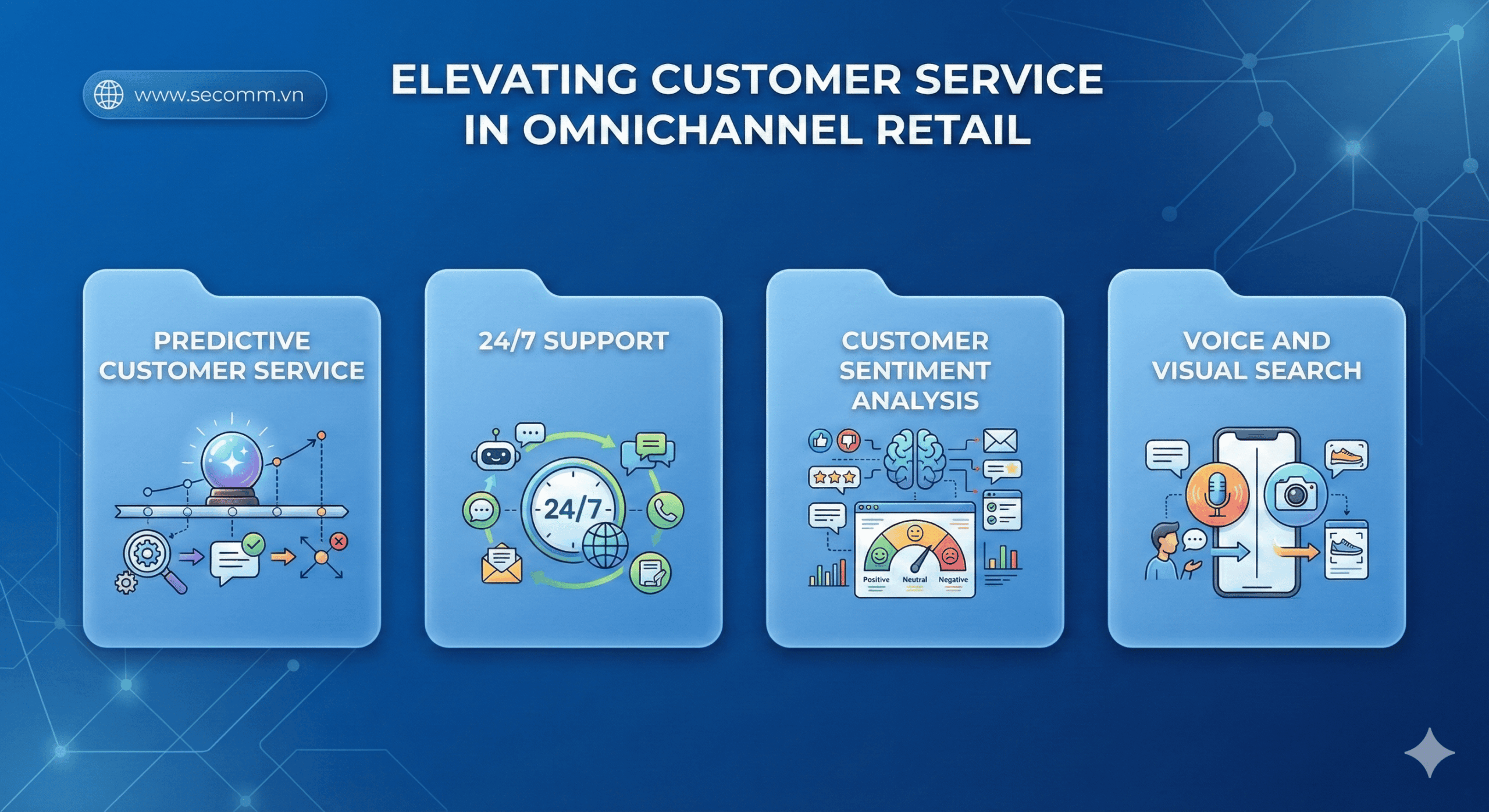
ECommerce Ecosystem Grasping For Efficiently Business-Driven








Vietnamese ecommerce businesses are welcoming transformational opportunities amidst the rapid development of technology, market, consumer, and major investor presence. However, for outstanding and sustainable growth, in addition to seizing opportunities, businesses need to build a comprehensive ecommerce ecosystem. Therefore, a best-finish of the ecosystem in general and its components, in particular, is the foundation stimulating businesses, markets, and user interactions.
So, what are the components of the ecosystem? How should the business develop the ecosystem in line with its business strategy?
1. What components are included in the ecommerce ecosystem?
The ecommerce ecosystem is an interconnected community implementing all interactions and connections of human organisms, social organisms, information technology and applications, and services to provide value and effectively operate the components in the ecosystem. (Based on the concept of Assoc. Prof. Dr. Nguyen Van Hong)
The ecosystem components are operated through consistent mechanisms, policies, and laws to create a secure data interchange system, ensuring the rights and duties of businesses and consumers.
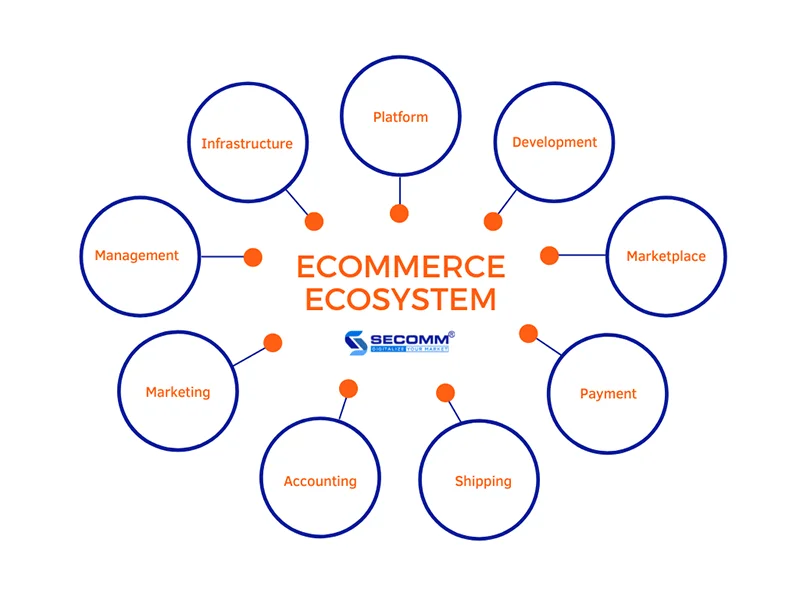
The main components:
- Ecommerce infrastructure system includes hardware (servers and devices), software (services/tools for managing and analyzing), networks, and facilities forming the basis for the remaining components and ensuring that all e-commerce processes run smoothly and efficiently.
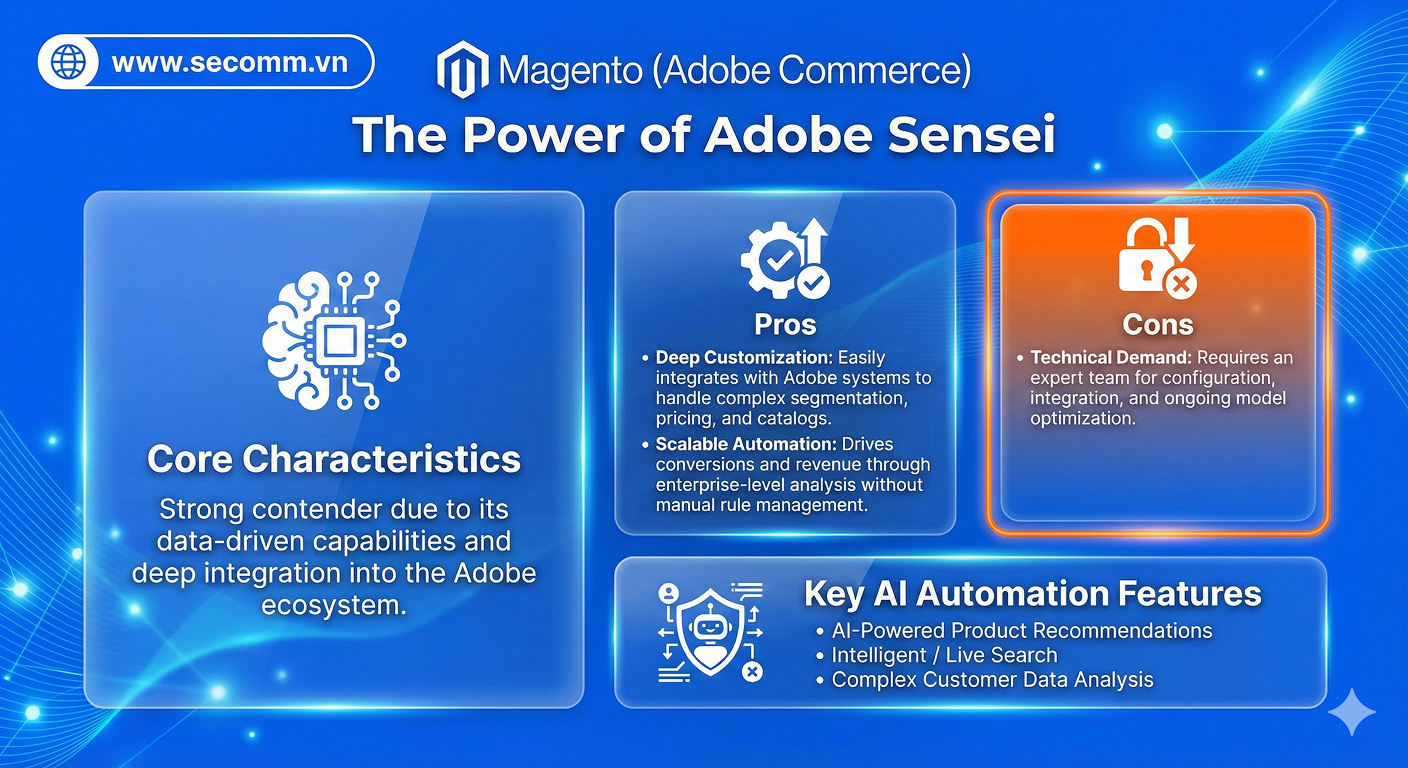
- Ecommerce platform is a software application to build and manage all the activities. Today’s well-known ecommerce platforms can be mentioned as Magento, Shopify, BigCommerce, WooCommerce, Haravan, Wix,…,
- The development component provides services and solutions for ecommerce websites, systems, and processes. In Vietnam, some of the notable ecommerce service and solution providers may include SmartOSC, Isobar, SECOMM,…
- Marketplace provides an environment and all services to support ecommerce, allowing commercial activities between plenty of sellers and buyers. The leading ecommerce marketplaces in Vietnam can point to Shopee, Lazada, Tiki, Sendo,…
- The payment includes networks, systems, and devices processing all ecommerce transactions. Currently, jointly with the payment, card types (domestic card, Visa, Mastercard,…), payment gateways (OnePay, PayPal, …) or e-wallets ( Momo, ZaloPay, ..) have been developing in Vietnam.
- The shipping system includes the entire process of managing and distributing goods from the warehouse, packaging and delivering to customers. Typically shipping providers are Giao Hang Tiet Kiem, Giao Hang Nhanh, ViettelPost, J&T, Ahamove,…
- Accounting software helps manage all data on ecommerce invoices, sales revenue, and cash flows. The birth of e-invoice software such as e-invoice, MISA meInvoice, FPT.eInvoice,… has maximally supported accounting processes.
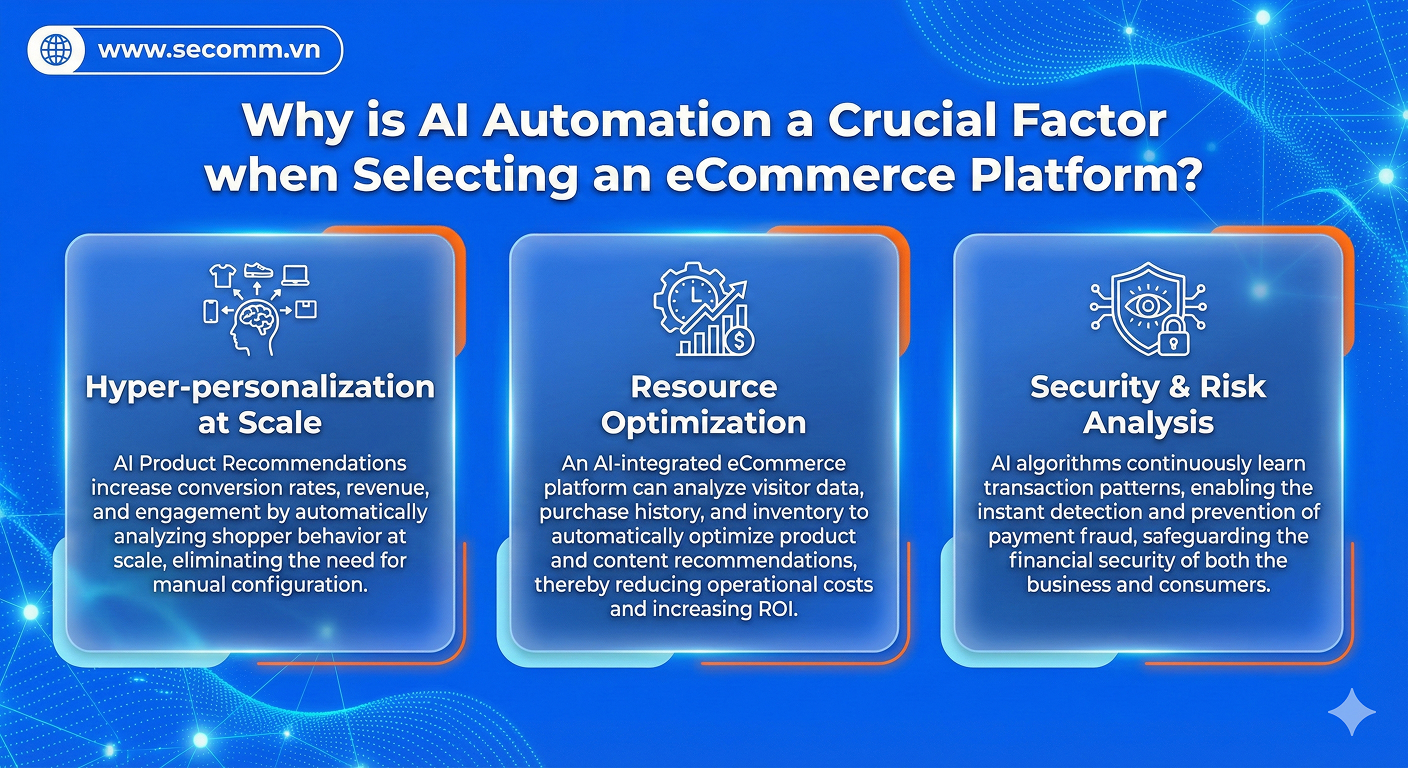
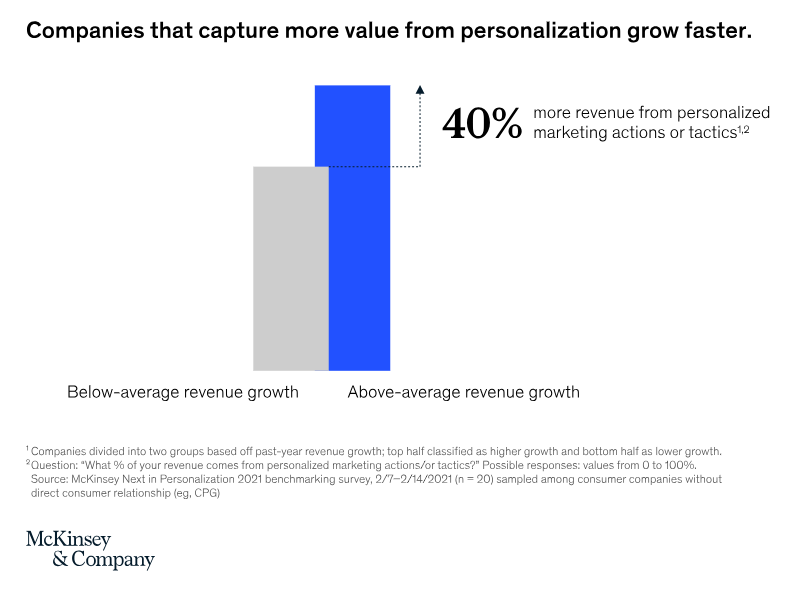
- Marketing supports promoting brands and products, and simultaneously approaches and personalizes customer experience through strategies, channels, and tools.
- Management system uses the resource and operational processes software to enhance the seamlessness and performance of the entire ecommerce system. The most popular management systems are ERP, CRM, IMS, POS, OFM, etc.
2. How has the ecommerce ecosystem developed and perfected?

Stage 1: The fundamental ecommerce ecosystem
In the 1st stage, while customers are not been aware of their purchasing needs, the ecommerce ecosystem has fundamentally formed, beginning to approach, educate and stimulate consumers’ concern about brands and products.
Basic components (4/9): Infrastructure, Platform, Marketplace, Marketing
- Infrastructure: essentially participating in the ecosystem, mainly using desktop and network devices, data systems, and facilities to support operating other components inside the ecosystem.
- Platform: building website on simple platforms, including simple ecommerce interface and functions.
- Marketplace: implementing sales on the ecommerce marketplaces to run sales-efficiency experiments, increase brand popularity, and approach a wide range of users for nurturing potential customers.
- Marketing: using social media, advertising, content, email,… to increase views, and traffic and build awareness of brands, products, and services in the potential customer mindset.
Highlight components: Marketplace, Marketing
Inchoate components: Development, Payment, Shipping, Accounting and Management
Stage 2: The basic-operating ecommerce ecosystem
Customers become aware of their needs at this stage. As a result, the ecosystem comes into operation to approach potential customer needs.
Basic components (8/9): Infrastructure, Marketplace, Platform, Development, Marketing, Payment, Shipping, Accounting
- Infrastructure: well-developed, ensuring all the seamless processes and interactions among components.
- Marketplace: maintaining sales operation with constantly renewed programs and events to attract potential customers.
- Platform: operating the end-to-end system, continuously updating new versions to enhance the increasing performance.
- Development: developing and operating the ecommerce system and continuously improving system productivity.
- Payment: perfecting the payment processing system and fully integrating payment gateways.
- Shipping: perfecting the shipping system and partnering with shipping providers to deliver the first orders.
- Accounting: completing the accounting and financial system to manage all ecommerce transactions
- Marketing:
- Increasing web-display frequency on search engines to increase brand and product identification and attract more potential targets.
- Continue promoting social channels, advertising, content, email,… to improve the experience, education, and conversions for target customers.
Highlight components: Marketing, Payment, Shipping, Accounting
Inchoate components: Management
Stage 3: The advance-operating ecommerce ecosystem
The ecosystem enhances operation with many essential functions to directly navigate customers’ searching and buying considerations, thereby increasing the customer funnel conversion.
Advanced components (8/9): Infrastructure, Development, Marketplace, Platform, Payment, Shipping, Accounting, Marketing
Maintaining components: Infrastructure, Development, Marketplace, Accounting
Highlight components: Platform, Payment, Shipping, Marketing
- Platform: investing in developing the ecommerce system with a dedicated platform to operate and process complicated functions optimally.
- Developing new functions to optimize user experience: interface renewal, promotion features (pop-up, banner,…), customer service (live-chat, chatbot),…
- Optimizing the “Call-to-action” function and gathering emails on the website, at the same time implementing sale-off, and promotion programs to increase conversion
- Payment: integrating more payment methods to diversify the checkout experience, from COD payment, and internet banking to VISA, Mastercard, or e-wallets.
- Shipping: optimizing the packaging process, improving delivery speed by partnering with transportation providers or building an in-house delivery team, in addition, optimizing operational processes for instant order fulfillment.
- Marketing:
- Website: concentrating on blog content and optimizing product detail content.
- Continuously maintaining Social Marketing performance
- Focusing on the email channel to nurture and stimulate potential customers.
Inchoate components: Management
Stage 4: The optimal-operating ecommerce ecosystem
When customers transition to the decision-making stage of purchasing, the ecosystem maximizes effectiveness in all processes and operational components, simultaneously focusing on developing conversion functions through continuous improvement and innovation of marketing components.
Optimal components (9/9): Infrastructure, Development, Marketplace, Platform, Payment, Shipping, Accounting, Marketing, Management
Maintaining components: Infrastructure, Development, Marketplace, Platform, Payment, Shipping, Accounting
Highlight components: Marketing, Management
- Marketing: focus on ecommerce marketing strategy
- Implementing email plans to remind abandoned carts to stimulate potential customers constantly
- Maintaining customer service using email channels to gather customer feedback and reviews while using products
- Promoting loyalty programs with discounts, accruing points, membership cards,… to increase return customers
- Management:
- Integrating ERP software to manage data, human resources, and processes more seamlessly
- Synchronizing Website with ERP and CRM to optimize operational processes and increase customer funnel conversion
Stage 5: The complete ecommerce ecosystem
All the ecosystem components are complete and effectively interact with each other. In addition, the ecosystem is directed towards operating maintenance to support product experience, customer retention, and return-customer stimulation.
Optimal components (9/9): Infrastructure, Development, Marketplace, Platform, Payment, Shipping, Accounting, Marketing, Management
Maintaining components: Infrastructure, Marketplace, Payment, Shipping, Accounting, Marketing
Highlight components: Platform, Development, Management
- Platform: using customer reviews to improve the quality of products, services, and system functions
- Development: providing solutions and developing specialized functions for a much more complex ecommerce system
- Management: seamlessly operating and managing all data, processes, and resources among website, ERP, CRM, and POS systems
3. Barriers Facing the ecommerce ecosystem in Vietnam
Although the ecommerce ecosystem in Vietnam is proliferating, it is being hampered by substantial barriers.
Outside barriers
Legal issues in ecommerce
In comparison to the general Vietnam market, ecommerce would be a relatively new business. As a result, the legal framework for ecommerce remains inadequate and disorganised. In which tax, security, and information authentication in e-transactions, intellectual property rights, etc., have not been adequately safeguarded by legal means.
The disparity between the legal framework’s perfection and the faster market change makes ecommerce challenging to control or at threat of unhealthy growth.
Circular No.47/2014/TT-BCT on the management of ecommerce websites, particularly, contains guidelines on the ecommerce business registration process and procedures. However, their controlling method has not been carried out properly, resulting in fewer registered businesses than actual statistics.
Therefore, most of the legalities of starting ecommerce business have not been verified, leading to transaction fraud and other fraud. More serious are domain misappropriation and spoofing by hackers to business counterfeiting, causing severe damage to businesses and consumers.
This shows that the current legal framework needs to enforce more specific steps to prevent attacks from cybercrime.
Consumer confidence
One of the significant barriers is the reality that occurs throughout the purchase process. For example, product and service quality issues, typically the quality assurance process (for counterfeits, poor quality products), transaction frauds (credit account takeover), and shipping (fraudulent goods exchange in packaging and shipping),… all have a direct impact on customer interests and the healthy, sustainable growth of the ecommerce ecosystem.
Investment barriers
Another significant barrier is the competition and investment budgets among businesses. In particular, data security requirements and infrastructure investments are putting financial pressure on existing ecommerce businesses. As a result, the ecommerce ecosystem is primarily controlled by the expansion of marketplaces and international businesses investing in the Vietnam market.
Inside barriers
Although the current number of ecommerce ecosystem components is fully completed, the uneven development level makes interactions and operational processes sporadic and challenging to achieve optimal growth. The challenges have mainly come from:
- Ecommerce infrastructure: The limitations of infrastructure, facilities, and capacity to access technology in rural areas create notable gaps compared to urban areas, affecting market coverage in Vietnam.
- Logistics: Logistics infrastructure has fallen behind ecommerce growth. The inequitable synchronization between logistics services and the lack of technology are still significant barriers for almost all SME logistics businesses in Vietnam.
- Payment: Cash payment (COD) accounts for a high percentage, 60%, of transactions in the entire e-payment market share. This creates more risk when parcel refusal and failed deliveries make the order fulfilment process more costly and time-consuming.
Besides, the most significant barrier is the lack of a strong connection among ecosystem components to bring unifying and synchronous ecommerce solutions. The current connections are commonly between marketplaces and shipping providers or digital banking/e-wallets to provide economical and intriguing solutions for consumers.
However, that seamless and unified connectivity has not yet evolved to maximize business interactions in the ecosystem and among businesses in the ecommerce market.
4. Solutions for SMEs
The ecommerce ecosystem completion is a sustainable foundation for SMEs to build and implement ecommerce business plans aligned with each business stage while generating a complete ecosystem for themselves.
About the number of components
Businesses should determine the suitable components according to each business model and growth stage.
For example, a small and medium-sized enterprise would use the essential ecommerce components, such as the platform, to develop a complete ecommerce system, complete payment, shipping, and integration processes integrating more management software, namely CRM, POS, accounting, and marketing tools.
Nevertheless, a medium/large-sized enterprise can integrate ERP for resource operation or omnichannel for efficient expansion.
About timeline
Following the identified ecosystem components, a business can estimate the appropriate timeline to promote in-time business processes, fully satisfying the market requirements and customer needs. Thereby, the satisfaction enhances the planning efficiency and the ecommerce ecosystem.
About the implementing budget
The budget would be distributed more specifically once the essential ecosystem components are clearly defined for your business model. Determining the proper budget is a critical factor for SMEs to successfully implement ecommerce and sustainably grow. This is especially important for existing SMEs due to the considerable budget pressures and the long-term investment process.

However, most of those SMEs still face many challenges in building their ecommerce plans. They have not adequately defined their business model’s needed and best-suited components, resulting in timeline and budget dilemmas.
With in-depth experience providing full-service ecommerce solutions, SECOMM will accompany businesses in respective stages of ecommerce implementation with tailor-made solutions.
Contact SECOMM to receive a comprehensive ecommerce consulting solution for your businesses.


























































Comment (0)