharmacy on a professional platform, businesses need resources to facilitate it effectively.
Businesses can decide to build an in-house team or seek a development agency. Regardless of the choice, it requires businesses to have practical experience on the selected platform.

For building an in-house team, businesses need to recruit and train IT and eCommerce personnel to develop on the selected platform. This option may take time and budget to establish a high-performing team but it allows the business to have better control over resources and actively adjust or develop the website system.
In case businesses hire a development agency, here are some criteria to consider:
Partnering with a professional development agency will help businesses gain specialized knowledge, enhance experience, and create an online pharmacy tailored to the specific needs of the industry.
During the platform migration process, businesses can keep the current website design without making any changes. However, some businesses tend to redesign their websites to align with new strategies and the new platform.
Similar to the previous phase, businesses have three options to design their pharmacy eCommerce websites: using ready-made themes, customizing themes, or designing a unique interface.
However, in phase 2, businesses often decide to customize themes or design a unique interface to express the brand image and the pharmaceutical eCommerce industry.
After the right eCommerce platform for migrating, businesses should carry out the process to minimize the risk of data loss or errors. Typically, the migration process is automated as much as possible to avoid potential issues.
The migration process includes the following steps:
After re-platforming, the business needs to perform thorough checks to ensure that the data has been migrated completely and accurately according to the plan.
Beyond core features, businesses should focus on building a system with more complex features, including advanced and industry-specific functionalities for pharmaceutical eCommerce.

In addition, businesses need to consistently update and enhance these features to meet user needs and keep pace with market trends.
When testing the eCommerce system, businesses need to thoroughly check the entire website and its features over a specific period to ensure order processing speed and website stability. If any issues arise, businesses should immediately contact the in-house team or development partner to adjust and improve the website accordingly before officially going live.
Once the pharmacy eCommerce website system is stable, businesses should focus on eCommerce marketing strategies or Omnichannel approaches to enhance their online pharmacy.
Additionally, regular maintenance, updates, and continuous system upgrades are essential to sustain growth and quickly adapt to changes in the eCommerce market in general and the healthcare market in particular.
The Bottom Line
In general, the journey of building a pharmacy eCommerce website in Vietnam is not an easy task. This work demands substantial investments of time and budget from businesses to research the most suitable eCommerce strategy for each stage of their development.
Understanding the challenges that businesses may encounter when building an online pharmacy, SECOMM is ready to provide custom solutions for developing an eCommerce system.
Contact SECOMM or call the hotline at 028 7108 9908 for a free consultation.
 2
2
 7,151
7,151
 0
0
 1
1
According to The Business Research Company, the global pharmaceutical eCommerce market is projected to reach $732.3 billion by 2027. This represents a significant opportunity for pharmacies, healthcare service providers, or hospitals/clinics to implement eCommerce and reach a broader range of potential customers. To achieve this, building an online pharmacy on a professional platform is a great idea to address industry-specific challenges.

When building a pharmacy eCommerce website, businesses must meet numerous criteria to ensure professionalism, safety, and legal compliance within this industry.
The typical customer profile in the pharmaceutical eCommerce sector consists of individuals seeking to purchase medications, medical equipment, and other healthcare products for themselves, family, or friends.
Thus, the website interface needs to be visually appealing, and user-friendly, and prioritize colors such as blue or white to create a sense of safety and cleanliness.
Other factors, such as layout, font choice, and imagery, should be carefully selected and coordinated to deliver the most professional user experience.
When building an online pharmacy, beyond default eCommerce features, businesses should focus on developing the following features to address industry-specific needs:
An online pharmacy is a system that contains various crucial information including personal details, payment information, and the health status of customers. Therefore, the security system of the website needs to be built and deployed carefully to ensure the safety of customer data.
Pharmaceutical eCommerce is a specialized business area subject to the regulations of the healthcare/pharmaceutical industry. eCommerce pharmaceutical businesses need to comply with these regulations to ensure that their operations are legal and safe for customers.
Below are some key legal regulations that e-commerce pharmaceutical businesses need to adhere to in Vietnam:
In addition, pharmaceutical eCommerce businesses also need to comply with other legal regulations, such as Cybersecurity Law, Consumer Protection Law, and eCommerce Law.
Although this industry has many challenges to deploy, businesses always have eCommerce platforms to create their online pharmacies. Here are the 5 leading platforms for building online pharmacy that businesses may consider.
BigCommerce is a cloud-based eCommerce platform operating on the Software as a Service (SaaS) model, enabling businesses to create and manage online stores.
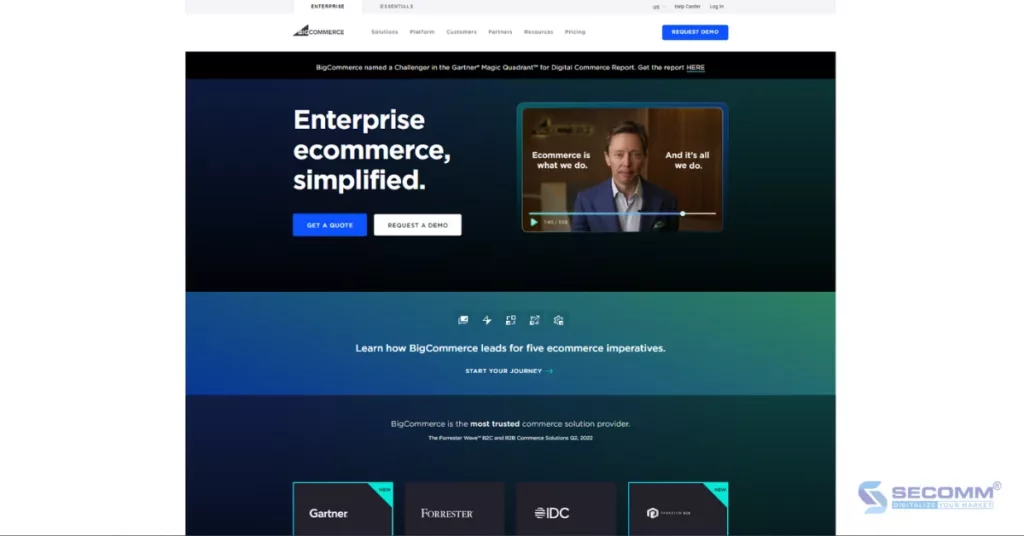
Currently, BigCommerce offers four main solutions, including
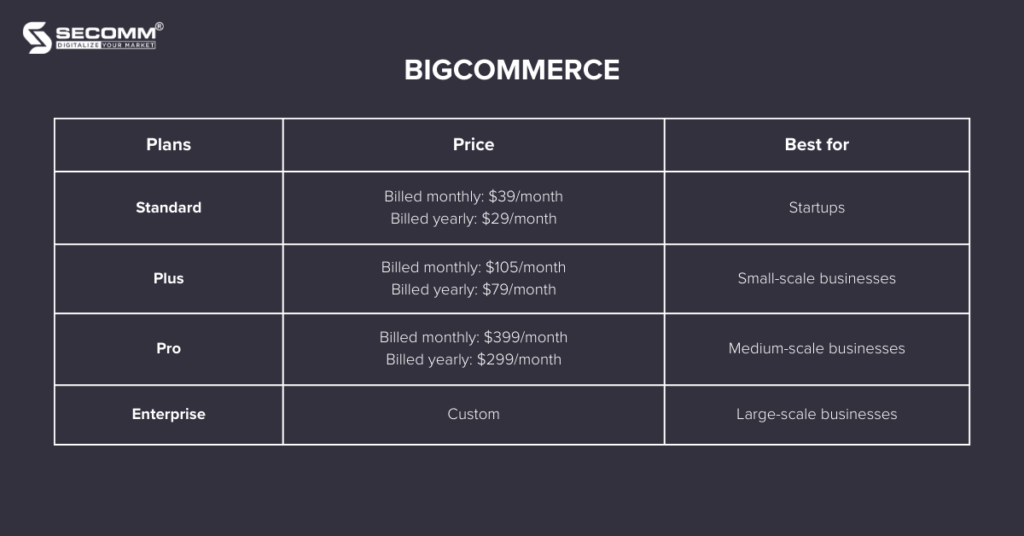
Pros:
Cons:
Some famous pharmaceutical eCommerce businesses currently utilizing BigCommerce include Victoria Health, Molton Brown, LARQ, and Zyppah.
Shopify is a SaaS eCommerce platform established in 2006. To date, Shopify has rapidly become one of the leading platforms in the eCommerce industry, supporting thousands of businesses worldwide to initiate and grow their online ventures.
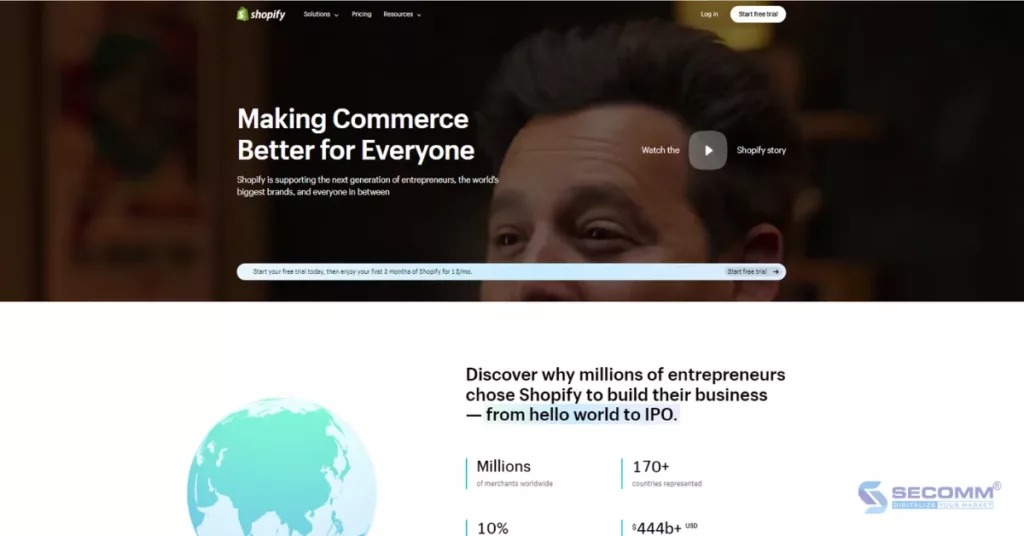
The cost to use the Shopify platform is quite diverse, including these three solutions:
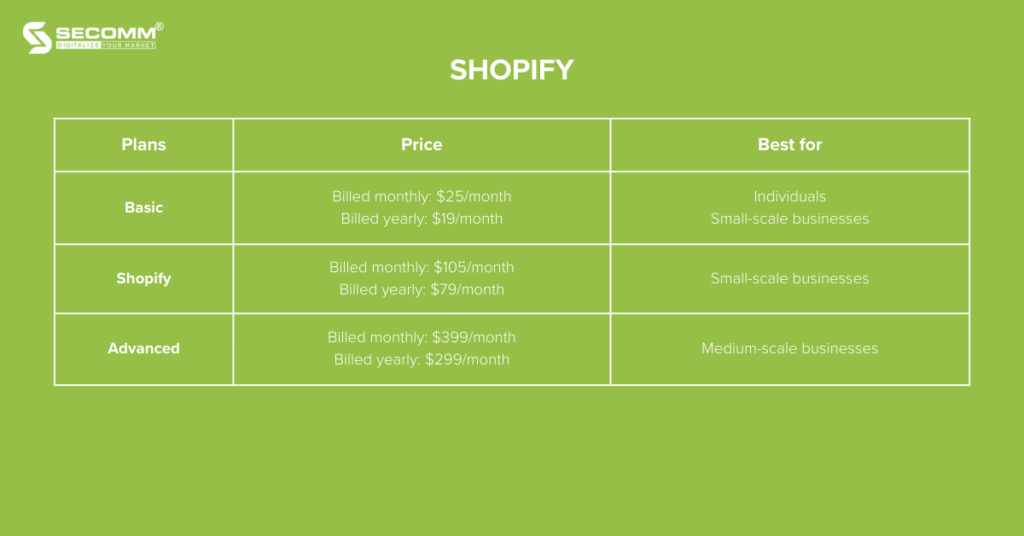
In addition, Shopify provides eCommerce solutions tailored to businesses with different needs and wants, such as:
Learn more: Top 5 benefits of Headless Commerce
Pros:
Cons:
Healthcare, pharmaceutical, and medical businesses using Shopify include Dr.Axe, 310 Nutrition, Hiya, and BUBS Naturals.
StoreHippo is a SaaS eCommerce platform established in 2014 in India. Over the years, this platform has consistently updated its technologies to meet the website-building needs of businesses, particularly those in the pharmaceutical eCommerce sector.

Similar to other SaaS platforms, StoreHippo offers a variety of solutions to choose from:
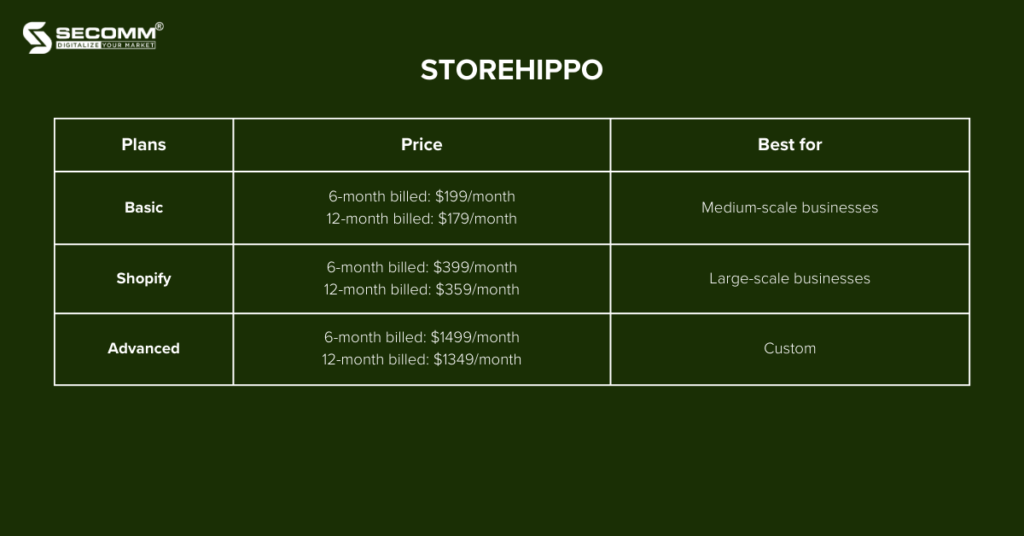
Pros:
Cons:
Some brands that built their online pharmacy with StoreHippo include WoundProfessional, Kunooz, and On A Healthy Note.
WooCommerce is an open-source eCommerce plugin developed for the WordPress platform, one of the most popular content management systems (CMS) globally. WooCommerce enables businesses to turn their WordPress websites into online stores or integrate eCommerce features into existing websites.
The license fee of WooCommerce depends on the complexity of each project, averaging around $1,000 for a basic eCommerce website and $10,000 for a more advanced eCommerce website.
Pros:
Cons:
Brands using WooCommerce to build online pharmacy include Dr. Scholl’s, myLAB Box, Superdrug Health Clinics, and Apothecanna.
Adobe Commerce, formerly known as Magento Commerce, is a professional and widely used eCommerce system. Adobe Commerce is part of the Adobe Experience Cloud product line and is designed to assist businesses in building eCommerce websites.
Currently, Adobe Commerce provides businesses with two main versions:
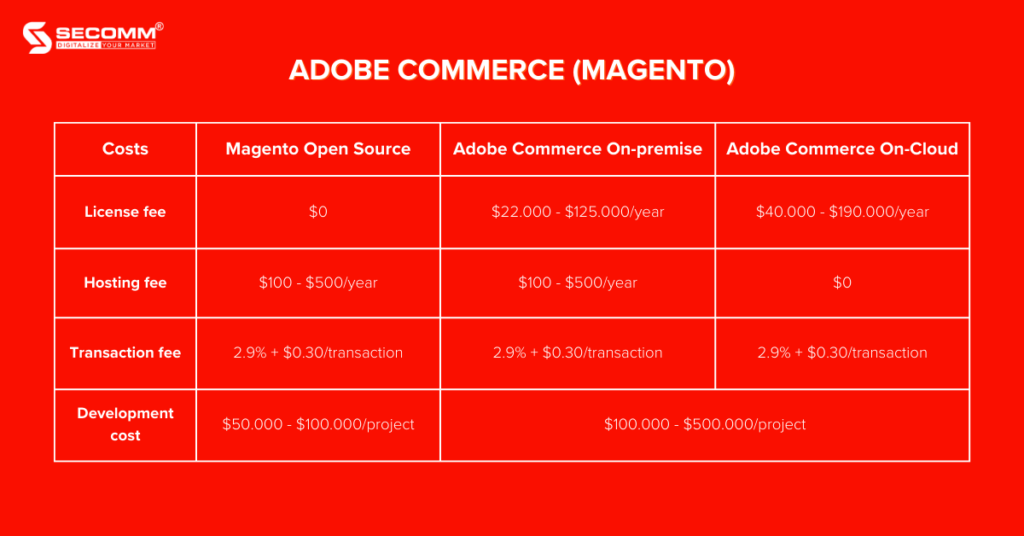
Pros:
Cons:
This list is just a few examples for businesses to reference; there are many other robust eCommerce platforms that businesses can consider based on specific needs and available resources.
With extensive experience in implementing eCommerce for clients in various countries, SECOMM understands the challenges and difficulties businesses face during the deployment of pharmaceutical eCommerce.
Contact SECOMM now or call the hotline at 02871089908 today for a free consultation.
 2
2
 9,407
9,407
 0
0
 1
1
In the ever-growing digital age, online drugstores have become an ideal destination for global users seeking convenient and safe ways to care for their health and purchase medications online. The robust growth of eCommerce and changes in user behavior have driven the expansion of this pharmaceutical eCommerce industry.
Below are some crucial insights into why pharmaceutical eCommerce has become an essential component of the modern healthcare system.
Pharmaceutical eCommerce has become a promising business model in recent years. According to the “Healthcare eCommerce Global Market Report” compiled by The Business Research Company, pharmaceutical eCommerce is categorized into three main models:

This is a model that enables consumers to order and purchase various products such as prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, vitamins, dietary supplements, healthcare, personal care, etc., through online shopping channels.
Some well-known pharmaceutical eCommerce by type examples include Droga Raia (Brazil), Netmeds (India), Pharmacity (Vietnam), etc.
Consumers can access healthcare consultation, advice, and diagnostic services through various applications for this type of pharmaceutical eCommerce. Under this model, consumers typically subscribe to and pay for these services through packages or on a subscription basis (monthly or yearly).
Companies adopting this service-oriented eCommerce model include Teladoc (USA), iCliniq (India), SBB Healthcare (Vietnam), and others.
This pharmaceutical eCommerce model often involves websites or applications created by hospitals/clinics to assist patients in scheduling appointments, offering healthcare packages, prescription medications, and more.
Examples of hospitals/clinics following the eCommerce model by end-users include The Royal Melbourne Hospital (Australia), NYC Health+ Hospital (USA), Vinmec (Vietnam), and others.
Certainly, Covid has not only led to a rise in traditional healthcare expenditures but has also acted as a driving force for pharmaceutical eCommerce. In the United States, telehealth visits witnessed a remarkable surge of 2,600% in March 2020 (during the peak of the COVID-19 outbreak in the U.S.) compared to the same month in 2019.
The growth of the pharmaceutical eCommerce market seems unabated. According to a recent report by CMS, total healthcare spending in the United States reached $3.8 trillion, marking a 4.6% increase in 2022. The Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to experience rapid growth in healthcare eCommerce, with a projected CAGR of 20.5% from 2020 to 2027.
Nielsen predicts that the pharmaceutical eCommerce market in Vietnam will attain a value of $10 billion by 2025.
Some other reasons for the rise of pharmaceutical eCommerce include:
Apollo Pharmacy is a well-known retail pharmacy chain in India, affiliated with the Apollo Hospitals. After years of operation in the healthcare sector, Apollo decided to establish an eCommerce website to serve millions of customers nationwide. The Apollo eCommerce website is built on the Magento platform, ensuring the capability to manage an extensive product catalog.
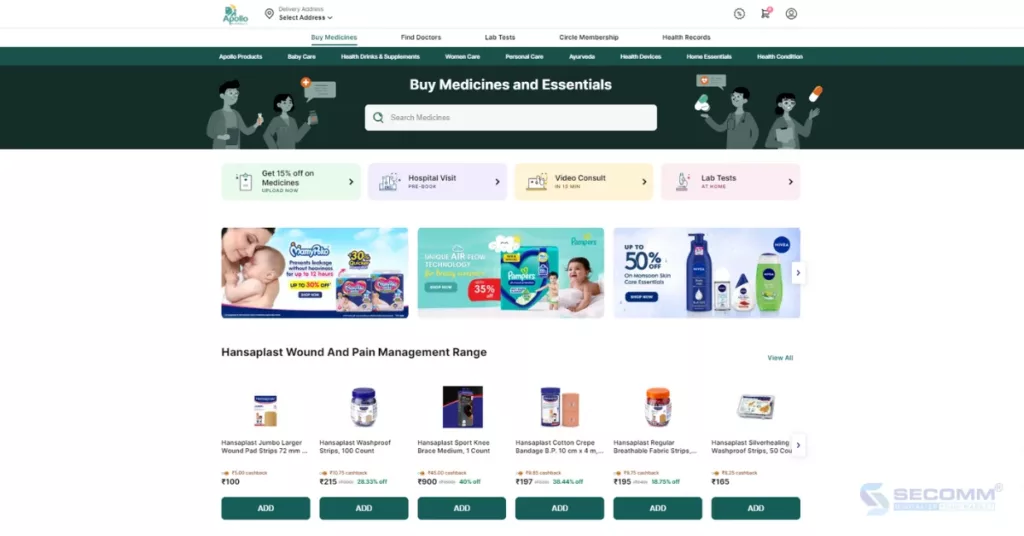
Beyond selling prescription and non-prescription drugs, as well as health care products, Apollo also provides various related services. Among these, notable offerings include online consultation services, health check-up appointments, vaccination appointments, and insurance sales.
Teladoc Health, Inc. is an American healthcare technology company headquartered in Purchase, New York. The company provides remote healthcare services, including video consultations, phone consultations, and remote health monitoring.
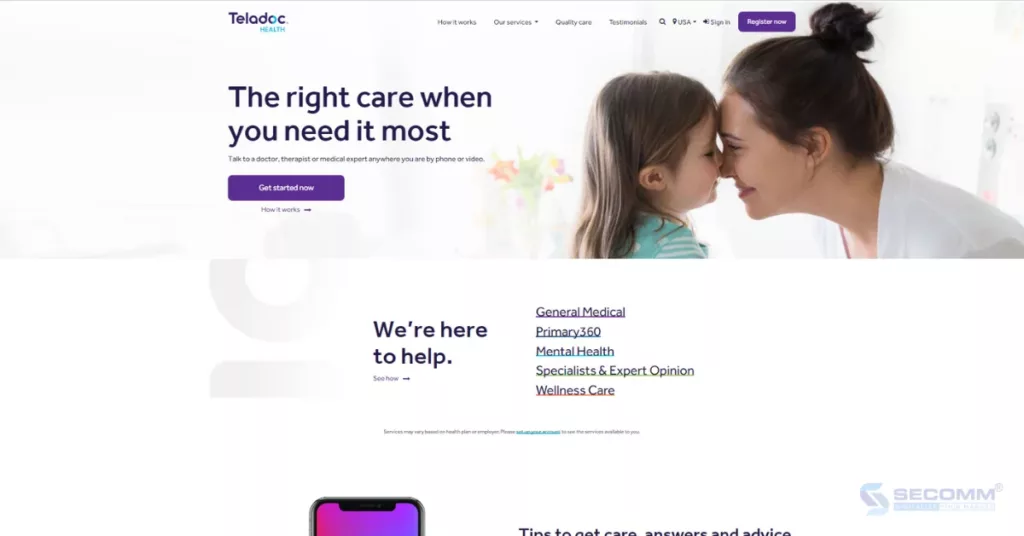
By rapidly deploying a website and eCommerce application, along with the utilization of cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and data analytics, Teladoc has been able to enhance customer experience and deliver improved remote healthcare services.
Mayo Clinic was founded in 1889 by Dr. William W. Mayo and his two sons, Dr. Charles and Dr. William J. Mayo. Initially, Mayo Clinic was a small clinic specializing in providing healthcare services to the local community. However, the hospital quickly expanded and became one of the leading hospitals in the world.
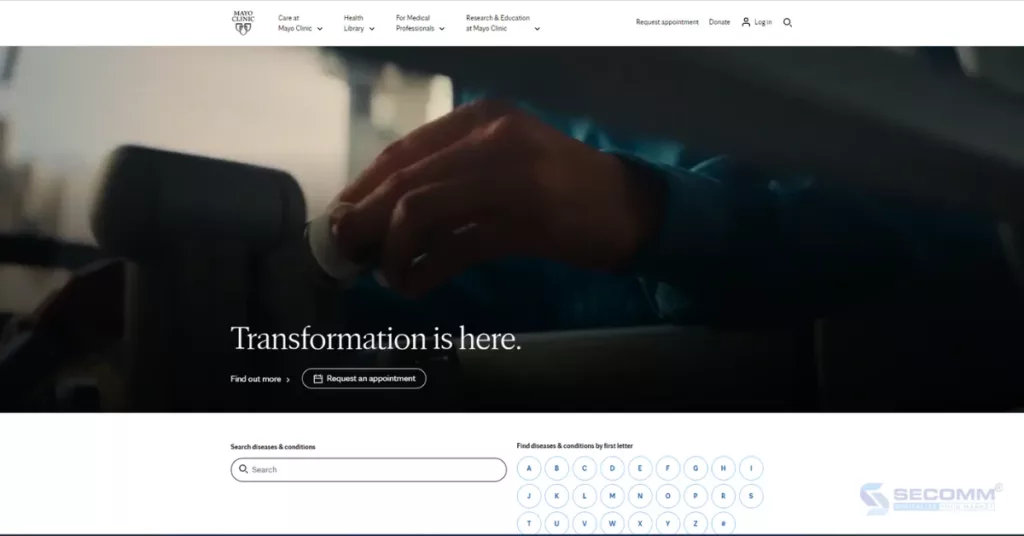
Much of Mayo Clinic’s success can be attributed to the early adoption of eCommerce, allowing patients to schedule appointments, check test results, and purchase medications online. This has helped patients save time and effort, contributing to Mayo Clinic’s overall success.
Learn more: The 10 Best Remarkable Pharmacy eCommerce Websites
The Bottom Line
Pharmaceutical eCommerce not only brings convenience and diverse choices for consumers but also presents attractive business opportunities for healthcare enterprises. If invested systematically and guided correctly, businesses in this field can seize significant opportunities in this promising market.
With extensive experience in implementing eCommerce for customers in various countries, SECOMM understands the difficulties and challenges that businesses face during the deployment process.
Contact SECOMM now or call directly at the hotline number (02871089908) today for a free consultation
 2
2
 14,184
14,184
 0
0
 1
1
OpenCart is an open-source eCommerce platform based on the PHP programming language, utilizing the MySQL database and HTML components to build eCommerce websites. According to Builtwith, the platform powers over 2,500 websites, with the majority in the United States and Russia.
OpenCart offers businesses various options for building eCommerce websites: Free (Open Source) and Cloud Store (Paid). Due to the flexibility of open-source code, many businesses choose this platform to meet specialized requirements in website development.
Below are some brands that have used OpenCart to create dedicated eCommerce websites
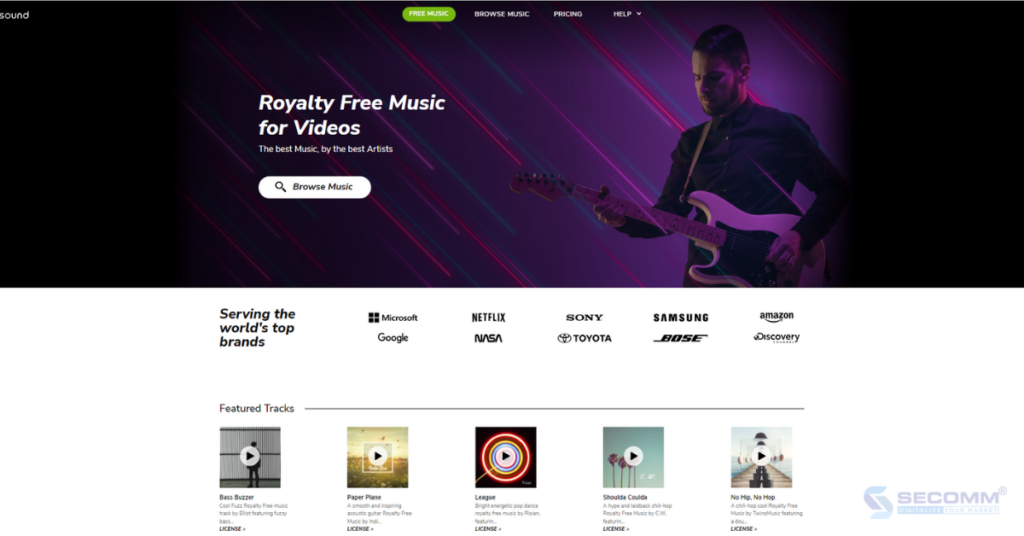
Bensound is the brainchild of musician Benjamin Tissot, founded in 2012. It is an eCommerce website specializing in providing free and licensed music, as well as sound effects. Initially, Benjamin Tissot composed and licensed only his songs on this platform.
However, as the service grew, Benjamin Tissot started accepting musical works from other artists, making it an ideal destination for content creators on platforms like YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram.
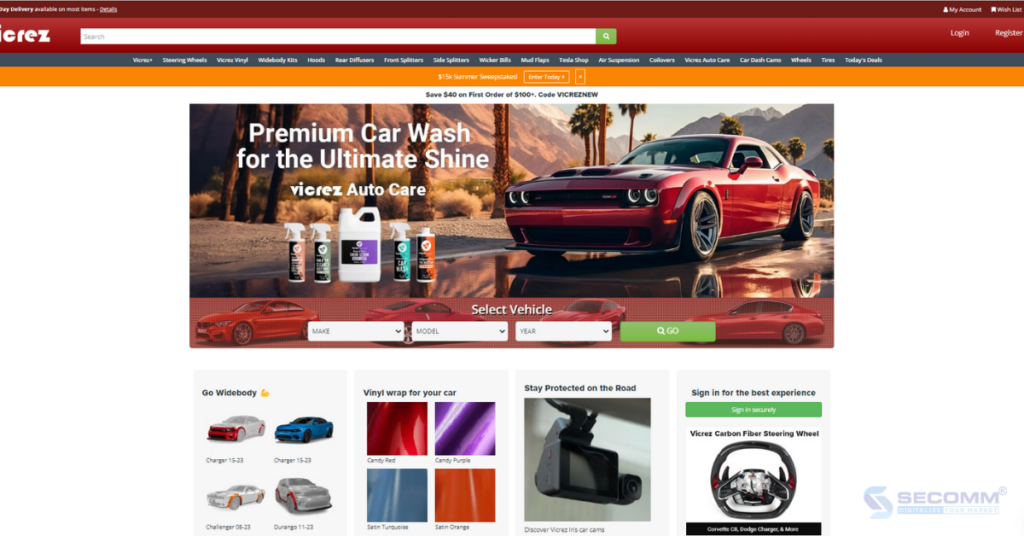
Vicrez is an online automotive parts retailer established in 2014 in the city of Whittier, Southern California, USA. What sets Vicrez apart is that customers can shop online for any external car parts and accessories to customize their vehicles according to their individual preferences.
Pharmacy Direct is the first online pharmacy to follow the eCommerce model, owned and operated by pharmacists in Australia since 1996. Initially, the brand operated on a small scale, serving local customers. However, as the demand for health products in Australia steadily increased, Pharmacy Direct experienced remarkable growth.
The business invested more in its eCommerce website to offer over 17,000 products, including vitamins, supplements, beauty products, fragrances, childcare products, prescription medications, and over-the-counter medicines from reputable pharmaceutical brands. This expansion allowed Pharmacy Direct to provide online services to the Australian population.

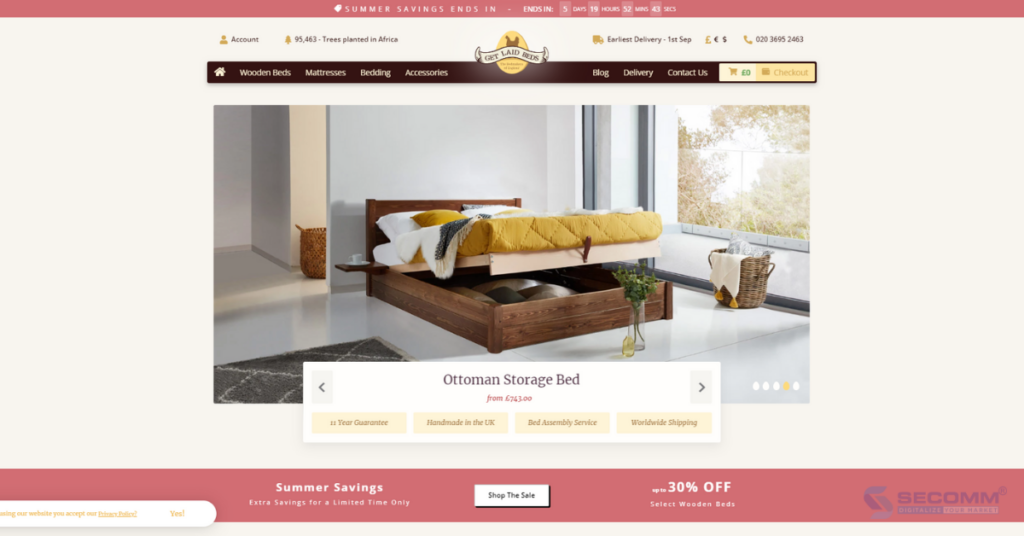
Get Laid Beds is a business specializing in handcrafting solid wood beds, founded in 2012 by John and Jean, a pair of architect and carpenter friends.
After more than 10 years of development, Get Laid Beds has expanded its product lines to include bedroom furniture, focusing on building its eCommerce website and enhancing customer service. This brand has gained popularity among customers in the UK and the US.
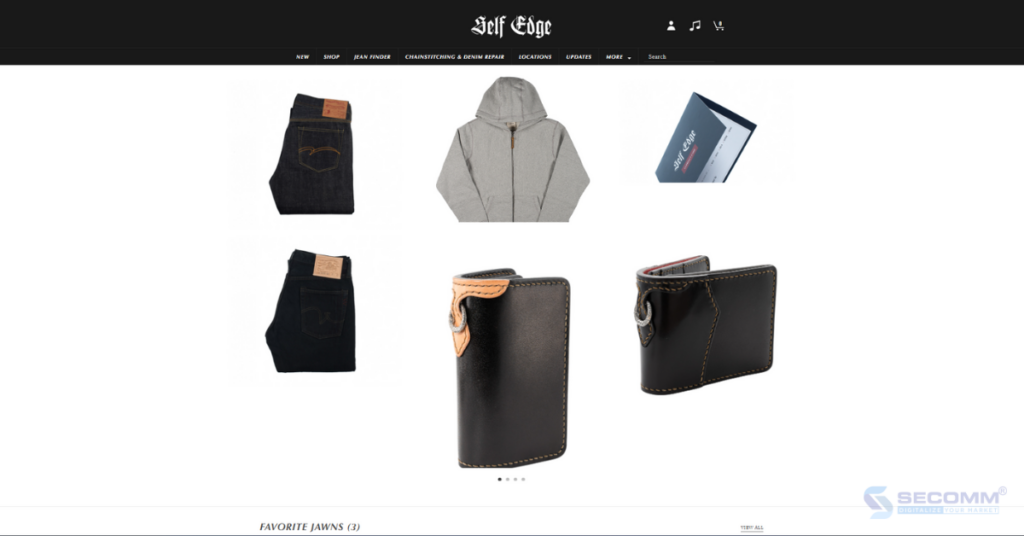
Self Edge is a men’s fashion brand with a vintage style, established in 2006 by the American couple Kiya and Demitra Babzani. Currently, Self Edge has a presence in major cities such as San Francisco, New York, Los Angeles, Portland, and San Jose del Cabo.
Additionally, Self Edge focuses on developing its eCommerce website to reach new customers across the United States and Mexico.
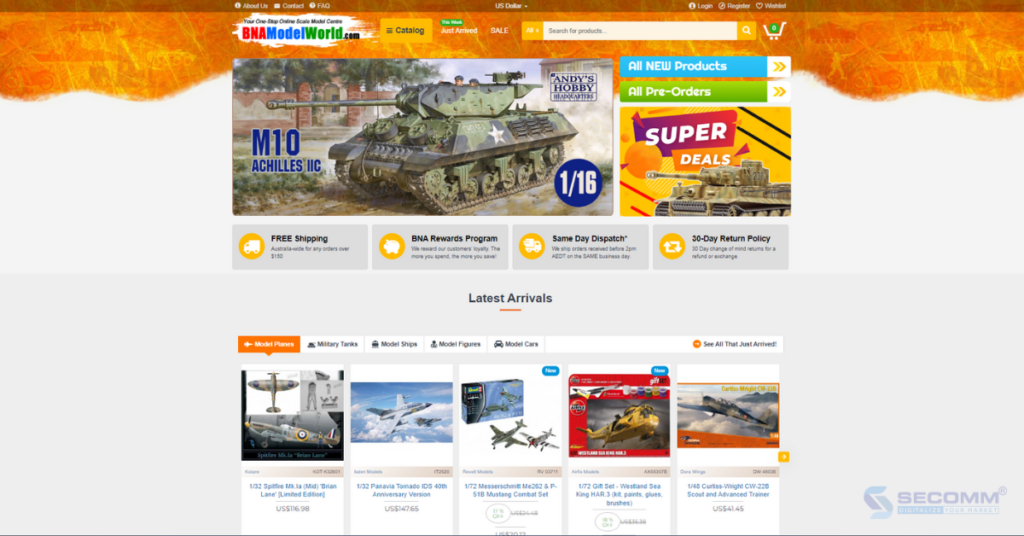
BNA Model World is a model business established in 2007 in Australia. Since its establishment, the brand’s management has focused on the eCommerce market and gradually upgraded its products/services. Currently, BNA Model World offers over 100,000 products from more than 1,000 manufacturers, serving over 104,000 customers worldwide.
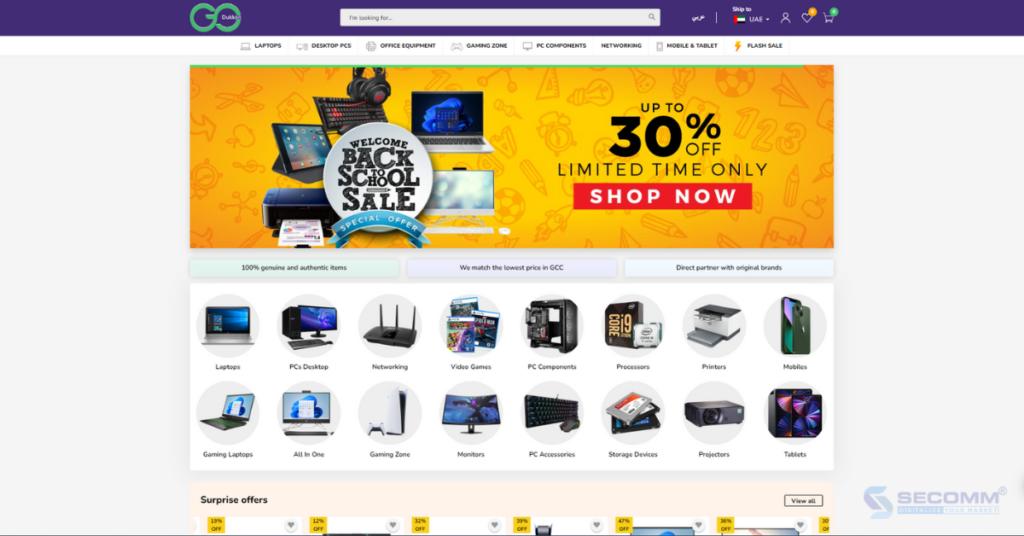
Godukkan is a consumer electronics retail business established in 2017 and headquartered in Dubai, United Arab Emirates (UAE). Godukkan’s main goal is to become the number one eCommerce website in the UAE, offering a wide range of products, including laptops, mobile phones, tablets, PCs, gaming equipment, and more.
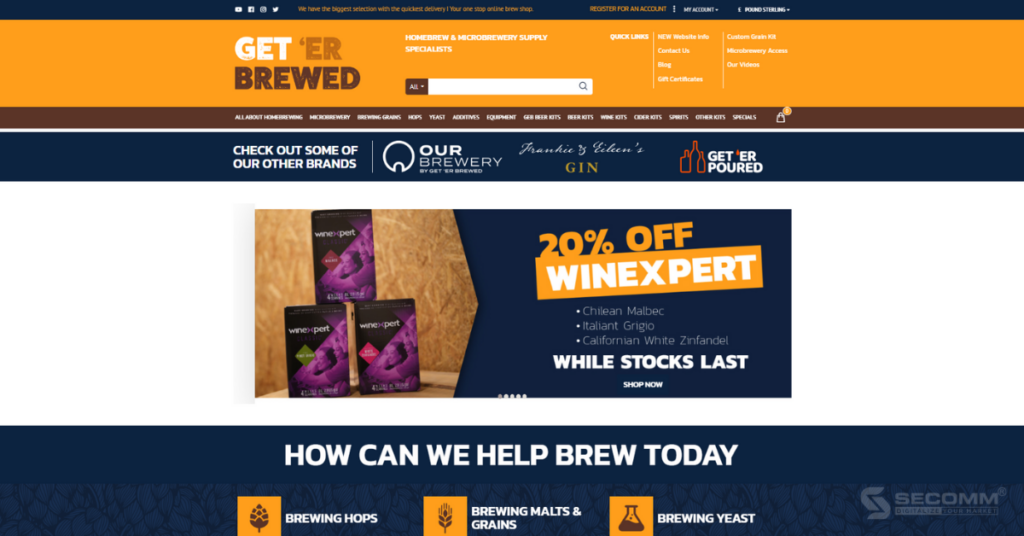
Get Er Brewed is a beverage brand specializing in brewing beer, wine, tea, etc., as well as supplying fermentation ingredients and brewing equipment. The business was established in 2013 and is based in Northern Ireland.
In recent years, Get Er Brewed has expanded its reach by launching an OpenCart website to cater to an international customer base, achieving certain successes, particularly in securing contracts for the installation of fermentation and brewing systems.
With over 20 years of experience in the pet industry, brothers Raymond and Roger decided to establish CatSmart, the largest cat-centric brand in Singapore. Currently, CatSmart is actively investing in its OpenCart website and expanding its presence beyond traditional retail branches in the “Lion City.”
Derails is a business specializing in designing and selling model trains, established in 2010. With the boom of eCommerce, Derails began building an OpenCart website to adapt to the changing market.
The Bottom Line
Here are 10 brands that have developed OpenCart websites and achieved success in both branding and revenue. This success serves as inspiration for other businesses seeking solutions to break through their operations and enhance competitiveness in the market.
Learn more: OpenCart vs Magento: Which Fits Your Business Best?
With extensive experience in deploying eCommerce for clients in many countries, SECOMM understands the difficulties and challenges that businesses face during implementation.
Contact SECOMM now or call the hotline at 02871089908 today for a free consultation.
 2
2
 11,117
11,117
 0
0
 1
1
The eCommerce world is growing, and the significance of building and developing eCommerce websites has never been more crucial. Among the popular SaaS platforms, Shopify stands out as a name that commands attention.
Shopify is a SaaS platform and an outstanding solution that helps thousands worldwide turn their online business ideas into reality.
So, what is it? Why it is the top choice for eCommerce businesses, ranging from small-scale to large-scale operations. Let’s explore the power of Shopify in this article.
Shopify is a widely used eCommerce platform that allows businesses to build, develop, and manage their online store. With its user-friendly interface, even those with limited technical expertise can effortlessly navigate it easily.
Shopify operates as a Software as a Service (SaaS), requiring businesses to pay a monthly fee for usage and adhere to the platform’s regulations. However, the platform manages hosting and takes responsibility for technical issues, ensuring the security and efficient operation of the business’s eCommerce website.
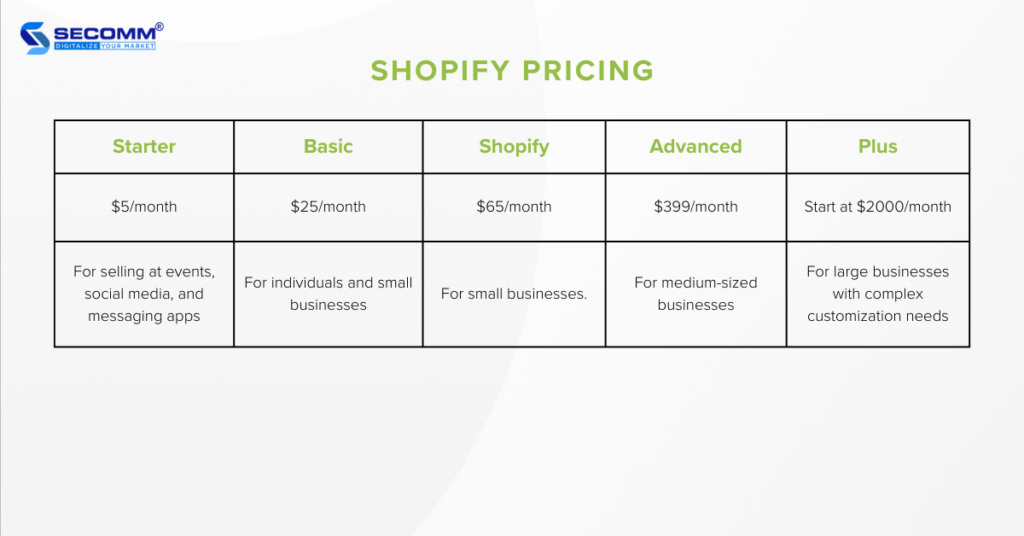
Until now, businesses have been familiar with 5 main solutions: Starter, Basic, Shopify, Advanced, and Plus. Recently, the platform introduced a new advanced solution called Commerce Components. This solution allows businesses to use the platform as a modular service, paying only for the features they need. It’s worth noting that this new solution is currently exclusive to the U.S. market.
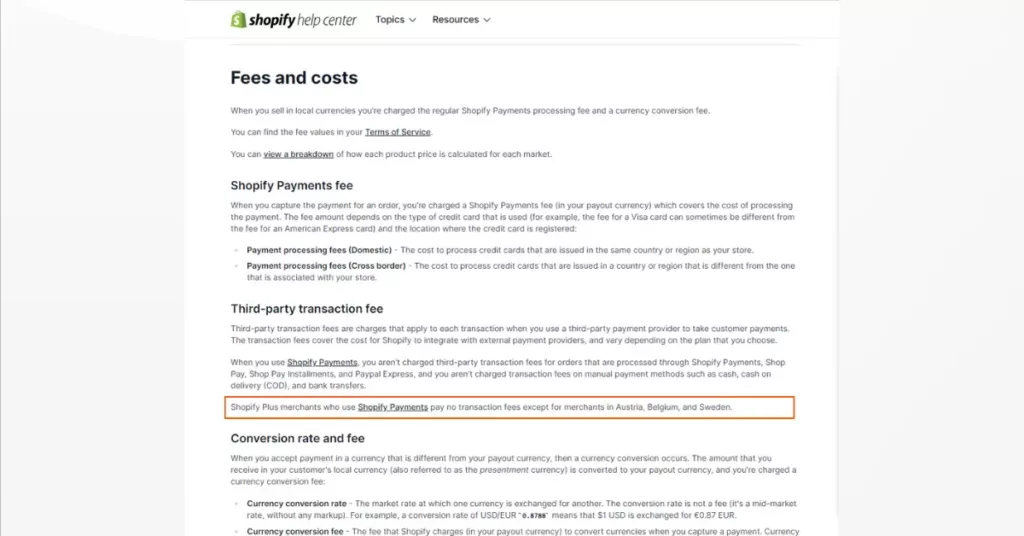
For the Basic, Shopify, Advanced, and Plus plans, transaction fees are waived when businesses use Shopify Payments. However, in reality, this payment method isn’t available for all countries. Currently, it only supports countries in this list.
Conversely, transaction fees will apply at rates of 2%, 1%, 0.5%, and 0.15%, respectively. For the Starter plan, whether or not using it, transaction fees still apply and are relatively high at 5%.
Plus businesses using this payment method will enjoy no transaction fees. However, this exemption doesn’t apply to businesses in Austria, Belgium, and Sweden, even though these countries are included in the list.
The platform is designed with an intuitive interface, allowing users with limited technical expertise to navigate it effortlessly. The platform offers a drag-and-drop editor, enabling businesses to easily add or remove products and make quick customizations.
Businesses also have the flexibility to customize layouts, colors, fonts, and font sizes, and add or remove elements and widgets from both free and premium themes.
Moreover, it offers businesses documentation and tutorial videos, ensuring a seamless and efficient setup and utilization experience.
The platform provides a range of cost-effective solutions suitable for startups and small to medium-sized businesses entering the eCommerce market. However, larger enterprises often prefer the Shopify Plus solution, given its reasonable costs of around $2,000, offering customization and scalability comparable to open-source platforms.
Moreover, as a SaaS platform, businesses pay a monthly fee for using it based on actual Gross Merchandise Volume (GMV), eliminating the need for a substantial one-time payment common with open-source platforms.
This is a versatile eCommerce platform suitable for businesses of all sizes and deployment needs. Whether for individuals, startups, or medium to large enterprises, it can provide features and tailored solutions to meet the specific needs of the business.
Some standout features that the platform brings to businesses include:
Beyond a diverse range of solutions and outstanding features, the platform offers businesses over 6,000 applications and integrations across various categories, from marketing, analytics, and shipping to inventory management and customer care. Each application is designed to address specific challenges and goals in the development of eCommerce.
Most applications and integrations in the App Store are developed by third-party businesses or independent developers. It provides resources, documentation, and tools for developers to create and release their applications on the store. While some apps offer a free version, it often comes with limited features, and businesses need to pay a monthly fee to access the full functionality.
Compared to other SaaS platforms, Shopify provides businesses with up to three mobile applications for effective remote management of eCommerce operations:
The SaaS platform offers 24/7 customer support through chat, hotline, and email to address any customer issues throughout the eCommerce website development process. The level of support is equivalent for both small and large businesses. Moreover, it provides Shopify Experts services to offer businesses in-depth technical support, including web development, web design, marketing, and sales.

While the fees for using the plans seem reasonable, depending on the need for additional features, apps, or extensions, monthly costs may increase significantly, posing challenges for cash flow management, especially for larger businesses.
While this popular SaaS platform serves as a versatile eCommerce platform, its regular plans come with limitations in terms of customization and scalability. If a business requires a unique design or seeks freedom in designing the website interface, customizing themes on it can be restrictive and may require advanced programming skills.
Moreover, customizing third-party features and apps may add extra costs and dependencies. As an eCommerce website grows and expands, performance may be affected by increased traffic, accompanied by significant cost increases due to transaction fees (if not using Shopify Payments), app fees, and platform fees.
In such cases, the regular pricing plans (Basic, Shopify, Advanced) may not meet the business’s expectations for scalability, and businesses should consider transitioning to the Plus platform for long-term goals.
As a SaaS platform, Shopify has full control over the source code and data within the entire eCommerce website system. This means that all data related to the eCommerce operations will be locked into the platform’s database.
If it declares bankruptcy or ceases operations, all business data on this platform could be lost. However, this risk is highly unlikely. In the second scenario, when a business switches to another eCommerce platform, the exported data is typically provided in the form of a CSV file.
Get started with Shopify today!
When Tobias Lütke transformed Shopify from a snowboard-selling website to an eCommerce platform for businesses, he probably couldn’t have envisioned the significant impact it would have on the global business and technology landscape. The figure of 4.5 million active eCommerce websites is sure to increase substantially in the coming years.
Having accompanied many businesses, both domestically and internationally, in deploying Shopify website, the SECOMM team has accumulated extensive experience in web development and a deep understanding of the platform.
Contact SECOMM or call the hotline at 028 7108 9908 to get started!
 2
2
 7,484
7,484
 0
0
 1
1
In the era of growing eCommerce, building an eCommerce website has become an essential part of how businesses approach and interact with customers. To successfully build and manage an online store, businesses will need to choose the right eCommerce platform that aligns with their business needs and wants. CS-Cart is one such eCommerce platform chosen by many medium and large-scale businesses.
According to BuiltWith, the platform currently supports approximately 13,232 websites globally, with Russia (about 3,772 websites) and the United States (about 2,809 websites) being the most prevalent markets.
In this article, SECOMM will share insights into what CS-Cart is and the advantages and disadvantages of this eCommerce platform.
CS-Cart is an open-source eCommerce platform that utilizes a SaaS (Software as a Service) model and was developed by Simbirsk Technologies Ltd. Launched for the first time in 2005, CS-Cart has gradually become one of the popular and trusted solutions used by many businesses worldwide.
Some eCommerce websites currently using the CS-Cart platform include TechAble (USA), Yumbles (UK), Bakeshop (Australia), ToolBrothers (Germany), Inasbay (Canada), Nguyễn Kim (Vietnam), and more.
Currently, CS-Cart offers two main solutions: No-Code (a no-code e-commerce website builder) and On-Premises (an open-source eCommerce solution for website customization).
No-Code solution pricing:
On-Premises solution pricing:
Moreover, CS-Cart provides a free open-source version for businesses to freely apply for building eCommerce websites.
One of the standout features of the CS-Cart platform is its flexibility, supporting businesses of both moderate and large scales in the eCommerce market.
Beyond employing open-source with the PHP language, CS-Cart also implements Headless architecture, allowing businesses extensive customization capabilities. This flexibility empowers businesses to create eCommerce websites tailored to their specific needs, delivering a unique and memorable shopping experience for customers.
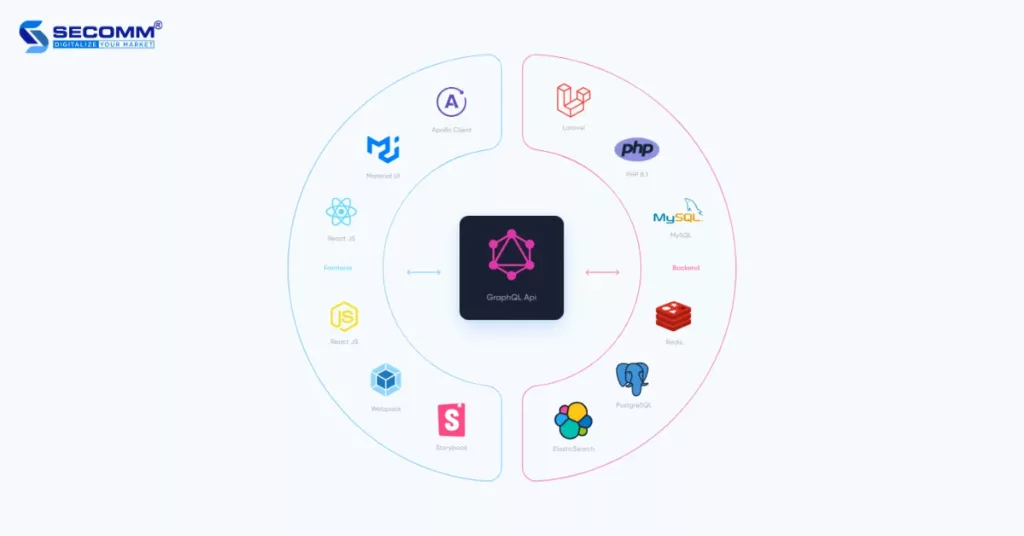
CS-Cart provides a comprehensive range of features from A to Z for operating an eCommerce system for businesses, including over 500 features and 2,000 available add-ons. From product management and order processing to marketing and SEO optimization, among others
This richness helps businesses minimize the need to integrate numerous third-party plugins, streamlining the technology stack of the eCommerce website.
CS-Cart is highly praised for its ability to connect and manage multiple suppliers with customers. This multi-vendor capability optimizes the management of different sellers, inventory, and payments, making the website system an ideal solution for businesses looking to oversee multiple suppliers on a single platform.
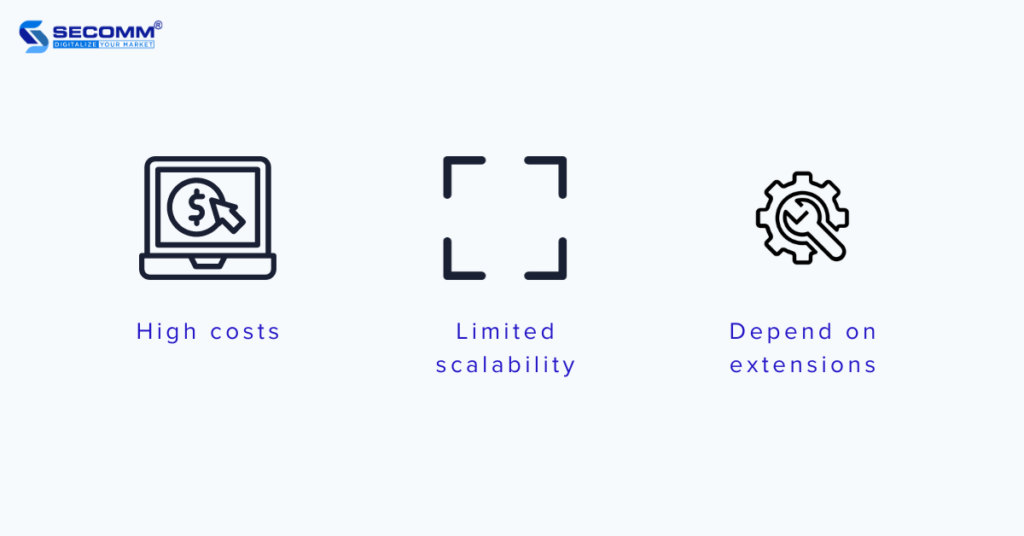
The paid versions, No-Code, and On-Premises, are considered to have relatively high usage costs. Additionally, the free version of CS-Cart may not be sufficient to meet the needs of building an eCommerce website for businesses, especially larger ones.
Businesses should note that many advanced features and functionalities will require purchasing licenses or additional add-ons. The costs associated with these add-ons and development and customization expenses can accumulate, particularly for small businesses or startups with limited budgets.
While CS-Cart is suitable for a variety of business scales, it may not be the most scalable solution for rapidly growing businesses with high levels of traffic and transactions. As businesses expand, performance issues may arise, necessitating improvements to the system’s performance or a transition to another platform.
Although CS-Cart provides many comprehensive features, some businesses feel the need for specific functionalities, requiring the purchase or development of additional third-party add-ons outside the CS-Cart ecosystem.
Relying heavily on third-party add-ons can lead to issues of compatibility, security concerns, and difficulties during the upgrade process.
The Bottom Line
In general, CS-Cart is an eCommerce platform suitable for businesses seeking an open-source solution, especially those with a medium scale. However, when upgrading to a more specialized and complex eCommerce website system, businesses will need to invest additional costs and resources to scale up the system.
These are the details about CS Cart, along with its notable advantages and disadvantages that businesses should consider when developing an eCommerce website.
After years of implementing eCommerce solutions for various businesses across different countries, SECOMM has accumulated valuable experience in helping businesses build and develop effective eCommerce websites.
Contact SECOMM or call the hotline at 02871089908 for advice on choosing a platform and deploying eCommerce today!
 2
2
 8,140
8,140
 0
0
 1
1
Businesses going headless aim to integrate with third-party applications or services to extend capabilities, boost performance, and enhance the flexibility of their eCommerce systems. Therefore, they have to understand eCommerce APIs or application programming interfaces.
This article will provide a brief overview of what eCommerce APIs are, how they work, the types, and roles for going headless, and the advantages gained through their integration.
Learn more: What is Headless Commerce?
eCommerce APIs are application programming interfaces (APIs) that enable external applications and systems to access and interact with the functionalities and data of an eCommerce platform.
For example, an eCommerce API allows businesses to access product information, place orders, handle payments, manage inventory, or integrate with third-party services such as shipping, analytics, email marketing, and delivery.
They operate based on a request-and-response model. When an application or system intends to access or perform a function on the eCommerce system, it sends a request to the API through an HTTP method such as GET, POST, PUT, or DELETE.
This request contains information like the URL address of the API and necessary data. Then, eCommerce APIs process the request and respond to the application or system that initiated the preceding request. This response includes an HTTP code indicating the outcome of the request (success or failure) and may contain data in formats like JSON, XML, etc.
APIs in the field of eCommerce are often published in the form of documentation known as “API documentation”. This documentation contains detailed instructions on how to establish connections and share data through the API. This helps businesses and developers understand how to use each type of API effectively.
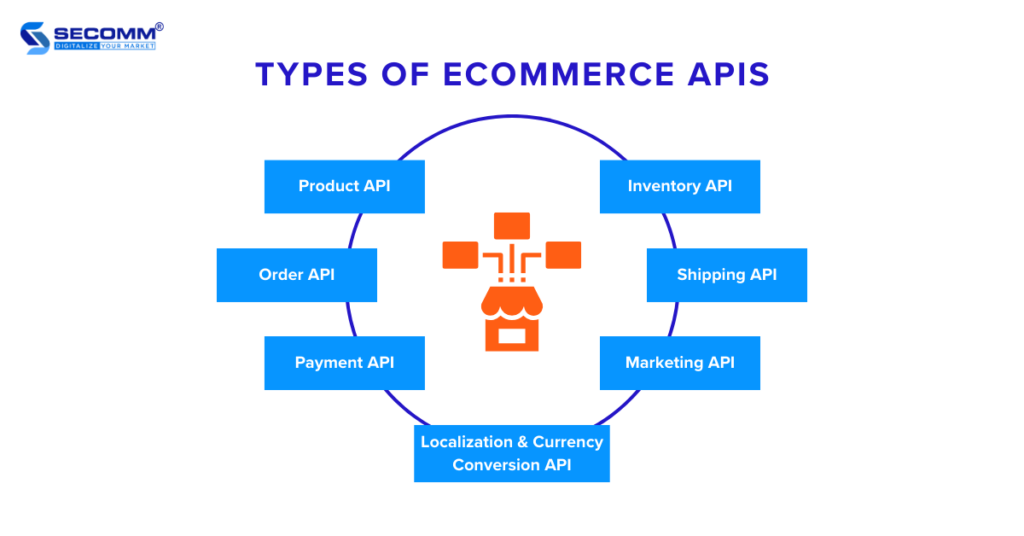
There are various types of eCommerce APIs depending on their functions and specific use cases. Some common include:
Headless is an eCommerce model that allows the separation of the user interface (frontend) and the management system (backend) of an eCommerce website. is also referred to as the “API-first” approach because the frontend and backend communicate with each other through an API layer.
Therefore, eCommerce APIs play a crucial role in connecting the frontend and backend. For instance, when a customer accesses a business’s eCommerce website and places an order, the website’s frontend can use eCommerce APIs to send requests to the backend to check product availability, calculate the order value, and create the order.
The backend can then process these requests and provide the necessary information to display to the customer.
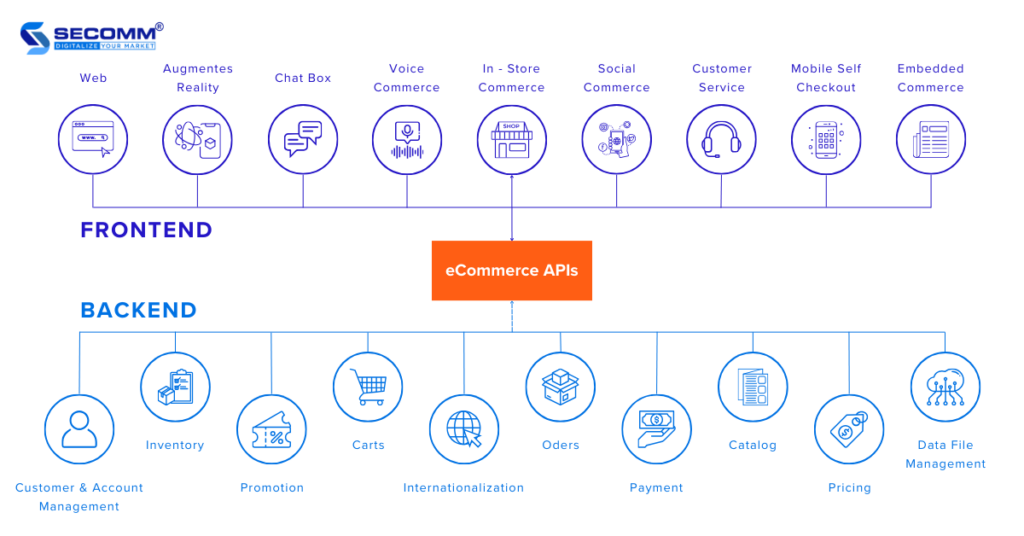
eCommerce APIs allow the frontend to access and interact with the functions and data of the backend. They also enable the backend to integrate with third-party services and systems such as CMS, CRM, ERP, and DXP. Additionally, eCommerce APIs help businesses create various user interfaces for diverse sales channels and devices, including websites, mobile apps, voice commerce, wearables, AR/VR.
These eCommerce APIs empower businesses to go headless flexibly, providing not only a multi-channel shopping experience but also facilitating rapid and efficient expansion and development in the international market.
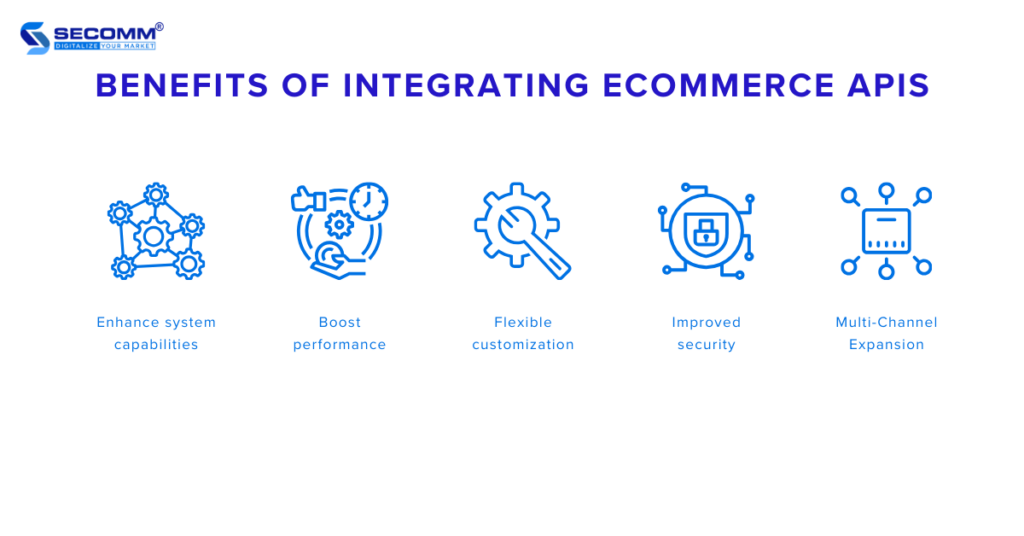
Businesses can add new functions and features to their eCommerce websites by using available APIs or creating their own APIs. This allows businesses to easily expand the capabilities of their eCommerce systems, providing customers with an enhanced shopping experience.
Businesses can optimize the performance of their eCommerce websites by leveraging eCommerce APIs to automate business processes, minimizing potential errors. For example, a business can use APIs to synchronize data across different systems for more efficient management and operations.
Businesses have the freedom to customize their eCommerce websites according to their needs and preferences by integrating APIs to connect with third-party applications and systems. For example, businesses can use APIs to create a unique user experience, incorporating new technologies such as AI, AR/VR, and blockchain.
Third-party applications and systems, especially payment systems, often include strict security protocols. Therefore, integrating them into a business’s website through APIs enhances the security of the site. This helps safeguard business data, customer information, and payment details from the risk of theft.
APIs enable businesses to integrate with various user interfaces, allowing them to expand their business operations across multiple sales channels, including websites, mobile apps, and even social media.
The Bottom Line
Here is what you need to know about eCommerce APIs – application programming interfaces that enable various applications and systems to interact with each other efficiently within the eCommerce system. In other words, eCommerce APIs act as a bridge between the frontend and backend in the Headless model, allowing businesses to customize operations flexibly and provide customers with a unique and seamless shopping experience.
Contact SECOMM or call the hotline at 028 7108 9908 to learn more about integrating eCommerce APIs and going headless. We have a team of experienced and specialized experts to turn your business ideas into reality and accompany businesses on their eCommerce journey.
 2
2
 6,972
6,972
 0
0
 1
1
Trong thời đại thương mại điện tử đang ngày càng lên ngôi như hiện nay, việc thu thập, phân tích và ứng dụng thông tin kinh doanh là một yếu tố quan trọng để nắm bắt được các cơ hội mới trong thị trường.
In the current era dominated by eCommerce, gathering, analyzing, and applying business information is crucial to seize new opportunities in the market. Business intelligence (BI) can be an invaluable tool for managing corporate data for enterprises.
So, what is Business Intelligence, and what makes it the perfect choice for large businesses?
Business Intelligence (BI), often referred to as intelligent business or corporate intelligence, is an information technology management system involved in collecting, organizing, analyzing, and transforming business data into valuable information to support decision-making and guide business strategy for enterprises.

BI systems help businesses track and measure key business performance indicators such as revenue, profit, profitability, customer satisfaction, consumer behaviour, favourite products, etc. Through the analysis and comparison of this collected data, BI systems enable the visualization of trends and the most suitable business models, thereby assisting corporate managers in developing appropriate business strategies.
A BI system is a collection of technologies, tools, and methods used to deploy the BI process in a business. This BI system typically includes components such as:
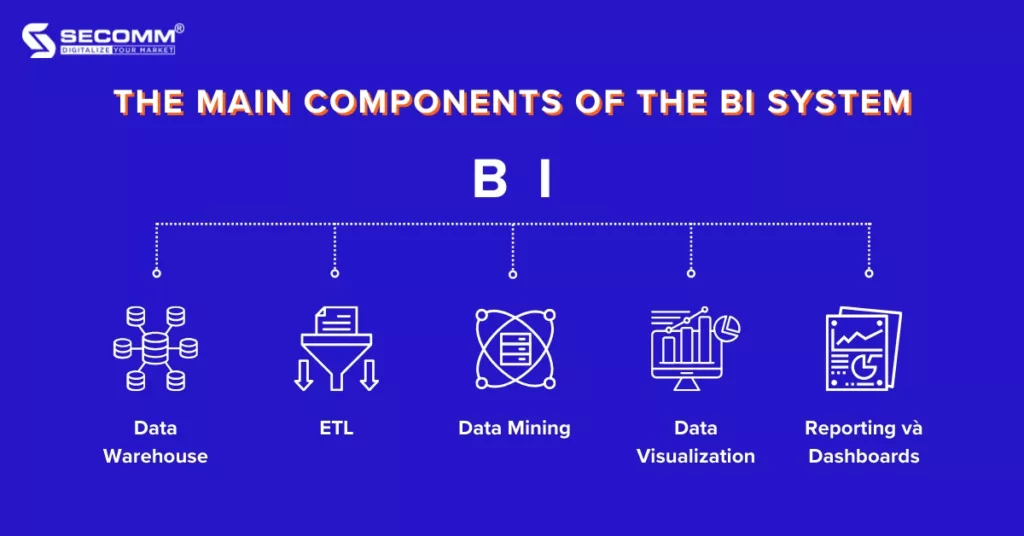
Tableau is an interactive data visualization software focused on business intelligence. Established in 2003 in Mountain View, California, and now headquartered in Seattle, Washington, Tableau was acquired by Salesforce in 2019 for $15.7 billion.

Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Microsoft Power BI is an interactive data visualization software developed by Microsoft in 2011, with a primary focus on business intelligence.

Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Looker is a popular BI system used for data visualization and analysis in large enterprises. This system allows users to access, explore, and analyze data most intuitively.

Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Amazon QuickSight is a serverless BI service operating on the cloud, developed by Amazon and released on February 22, 2022. Amazon QuickSight provides tools for data visualization, interactive dashboards, and machine-learning-supported data analysis.

Advantages:
Disadvantages:
ThoughtSpot is a self-service BI system developed in 2012. This system allows users to easily search, query, and visualize data, making it a popular choice among businesses.

Advantages:
Disadvantages:
View more: What is PIM? The 5 best PIM software for large enterprises
The above is a summary of 5 BI software options for large-scale enterprises, detailing the individual advantages and disadvantages of each system. Depending on the needs for BI system development and budget planning, businesses can consider and choose the most suitable BI solutions.
Contact SECOMM to learn more detailed information!
 2
2
 12,683
12,683
 0
0
 1
1
eCommerce has become an essential trend for successful business in the Vietnamese market. According to a report from Facebook’s SYNC Southeast Asia and consulting firm Bain & Company, Vietnam is expected to be the fastest-growing eCommerce market in Southeast Asia by 2026, with a total eCommerce goods value reaching $56 billion, 4.5 times that of 2021, ranking second in the region.
To harness the advantages of this thriving market, businesses need an eCommerce website system with a full range of functionalities, from basic to advanced. Therefore, planning a step-by-step construction of the functional system is crucial to avoid situations where there are ‘missing essentials’ or ‘unnecessary features’ for the business.
Here are some specialized functionalities that any eCommerce website system for businesses in this lucrative market should have!
Images and videos play a crucial role in allowing customers to evaluate the quality of products, especially high-involvement items like jewellery, watches, gemstones, etc.
Additionally, businesses can incorporate features such as 360-degree views, Augmented Reality (AR), or Virtual Reality (VR) to help customers get a comprehensive and realistic view of the product’s quality on the eCommerce website.
In today’s era where ‘good wood comes with good paint,’ investing in high-quality images or videos enhances the impression of a business’s products in the eyes of consumers and demonstrates the professionalism of the brand. Consequently, businesses can keep customers engaged on the website for longer periods, reduce bounce rates, and boost online sales.

One of the essential features of modern eCommerce systems is the ability to filter and search for products effectively, such as live search or ElasticSearch in Magento.
This feature plays a role in directing customers to the detailed product information they are looking to purchase, enhancing the overall customer experience and shortening the shopping journey.
As a result, businesses can improve customer satisfaction and streamline the purchasing process.

Sometimes, customers may be interested in a particular product but decide to purchase it later, or they might find an intriguing product and want to check detailed information before making a buying decision. In such cases, a wishlist allows customers to store these products for easy retrieval when they are ready to make a purchase decision.

Although promotional programs are not unfamiliar to consumers in the eCommerce market, this feature has never gone out of fashion for businesses. According to Google, up to 75% of customers view advertisements before making a purchase, and 84% of customers use information from ads to research product details.

Frequently displaying promotional programs/deals such as flash sales, D-Day promotions, festive season offers, etc., will stimulate customers’ ‘sale hunting’ desires, increase website traffic significantly, and boost sales for businesses.
After leveraging and analyzing the collected data from customers, an advanced eCommerce website system can provide suggestions for similar or related products, aiming to increase the quantity and value of orders. This, in turn, contributes to the growth of online sales revenue for the business.

Up-selling is a technique aimed at selling a more expensive version of a product that a customer already has or intends to purchase by adding new features or accessories to that product. Meanwhile, Cross-selling is a technique aimed at selling complementary products, items that may be related to the product a customer has purchased or intends to buy.
In addition to suggestions for similar and related products on the homepage, product category page, product detail page, and search results page, Up-selling and Cross-selling are also designed to appear on the checkout page to encourage customers to spend more.
The quick order placement feature is an essential function for an eCommerce website. To expedite the shopping process, it’s not enough to have a step-by-step ordering process. Businesses need to design a ‘quick order’ function that allows customers to add products to the checkout page immediately. This will be a significant advantage for businesses to expedite the customer’s ‘order confirmation’ process, thereby generating a surge in online sales.

Typically, the default checkout process on an eCommerce website is a step-by-step procedure, meaning that each step is completed automatically only after the customer finishes the previous one until the entire process is completed.
According to a report from Adobe, 88% of customers abandon their purchases simply because the checkout process takes too much time and is complicated. To streamline this cumbersome payment process, the One Step Checkout feature has been introduced. This feature provides essential information to customers in just one step, facilitating faster transactions and creating a smoother payment process.

Diverse payment methods, including card payments (local cards, VISA, Mastercard), e-wallets (MOMO, Zalopay), payment gateways (OnePay, VNPay, PayPal, Stripe), and Cash on Delivery (COD), will enhance the shopping experience for customers. Additionally, businesses should stay updated on emerging payment trends in the eCommerce market, such as creating their digital wallets, implementing Buy Now – Pay Later options, etc., to build a Loyalty Program and provide more payment choices for customers.

However, to diversify payment methods, businesses should choose open-source eCommerce platforms such as Magento, WooCommerce, and OpenCart to have high integration capabilities and ensure compatibility between payment software and the company’s website.
According to a report from Customer Gauge, 92% of customers will read product reviews from other users before making a purchasing decision. Therefore, the product review feature is always prioritized by businesses to be included in the functionality system from the beginning to enhance the brand’s credibility.
A website with many positive comments from previous users will attract attention and trust from potential new customers, laying the foundation for revenue growth for the business. In addition, negative reviews will help businesses identify the weaknesses of the product, thereby motivating them to improve product quality and services for the future.

In addition to a visually appealing interface and standard UI/UX, the ability to be compatible across multiple devices such as desktops, smartphones, and tablets is a mandatory feature that must be present on the interface of an eCommerce website. This is not only a factor affecting the Omnichannel experience of customers but also a criterion that influences SEO and rankings from Google.

Furthermore, many other features need to be considered for integration into the functional system of the eCommerce website of the business. This will depend on the strategy and business model of each enterprise, as well as the eCommerce platform the business is using.
With SaaS platforms, businesses will not have many options for features since these systems are pre-built, making it difficult to modify the source code and potentially causing instability if there are automatic edits or additions/removals of features.
In contrast, with open-source platforms, businesses have the freedom to choose features to build at each stage of brand development, as well as the ability to integrate with third-party utilities more easily than SaaS platforms.
With deep expertise and experience in developing complex eCommerce systems across multiple countries such as Vietnam, Australia, the US, and New Zealand, SECOMM understands the challenges in the process of building and deploying eCommerce functions that businesses are currently facing.
Contact SECOMM now for a free consultation on detailed eCommerce system development solutions!
 2
2
 10,299
10,299
 0
0
 1
1
Mini Apps or Mini Programs are small applications developed within Super Apps, allowing users to access them without the need for frequent downloads or updates like Native Apps (applications for Android and iOS) or Hybrid Apps (cross-platform applications)
Currently, there are various types of these apps, but the most popular ones include:
For example: Mini App on Momo
In addition to internal apps like ‘Heo Đất Momo’ or ‘Đi bộ cùng MoMo,’ MoMo has ambitious plans to expand its ecosystem by integrating these apps from partner brands. This e-wallet has allowed the integration of these apps from various brands in different sectors such as 7Eleven, AhaMart, Highlands Coffee, etc.
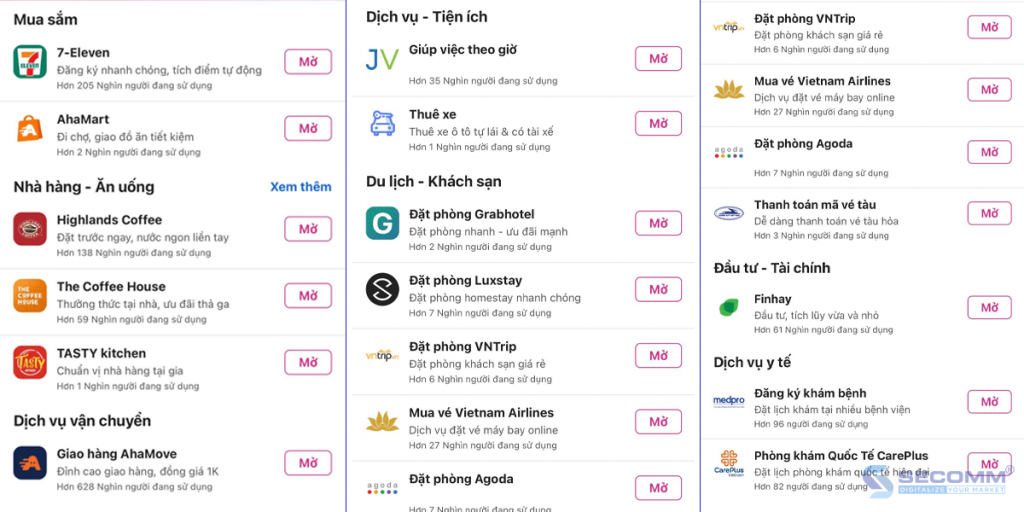
All Super Apps such as MoMo, Tiki, Shopee, Lazada, and Zalo allow other brands to register for free. However, businesses must pay for in-house IT teams or outsource to external units to develop these apps.
Compared to Native Apps or Hybrid Apps, Mini Apps have a simpler framework (pre-written code segments) and useful APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), enabling developers to deploy applications quickly within a cost-effective budget.
When businesses release these apps on Super Apps such as MoMo, Zalo, Tiki, Lazada, and Shopee, these brands gain access to and leverage millions of existing users. Here are the user statistics for some of these platforms:
Moreover, these apps can also take advantage of the existing utilities within the ecosystem of these “Giant” Apps, such as online payment, delivery services, marketing tools, etc.
These apps typically have very low file sizes, averaging around 10MB. This allows these applications to deliver a smooth user experience. By leveraging the ecosystem provided by “Giant” Apps, customers can have a seamless experience encompassing various activities such as shopping, payment, order tracking, customer support communication, voucher accumulation, etc., all within a single application.
During the eCommerce journey, businesses go through various stages: Social media commerce (Facebook, Zalo) → Selling on eCommerce platforms (Shopee, Lazada, Tiki, Sendo) → Mini App → Basic eCommerce website and app → Advanced eCommerce website and app.
Among these, these apps serves as a perfect stepping stone for businesses to adapt to technological infrastructure, navigate the eCommerce environment, and launch more effective online business campaigns.
While these apps are no longer unfamiliar globally, the term is still relatively new in Vietnam. Currently, in Vietnam, only Tiki has a dedicated team developing Mini Apps for businesses on the Tiki platform (Tini App). To develop these apps on other Super Apps, businesses must engage with development teams or agencies specialising in this area.
When releasing a Mini App, businesses must trade off the risk of customer data being in the hands of the ‘big players’ because all source code and data are stored on the servers of the “Giant” Apps.
Not expressing the full uniqueness of the business: Although each app is unique to individual businesses, it has to adhere to certain standards set by the “Giant” Apps, including frameworks, APIs, UI components, etc., to synchronize the interface with the ‘parent app.’ While this can provide a consistent user experience, it may not showcase the brand’s distinct personality.
In general, these apps serve as a perfect stepping stone for any business looking to enter the eCommerce market by leveraging the advantages of “Giant” Apps. However, limitations such as technical resources, user data, and brand positioning need to be carefully weighed before making a final decision.
 2
2
 18,347
18,347
 0
0
 1
1
In just a decade, eCommerce has become the epicentre of the online business market, undergoing continuous and robust growth. This is evident in the explosion of mobile commerce (m-commerce), the emergence of social commerce, and shifts in consumer behaviour and expectations.
So, how can businesses adapt to the ceaseless changes in the market? The answer lies in embracing new eCommerce technologies, one of which is Headless Commerce.
Today, businesses have many choices for building an eCommerce website, but fundamentally, the structure of a website includes the following main parts:
In traditional eCommerce models, businesses often use the monolithic model, which was developed over two decades ago. At that time, the monolithic architecture was the only choice for eCommerce businesses because there were no alternatives other than building, continuously updating, and maintaining.
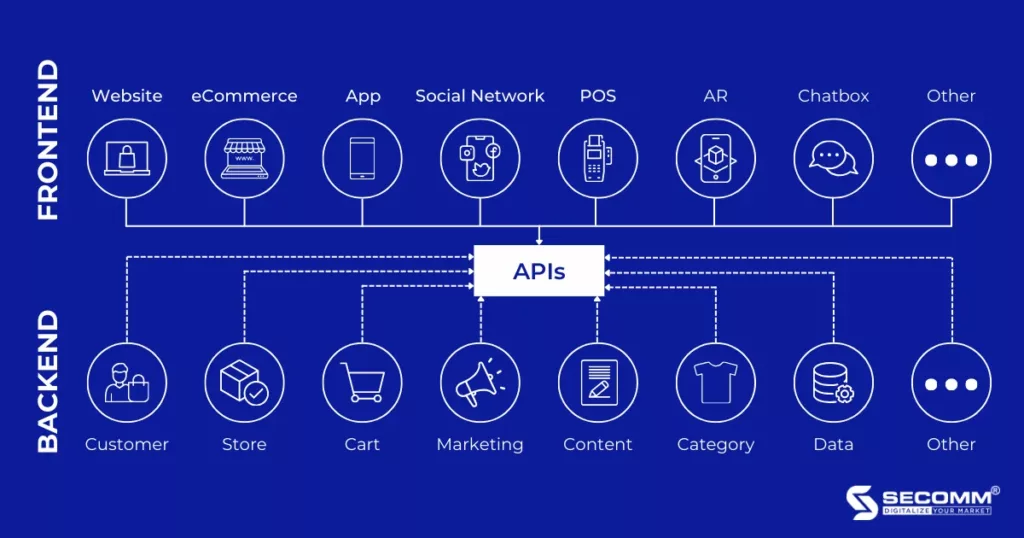
In the Monolithic Model, the frontend and backend are tightly connected, so any changes to the website require improvements in both. Therefore, every frontend change leads to a change in the backend structure and vice versa. Hence, every technology decision becomes riskier, and more complex, directly impacting the entire eCommerce website system.
On the other hand, Headless Commerce is an eCommerce architecture in which the frontend is separated from the backend, and connected through APIs. This allows businesses to easily customize and update functionality without interfering with the user interface or CMS pages.
For that reason, Headless Commerce has many competitive advantages compared to Monolithic Model:
| Headless Commerce | Monolithic Model |
| Separate frontend and backend but still “connect” seamlessly with API | Connect frontend and backend using common protocols (HTML, CSS, etc) |
| Enhance page loading speed | Page load times are slower due to multiple API calls from the platform in use |
| Flexible develop the frontend without needing to update or impact the backend | The backend is susceptible to frontend customization (especially unique designs) |
| Increase integration with third-party services/utilities | Although it is easy to integrate with services/utilities from third parties, it often leads to code bloat (too much source code) slowing down the website system |
| Adapting quickly to new channels enhances seamless customer experiences | Most are difficult to adapt to new sales channels |
Comparison table between Headless Commerce and Monolithic Model
According to Forbes, more than $1.65 billion in funding has been raised for Headless Commerce technologies during the 2020-2021 period.
Several platforms support Headless Commerce technology, including Magento Commerce (or Adobe Commerce), Shopify Plus, BigCommerce Enterprise, SAP, etc.

In Headless Commerce application platforms, separating frontend and backend into distinct components allows businesses to achieve limitless customization for designing an eCommerce system. For example, optimizing eCommerce functionalities and customizing the user interface can be done independently without impacting the overall system’s operation. As a result, businesses can better seize new opportunities in this competitive market.
Another crucial aspect of the Headless Commerce architecture is the connections between the frontend and backend through APIs. Thanks to these API connections, businesses can easily modify existing functionalities and develop new features when expanding the system and business model.
In platforms applying Headless Commerce technology, the frontend and backend are no longer tightly integrated into a unified entity. This separation allows for more independent and centralized data storage through API connections. This approach significantly accelerates the processing of API calls compared to traditional eCommerce platforms.
This enhancement reduces the amount of user data to be received and downloaded, thereby improving page loading speed. Given that page loading speed is a component of SEO (Search Engine Optimization), improving this aspect helps boost the website’s ranking on search engines such as Google, Safari, Cốc Cốc, and others.
Another notable advantage of API connections is the seamless integration they offer for eCommerce systems. This is particularly evident in the integration with various third-party services and utilities, such as CRM, ERP, PIM, BI, or other pre-integrated tools. Additionally, this architecture enables businesses to rapidly test services, and utilities, and measure their suitability for eCommerce campaigns.
This flexibility in integration allows businesses to adapt their technology stack to evolving needs and take advantage of the latest tools and services in the market, fostering innovation and efficiency.
In the Headless Commerce structure, API connections facilitate seamless integration with various sales channels, including eCommerce platforms, websites, mobile apps, social media, or any future channels with available APIs.
Simultaneously, Headless CMS (Headless Content Management System) aids in optimizing content across devices such as desktop, tablet, and mobile, connected through the Internet of Things (IoT), to provide a seamless shopping experience for customers. This approach ensures that content is consistently delivered and tailored for diverse devices, enhancing the overall customer journey.
Headless Commerce finds widespread applications in eCommerce implementation. Some common use cases include:
Allows administrators to manage products, marketing campaigns, and inventory through the eCommerce website’s backend system.
Changes in the backend system do not impact the frontend user interface, and APIs can be controlled to display information on the user’s mobile app frontend.
Utilized by eCommerce businesses to implement AR technology.
Users can view dynamic simulated images of products through augmented reality devices, acting as a frontend linked to the backend through APIs in a Headless Commerce application.
PIM (Product Information Management) and CRM (Customer Relationship Management) function as back-office software for processing product information and customer data in the backend system.
In a Headless Commerce structure, backend data can be controlled and displayed on various frontend interfaces through API links, such as eCommerce platforms, websites, mobile apps, and social media.
Enables businesses to deploy eCommerce concurrently with Headless Commerce, offering various advantages.
The decision to adopt Headless Commerce depends on the long-term eCommerce business strategies of a company.
In summary, the implementation of Headless Commerce alongside eCommerce is becoming a realistic option for businesses with long-term market strategies, thanks to the numerous benefits it offers. Whether or not to adopt Headless Commerce and when depends on various eCommerce business strategies.
With over 8 years of experience designing complex eCommerce systems for companies like An Nam Gourmet, Laybyland, Jasnor, etc., SECOMM understands the challenges that businesses face when exploring new eCommerce technologies.
Contact SECOMM now for a free consultation on detailed eCommerce system development solutions!
 2
2
 12,175
12,175
 0
0
 1
1
eCommerce has been booming more than ever, driving the demand for new technologies to adapt to the continuous growth of the market. Some emerging eCommerce technologies include VR/AR, MSI (Multi-Source Inventory), PWA (Progressive Web Apps), Headless Commerce, etc. However, among these, the technology that developers and businesses are currently paying the most attention to is Cloud eCommerce.
Cloud eCommerce utilizes server clusters and cloud computing systems from cloud service providers to process large transaction volumes and online sales channel traffic. In simpler terms, Cloud eCommerce involves renting Internet servers based on cloud platforms to process, store, or use applications for various eCommerce business purposes.

Before cloud-based eCommerce platforms and other solutions emerged, traditional eCommerce platforms like IBM WebSphere and Oracle ATG required on-premise server setups and continuous maintenance. Unlike those “on-premise” eCommerce solutions, cloud-based eCommerce allows companies to outsource their IT infrastructure without the need to invest in equipment and continuous maintenance as before.
This solution helps businesses adapt to the increasing demands of customers, enhance security, simplify maintenance, and integrate new eCommerce applications as needed. For these reasons, Cloud eCommerce is often combined with eCommerce platforms such as Shopify Plus, Salesforce, Magento, etc.
There are several cloud eCommerce solutions to choose from, including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, each with different resource requirements.
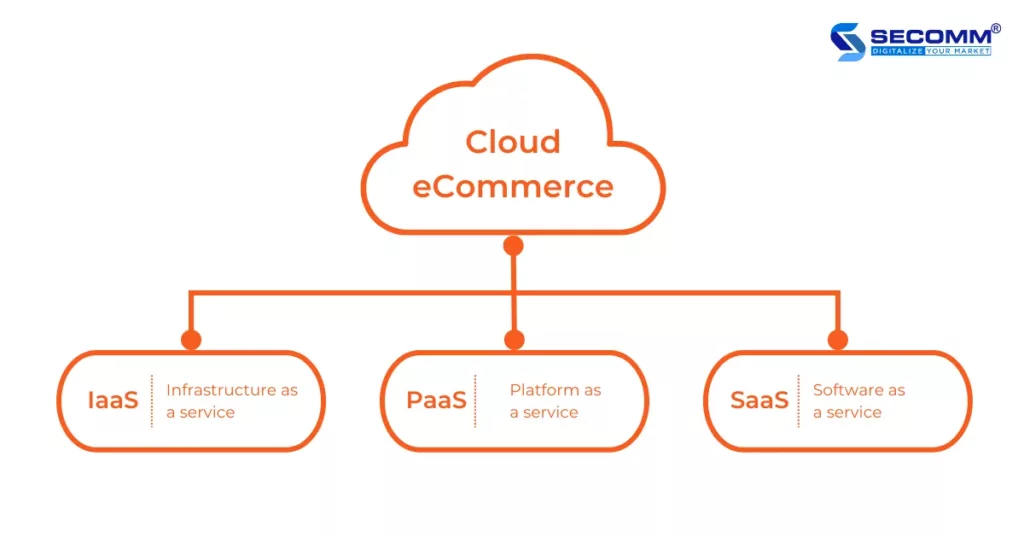
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is where businesses rent physical resources such as servers, databases, and network equipment to build a sustainable eCommerce architecture. IaaS eCommerce focuses on providing on-demand data storage on disks and virtual servers, making it easy for businesses to use database services rather than dealing with hardware. However, businesses are responsible for managing applications, data, runtime, middleware, and the operating system on this infrastructure.
Notable IaaS providers include Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Digital Ocean. IaaS is suitable for businesses wanting full control over the system without the complexity of on-premise eCommerce.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is similar to IaaS but requires less infrastructure management, allowing more time to build eCommerce applications using predefined infrastructure with pre-defined operating systems and processes to handle resources, planning, and error correction.
For example, Google App Engine provides a PaaS environment for developers to build web applications without worrying about infrastructure. PaaS eCommerce is suitable for businesses needing to build specialized eCommerce applications and are willing to eliminate infrastructure-related factors in their technology stack.
Software as a Service (SaaS) provides ready-made eCommerce services, including complete eCommerce solutions or individual eCommerce applications like Product Information Management (PIM) software, Order Management System (OMS), etc. SaaS eCommerce providers are responsible for managing both the infrastructure and software and businesses only need to configure the desired software. Additionally, SaaS eCommerce developers can work outside the user interface with APIs to develop custom solutions without the need for custom software development.
SaaS eCommerce is suitable for businesses that want to quickly deploy eCommerce solutions without significant involvement in infrastructure and software management.
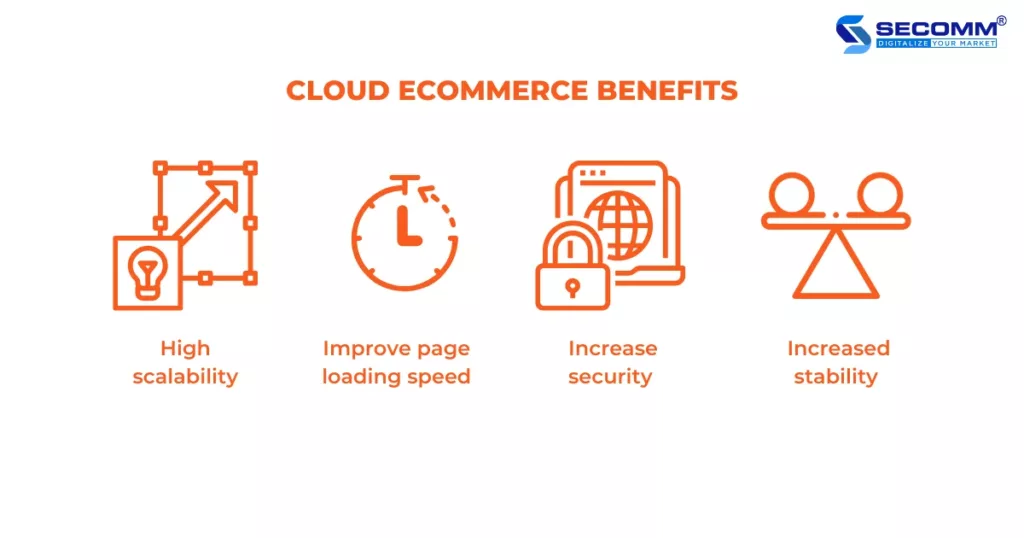
Cloud eCommerce inherits features from PaaS, making it easier to expand system functionality.
Typically, when fashion businesses start, they may not initially focus on scalability. However, from a strategic perspective, investing in technologies with scalability capabilities, such as Cloud eCommerce, can help businesses expand system functionality in each stage of eCommerce website development to foster business growth.
According to Think with Google, if a website takes up to 6 seconds to load, the probability of users bouncing increases by 106%. That’s why businesses need to focus on page load speed.
When an eCommerce website leverages Cloud eCommerce with data stored on a cloud platform, the speed of processing queries and API calls is significantly faster.
In the current era of the 4.0 technological revolution, the concern for data loss is a major focus for business leaders. As a response to this, numerous new technologies have emerged to address this goal.
According to PC Magazine, Cloud eCommerce provides control over data and storage locations, along with options such as physical backups and file synchronization to ensure data safety. Additionally, Cloud eCommerce supports businesses in obtaining PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) certification, enhancing the credibility of their website.
Typically, businesses struggle to optimize storage capacity on their websites, especially when facing a massive surge in traffic during peak seasons, such as the “sale hunting” period. This sudden increase in workload poses a significant challenge to storage operations.
Cloud eCommerce offers a flexible solution to meet the demands of unpredictable spikes in traffic, whether seasonal or even hourly. It can dynamically scale up or down to support the real-time needs of a business. Overall, Cloud eCommerce is becoming a widely adopted technology in the digital transformation journey, helping businesses expand their functionality, improve page loading speeds, and enhance the security and stability of their websites.
However, mastering these new technologies requires programmers to possess a significant amount of specialized knowledge and hands-on experience with various complex projects. As a result, the costs associated with implementing Cloud eCommerce can be relatively high.
With over 9 years of experience designing complex eCommerce systems for companies like An Nam Gourmet, Laybyland, Jasnor, etc., SECOMM understands the challenges that businesses face when exploring new eCommerce technologies.
Contact SECOMM today for a free consultation on detailed eCommerce system development solutions!
 3
3
 11,850
11,850
 0
0
 2
2Subscribe to get the latest eBook!
Hotline