It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Sign Up for newsletter!
Subscribe to get the latest eBook!
Hotline






Unlike building eCommerce websites for simpler models like B2C or B2B, implementing an online marketplace requires a higher level of technical knowledge, programming skills, database management, system administration, and more.
In this article, SECOMM will share the essential steps for successfully developing an eCommerce marketplace, from market research and business planning to designing an appealing user interface, developing functional systems, and more.
Market research and business planning are essential and indispensable initial steps in starting an eCommerce marketplace or any business operation.
Here are some considerations for businesses when undertaking these activities:
The eCommerce platform is a crucial element in the process of building an online marketplace. If the right choice is not made from the beginning, businesses may find themselves entangled in the whirlpool of technology when implementing their marketplace.
Typically, there are two types of eCommerce platforms for businesses to choose from: SaaS and Open Source.
SaaS (Software as a Service) eCommerce platforms are a software distribution model for building websites.
In this model, data is stored on the provider’s server, and the platform is responsible for handling technical aspects for businesses. Some popular SaaS platforms today include Haravan, Shopify, BigCommerce, and more.
An Open Source platform, or open-source software, is software with publicly available source code that anyone can use for free. Open-source platforms are an optimal choice for businesses looking to develop complex eCommerce systems, especially tailored to the specific needs of an online marketplace.
Prominent examples of Open Source online marketplaces include Magento, WooCommerce (a plugin for WordPress), OpenCart, and more.
Each platform type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, businesses should either have an in-house team or collaborate with an experienced and highly skilled eCommerce marketplace development agency to effectively advise on the selection, development, and operation of the chosen platform.
The initial decision regarding resource allocation for starting an eCommerce marketplace system has a profound impact on a company’s early business direction. Companies can choose to either collaborate with specialised development firms or establish their own in-house teams.
Opting for an in-house team entails investing time and budget into the recruitment and training of staff. However, it provides effective resource management, enabling businesses to adapt and develop the online marketplace system in alignment with their original vision.
Alternatively, when companies decide to seek external partners, they need to collaborate with various firms to identify the most reputable one. However, upon finding a partner with extensive practical experience in marketplaces across multiple platforms, businesses benefit from consultations and a multitude of solutions from diverse perspectives even before system development begins.
Moreover, these firms possess a wealth of experience in promptly addressing emerging issues during system development and operation. This not only ensures that the requirements are met as anticipated but also facilitates valuable knowledge and experience exchange among all parties involved.
The User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) are often considered two inseparable aspects in the process of designing the interface for an eCommerce marketplace.
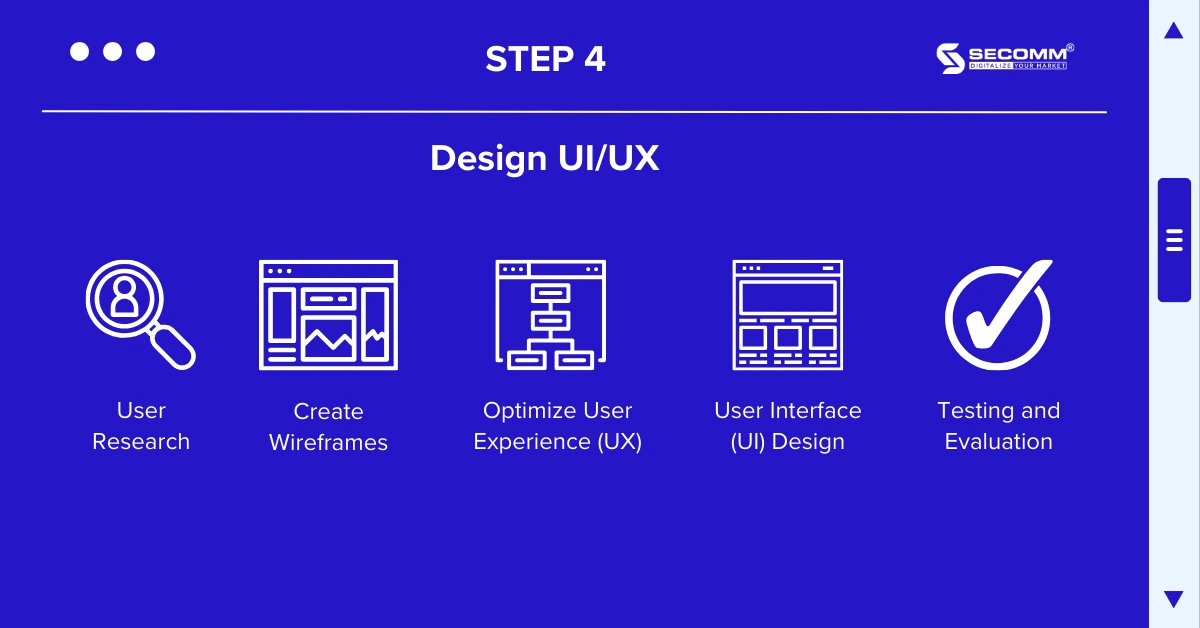
Here are the key steps in the UI/UX design process:
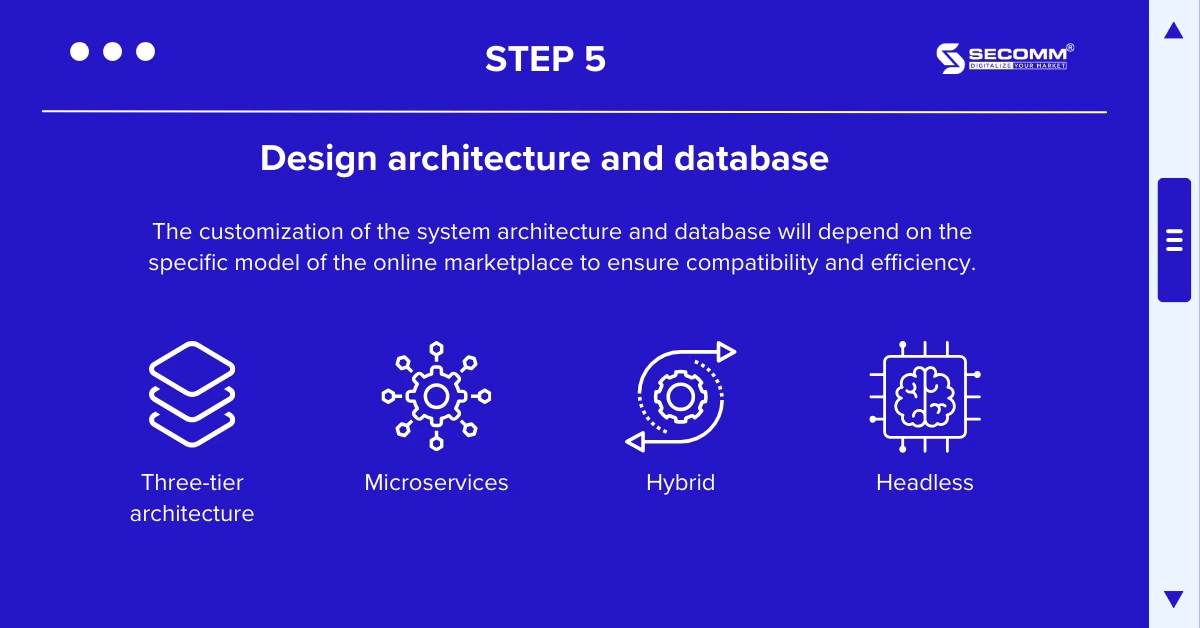
Starting from business requirements, the technical team will build the system architecture for the eCommerce marketplace based on the appropriate technology framework or platform. Various architectures can be used, such as three-tier architecture, microservices architecture, hybrid architecture, headless architecture, etc. Each type of architecture has its own advantages and limitations, so businesses need to carefully consider and work with experts on the team or partners to choose the most suitable system architecture for each stage.
Another equally important next step is to establish security and data management. Businesses need to define security measures to protect user data, payment information, and other critical data. Ensure that data is encrypted and transmitted securely via an SSL connection. Implement data protection measures such as access control, user authentication, data encryption, and data integrity checks.
Depending on the operating model of the marketplace, system and database design may need to be customized to be suitable and effective.
After completing the essential functional systems, businesses should continue to develop specific features for their online marketplace, such as:
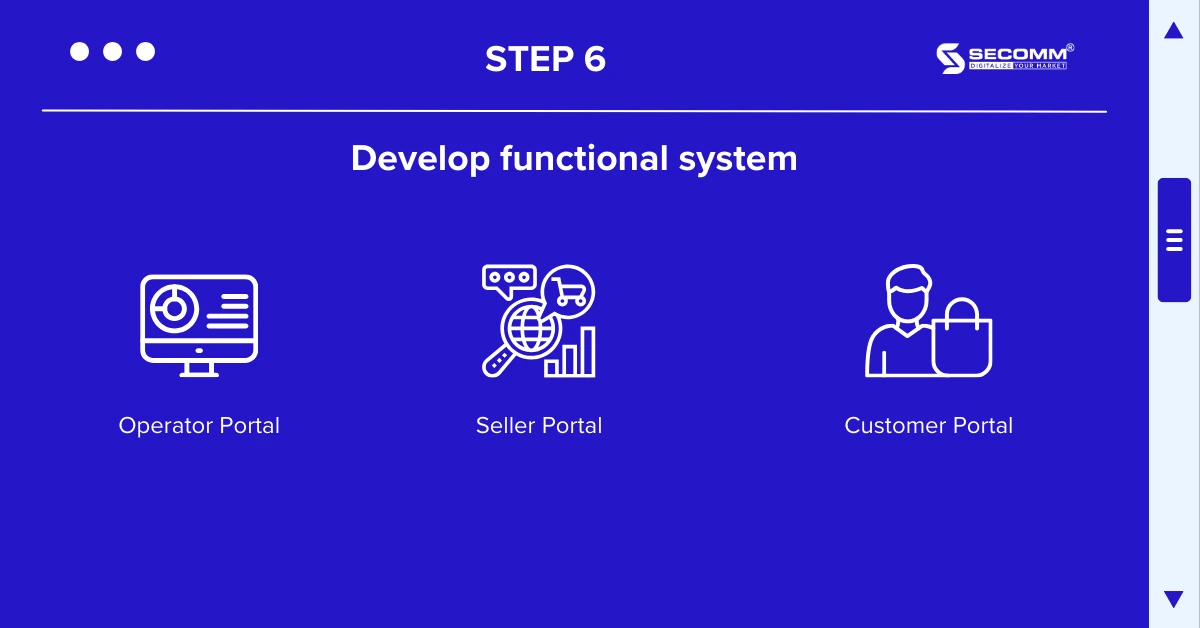
Operator Portal: Full control of platform information, including seller management, product categorization, customer segments, supply chain management, ad content control, and more.
Seller Portal: Sellers self-manage their presence in the marketplace, including product listings, orders, and activities, etc
Customer Portal: Allow users to perform and manage basic information such as phone numbers, email addresses, delivery addresses, adjust payment options, request quotes, manage shopping lists, check order status, etc.
Whether you’re building an in-house team or enlisting the services of external development agencies, the quality testing phase of a project holds immense significance. This critical stage is where businesses validate that the system functions as expected and complies with the initial requirements.
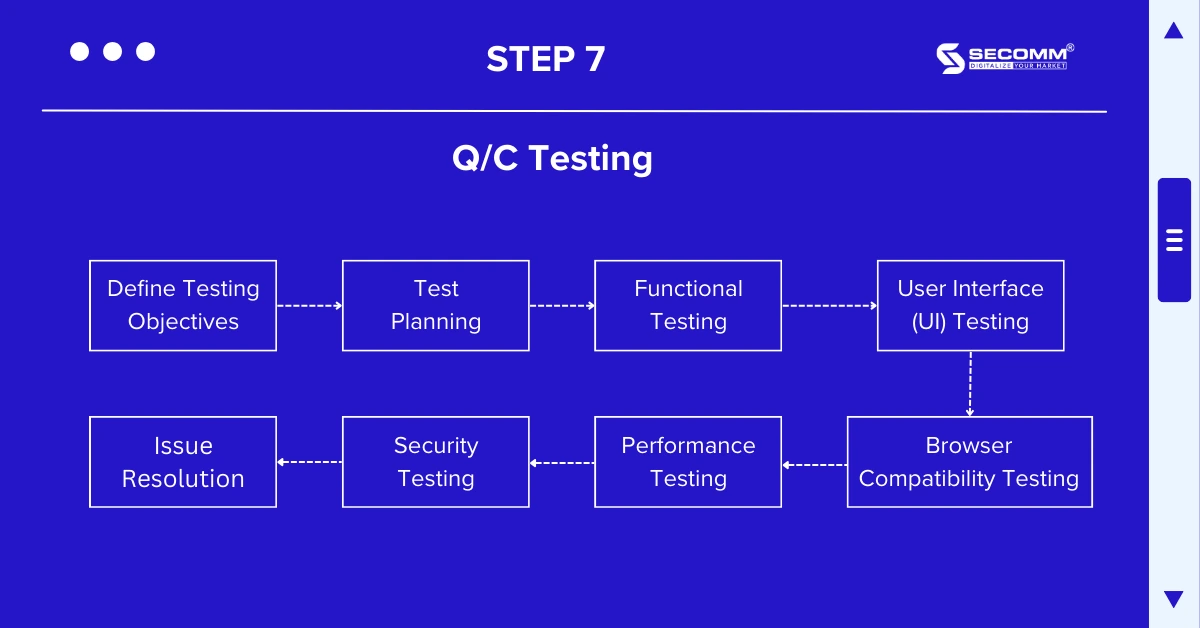
Step 1: Define Testing Objectives
Identify the objectives and scope of the testing process. Set specific criteria and requirements that the business wants to verify to ensure the platform operates accurately and meets the specified requirements.
Step 2: Test Planning
Determine a detailed test plan, including test cases, scenarios, and data. Identify the resources, timeline, and scope of the testing phases.
Step 3: Functional Testing
Verify all website functions to ensure they are working correctly as expected. If the business’s website supports multiple languages and regions, it should also verify compatibility and display of each feature in different geographical areas.
Step 4: User Interface (UI) Testing
Ensure the interface is designed beautifully and user-friendly. Evaluate information display, buttons, links, and user experience on various devices, including mobile and tablet.
Step 5: Browser Compatibility Testing
Test the website on popular browsers such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, and Microsoft Edge to ensure compatibility and correct display on all platforms.
Step 6: Performance Testing
Assess website performance, including page load speed, concurrent processing, and scalability. Ensure the website operates smoothly and can handle the expected traffic load.
Step 7: Security Testing
Examine the platform’s security by testing intrusion potential, data security, and user authentication. Verify security methods such as SSL, data encryption, and security certificates.
Step 8: Issue Resolution
Document and track any errors and issues that arise during testing. Identify the root causes, rectify the errors, and retest until the testing process is approved, and the entire system is ready for go-live and operation.
Go-live is the final stage in the process of starting an eCommerce marketplace when the system is officially launched and becomes operational.

To ensure a successful go-live process, businesses should prepare a checklist known as the Go-live checklist. This is a list of tasks that the deployment team needs to perform to prepare the system for go-live. The checklist includes task items, responsible individuals, status, and how they affect the system.
Regularly updating the system is important for businesses to adapt to the ever-changing customer needs, improve customer experience, stay abreast of emerging technology trends, enhance competitiveness, and more. Moreover, continuous bug fixes and security patch updates enhance the brand’s credibility, safeguard users from internet threats, and so on.
Moreover, the development of new features empowers businesses to capitalize on market opportunities and scale their operations more professionally. For example, after a period of operation and accumulating a specific customer base, businesses can introduce features tailored to loyal customers.

Running a thriving marketplace involves a multitude of factors, such as the business model, financial capabilities, and building strategic partnerships with diverse brands. However, a well-functioning eCommerce platform with high performance plays a vital role in the path to success. The journey of marketplace development is anything but straightforward. It requires substantial investments of time and resources for thorough research and the seamless alignment of solutions with each development phase.
Recognizing the challenges and hurdles that businesses face during the process of starting their eCommerce marketplace, feel free to contact or call SECOMM directly at (02871089908) for a free consultation.
 2
2
 16,152
16,152
 0
0
 1
1Subscribe to get the latest eBook!
Hotline