It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.




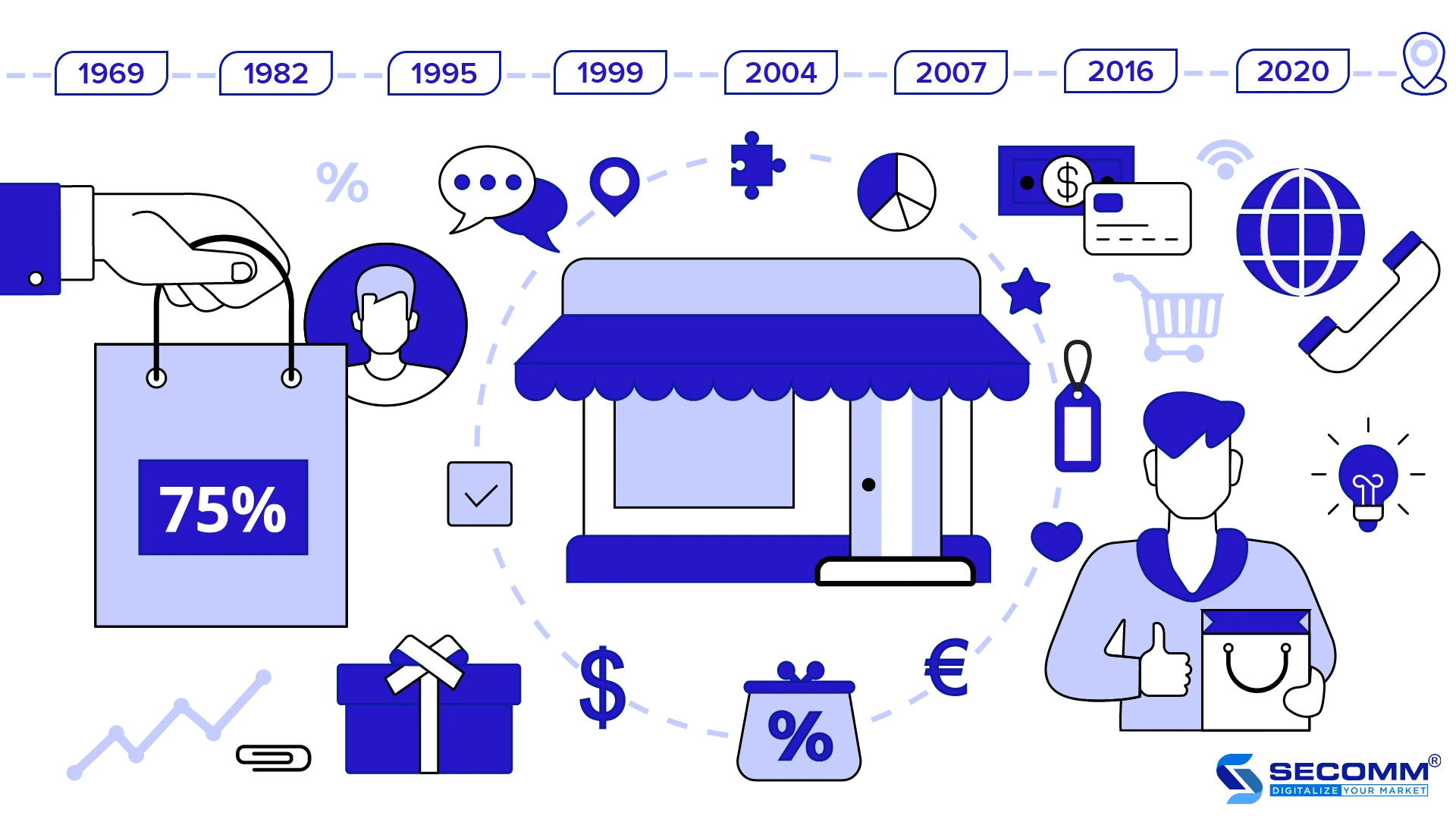
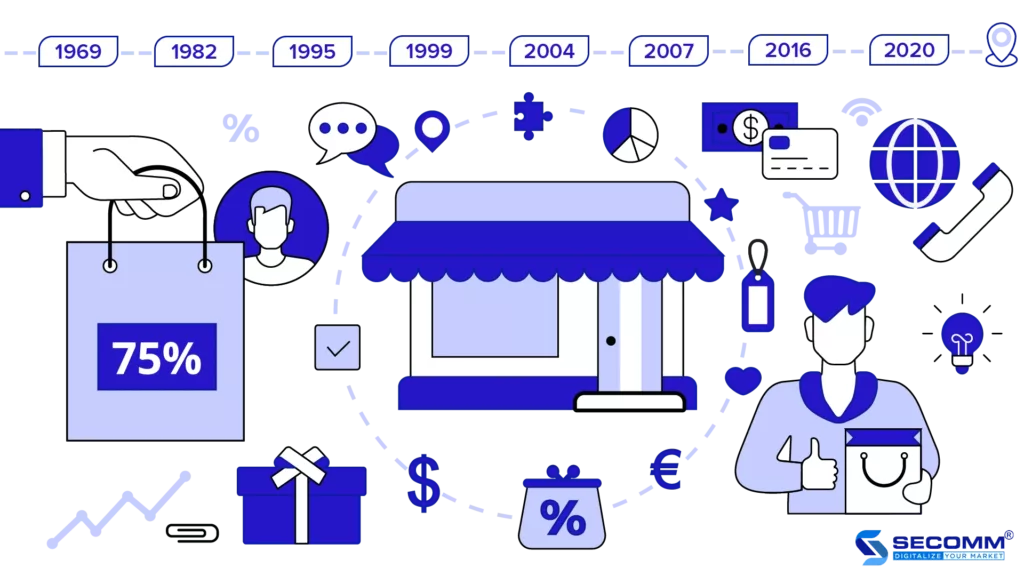
OVER 50 YEARS OF GLOBAL ECOMMERCE JOURNEY (1969 – 2020)
OVER 50 YEARS OF GLOBAL E-COMMERCE JOURNEY (1969 – 2020)
1969: The first online service provider – CompuServe
In 1969, Dr. John R. Goltz, Jeffrey Wilkins, and electrical engineering students founded CompuServe – a service that provided an information-sharing portal through the Internet and email network connections.
1979: Father of electronic commerce (EC) system – Michael Aldrich
Michael Aldrich pioneered the first EC system by connecting a television and a computer for transaction processing via telephone lines, enabling a secure information system to be opened and shared externally. This innovation laid the foundation for the development of modern EC systems.
1982: The first ecommerce company – Boston Computer Exchange
Initially a store supporting the resale of used computers, Boston Computer Exchange became one of the earliest models for today’s EC companies.
1992: The first online book market – Book Stacks Unlimited
Charles M. Stack established the brand Book Stacks Unlimited as the world’s first online book store. Initially using a dial-up bulletin board format, the company later transitioned to the Internet to create an online book trading market.
1995: Birth of the ecommerce giant – Amazon
Jeff Bezos founded Amazon initially as a book-selling business but later expanded its business model to include various products by incorporating new technologies such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence. Amazon ushered in a new era for the EC industry by integrating Internet technology into its business strategy.
1998: Online payment gateway, a platform for ecommerce development – PayPal
Confinity (the predecessor of PayPal) was founded by Max Levchin, Peter Thiel, Luke Nosek, and Ken Howery. In 2000, eBay acquired Confinity and renamed it PayPal, the world’s largest online payment gateway. PayPal addressed many limitations of traditional payment methods, making the buying and payment process more convenient and laying the foundation for EC development.
1999: The king of the ecommerce industry in China – Alibaba
Alibaba officially entered the EC market, successfully raising $25 million in capital. By 2001, the company became profitable and led the EC platform under the B2B, C2C, and B2C business models. In 2020, Alibaba contributed $12.2 billion to global EC revenue.
2000: Online advertising tool serving ecommerce marketing – Google AdWords
Google introduced Google AdWords, the world’s first online advertising tool. This tool supported businesses in marketing their products on Google’s search network, boosting sales for EC companies at that time.
2004: The first ecommerce website development platform – Shopify
After unsuccessful attempts to build an e-commerce website selling snowboarding equipment on various platforms, Tobias Lütke and Scott Lake founded Shopify – the first platform supporting the development of EC websites worldwide. This platform enables users to easily create online stores without requiring extensive technical knowledge.
2005: Ecommerce event – Cyber Monday
The National Retail Federation (USA) coined the term “Cyber Monday” to describe the first Monday after Black Friday, initiating the online shopping season between Thanksgiving and Christmas. This event marked economists’ interest in the global retail market.
2007: Sustainable ecommerce development platform – Magento
Developed by Roy Rubin and Yoav Kutner in 2007, Magento is an open-source platform written based on the Zend Framework and PHP programming language, specifically designed to build complex EC websites. Magento, known for its multitasking capability, high performance, flexible customization, and easy scalability, has become the top choice for enterprises with 200,000 partners and 2.5 million downloads worldwide.
Multinational corporations using Magento to build sophisticated EC systems include Samsung, Nike, Coca-Cola, Asus, HP, Lenovo, Canon, Sigma, Olympus, Port, Pox, Nestle, BevMo, Burger King, and millions of small and medium-sized EC sites globally.
2016: Facebook joins the ecommerce
game – Facebook Marketplace
With the ambition to dominate the EC market, Facebook, a tech giant, continuously introduced new features on Facebook Marketplace, Instagram, and WhatsApp, and collaborated with various EC platforms (Shopify, OpenCart, BigCommerce, WooCommerce, and Magento). This made giants like Amazon, Lazada, and Shopee wary, demonstrating the strong allure of the EC market.
2017: Growth of ecommerce
The global EC industry set a new revenue record of $2.352 trillion in 2017, a 25% increase from 2016 (according to eMarketer – a US market research company). Cyber Monday alone surpassed $6.5 billion in online sales. Economists predict that EC will be the world’s focal industry by 2025.
2020: COVID-19 boosts the ecommerce explosion
2020 marked a significant turning point for the global EC industry. The impact of COVID-19 accelerated the construction of EC systems to meet consumer demands promptly. Currently, EC is not only present on platforms like Amazon, Shopee, and Lazada but also brands are starting to build their own EC websites. Additionally, EC spans various sectors from fast-moving consumer goods (fashion, food, technology) to service sectors (travel, finance, education, furniture, and real estate).
According to the “Southeast Asia Internet Economy 2020” report by Google & Temasek, consumers tend to spend more time shopping online than before COVID-19 (increased from 3.7 hours/day to 4.7 hours/day). Global B2C EC revenue increased from $1.948 trillion to $4.280 trillion, doubling Statista.com’s forecast of $2.238 trillion.
COVID-19 has brought positive effects on the global rise of the EC industry and opened up new opportunities for the Vietnamese economy.
 2
2

 4,525
4,525

 0
0

 1
1

TOP 3 SAAS ECOMMERCE PLATFORMS: HARAVAN, SHOPIFY, AND BIG COMMERCE
Many firms have selected SaaS eCommerce platforms to create e-commerce enterprises for brands because of their essential qualities, which can rapidly install eCommerce at a low cost.
Haravan
In Vietnam, Haravan is the most popular eCommerce platform that allows multi-channel sales. This platform was officially launched in 2014, aims to assist companies in developing professional e-commerce websites at an affordable cost.
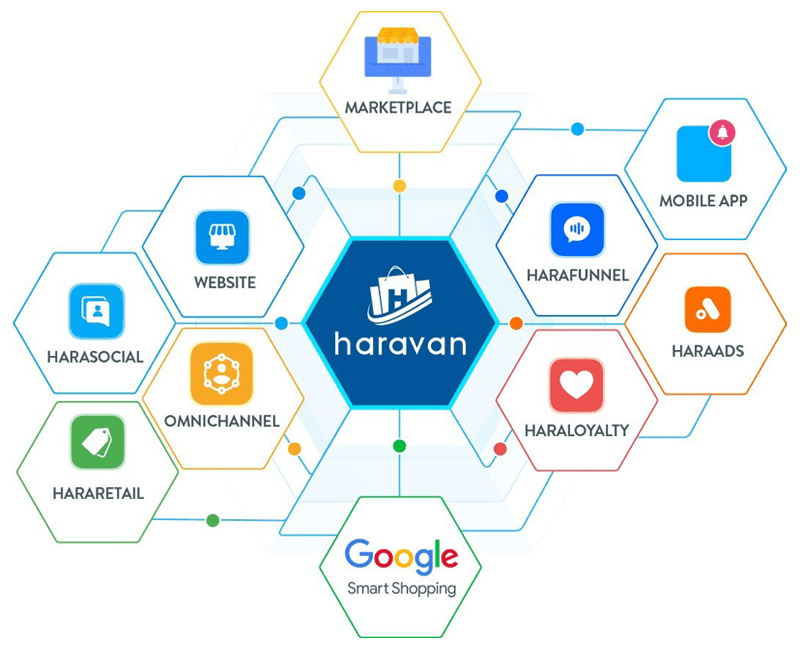
Themes
Haravan provides many UI/UX themes so that firms may select a design that suits the brand’s image. At the same time, many organizations regard the admin interface to be easy to use. However, companies must pay additional fees to raise the number of admin accounts.
Features
Haravan’s essential features, on the other hand, are just enough for businesses to run their web operations successfully but not ideal sufficient for long-term development. In addition, because Haravan is a SaaS platform, organizations find it difficult to customize or expand functionality outside of its ecosystem.
Deployment time
Haravan’s drag-and-drop manipulation allows companies to create an eCommerce website with all the critical functionality for business online in around 30 minutes.
Deployment costs
Businesses must pay a monthly charge ranging from 200,000 VND to 3,000,000 VND based on their demands:
- Standard (200,000 VND/month): Appropriate for independent sellers
- Pro (600,000 VND/month): For organizations who wish to implement Omnichannel
- Grow (1,500,000 VND/month): For firms need automating processes to take care of and resell current customers
- Scale (3,000,000 VND/month): Help establish loyal customers
Haravan is now gaining popularity in the Vietnamese eCommerce business, particularly in the B2C model or low-involvement product business, due to its ability to deploy with affordable charges swiftly. Vinamilk, Juno, and L’Oréal are some companies that use Haravan.
Shopify
Shopify is a software-as-a-service platform for online retailers and point-of-sale systems. Shopify is popular among the eCommerce community due to its simplicity, quick development timelines, and low setup expenses.

Themes
Shopify provides many attractive themes that are device-agnostic and ideal for a broad array of industries. Shopify’s admin dashboard is simple to use, and it offers a Vietnamese version for Vietnamese firms. Like Haravan, firms must upgrade their service packs to expand the number of admin accounts.
Features
Deployment time
Depending on the system’s complexity, each business will need some time to get used to Shopify. Still, in general, it will not take long for companies to establish a website, taking between 1 and 2 days on average.
Deployment costs
Shopify has created a variety of packs for companies to choose from:
- Basic Shopify ($29/month): Suitable for new businesses with small sales.
- Shopify ($79/month): Appropriate for growing online enterprises
- Advanced Shopify ($299/month): Ideal for firms that need to expand and want advanced reporting capabilities.
Shopify also creates different service bundles to meet a range of organizations:
- Shopify Lite ($9/month): Ideal for businesses to integrate sales buttons and payment services into an existing website or blog.
- Shopify Plus ($2000/month): Offer a sophisticated eCommerce solution for large enterprises that need to process high-volume orders.
Shopify is constantly developing and enhancing its offerings to meet a wide range of customer requests rapidly and effectively, making it perfect for B2C enterprises. However, the monthly cost is a significant impediment because firms must pay significantly more to use extra functions. Sony Vietnam, Vsmart, and DHC Vietnam are some Vietnamese companies that use Shopify.
BigCommerce
BigCommerce is a SaaS platform that launched in 2009 and has made a significant impact on the eCommerce developer community. Despite being founded later than other platforms, BigCommerce does not fall behind in terms of a functional system, theme store, and so all.

Themes
BigCommerce provides a wide range of visually appealing themes and adapts to customer behavior, including 12 free versions and over 160 professional ones. BigCommerce’s admin dashboard is easy to use, and it supports businesses in rapidly setting up eCommerce websites. However, since BigCommerce does not offer a Vietnamese version, firms must hire and train English-qualified employees to manage the site.
Features
BigCommerce’ packages are jam-packed with features and add-ons to help businesses achieve solid internet business. However, BigCommerce’s capacity to customize and expand functionalities remains limited, restricting firms from adapting to their needs to deal with industry-specific difficulties.
Deployment time
Thanks to its drag-and-drop page builder feature, the time it takes to establish a website on BigCommerce is shortish. BigCommerce construction process takes about 1-2 days on average.
Deployment costs
BigCommerce now supports three package options and one on-demand solution:
- Standard: $29.95/month for businesses with more than $50,000 in revenue
- Plus: $79.95/month for enterprises with more than $180,000 in revenue
- Pro: $299.95/month for companies with more than $400.000 in revenue
- Enterprise: For firms with high sales volumes, costs will be calculated depending on the brand’s online sales
Moreover, BigCommerce will charge you additional fees based on your online sales.
Overall, BigCommerce is not inferior to Haravan or Shopify in every way; nevertheless, the central issue right now is that this platform does not support Vietnamese enterprises.
Which SaaS eCommerce platform is best for your company?
Inheriting the advantages of a SaaS eCommerce platform, all three platforms are easy to use, with various themes and functions for quick construction at a reasonable cost.

Businesses that solely conduct business in Vietnam may choose to use Haravan to take advantage of cost-competitive benefits and functionalities tailored to suit Vietnamese shopping habits. Shopify and BigCommerce are options to explore if you want to develop your business worldwide. Simultaneously, Shopify is ranked higher for providing great 24/7 live chat support, which will aid companies in addressing difficulties as quickly as possible. As a consequence, Shopify will be ideal for large-scale and high-volume enterprises. BigCommerce, on the other hand, compresses functionality into more affordable solutions and is not restricted to the number of administrators like Shopify, making it suitable for small or medium-sized businesses.
However, using SaaS eCommerce platforms like Haravan, Shopify, and BigCommerce in the long term would result in the following deficiencies:
- Duplicate design ideas: Using the given interface will easily be similar to other websites, making it hard to show the brand’s distinctive qualities.
- Difficult to customize functionality: Because these platforms are not as flexible as Open Source eCommerce platforms, firms may only select from existing options and customize to the extent permitted. In the future, it will be essential to change to build advanced and specialized functions based on the features of products and industries to meet the demands of customers and the expansion of companies through time. Switching to an Open Source eCommerce platform such as Magento, OpenCart, WooCommerce, etc will take a significant amount of time and money.
- A lot of fees: Because of the monthly charge, the longer you use it, the more expensive it is to use the website. Furthermore, Shopify and BigCommerce impose extra fees based on online revenue.
- Do not own the source code: If the contract with these platforms is canceled, the company will no longer utilize the source code of the website and will have to rebuild it from scratch on the new platform. Switching platforms is not only time-consuming and expensive, but it may also result in data loss or misalignment.
SECOMM has significant experience developing complicated eCommerce websites in different countries, and we know the challenges that businesses face when selecting and implementing an e-commerce platform.
Contact SECOMM for a free consultation on eCommerce website development!
 2
2

 4,502
4,502

 0
0

 1
1

SAAS ECOMMERCE PLATFORMS VS OPEN SOURCE ECOMMERCE PLATFORMS
SaaS eCommerce Platform
A SaaS eCommerce Platform is a service delivery paradigm for developing a software-based website system. Data is kept on the provider’s server system under this approach, and that platform is in charge of dealing with technical concerns for the business.

Advantages of SaaS eCommerce Platform
Available eCommerce system
The provider pre-designs the SaaS platform for the full system, from hosting, interface, and features to technological infrastructure maintenance. As a result, organizations can quickly create and manage a website system without worrying about technological concerns.
Furthermore, the platform developer offers firms 24/7 assistance through live chat, desk help, or a hotline while the platform is in operation.
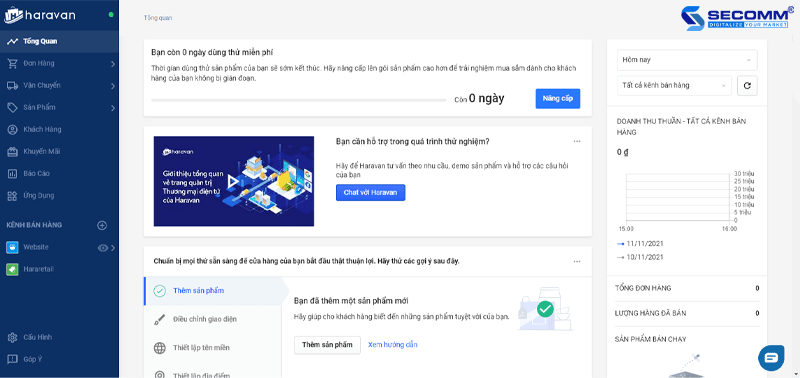
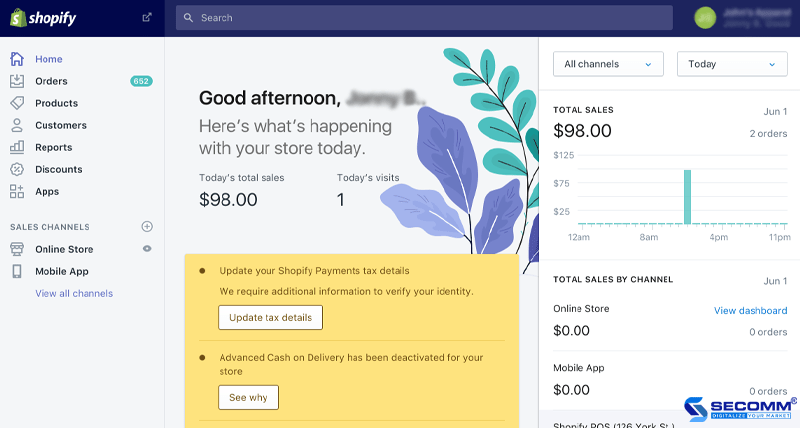
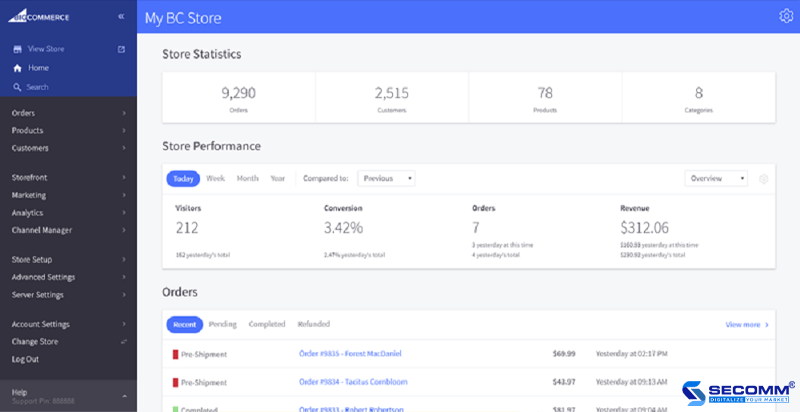
Various interfaces and functionalities
The SaaS eCommerce Platform includes a multitude of functionality and appealing UX/UI interfaces, making it suitable for a variety of businesses.
Furthermore, these platforms include a wide range of essential eCommerce functions, including product administration, order management, customer management, marketing, business analysis, and reporting to let firms quickly develop an e-commerce website. Moreover, extensions such as Omni-channel, Affiliate Marketing, E-Payment, E-Logistic, and so on are constantly added to these platforms to strengthen the e-commerce system.
Quick implementation
The time it takes to establish a website on a SaaS eCommerce Platform is quite fast, ranging from 1 to 7 days on average, depending on the website’s setup.
Affordable investment budget
The initial building cost is pretty cheap because firms would pay monthly or yearly use fees (subscription-based) to establish a website using SaaS eCommerce Platforms, such as:
- Haravan:
- Standard (200,000 VND/month): Appropriate for independent sellers
- Pro (600,000 VND/month): For organizations who wish to implement Omnichannel
- Grow (1,500,000 VND/month): For firms need automating processes to take care of and resell current customers
- Scale (3,000,000 VND/month): Help establish loyal customers
- Shopify:
- Basic Shopify ($29/month): Suitable for new businesses with small sales.
- Shopify ($79/month): Appropriate for growing online enterprises
- Advanced Shopify ($299/month): Ideal for firms that need to expand and want advanced reporting capabilities.
- BigCommerce:
- Standard: $29.95/month for businesses with more than $50,000 in revenue
- Plus: $79.95/month for enterprises with more than $180,000 in revenue
- Pro: $299.95/month for companies with more than $400.000 in revenue
- Enterprise: For firms with high sales volumes, costs will be calculated depending on the brand’s online sales
Aside from the monthly/yearly licensing charge, businesses must pay extra expenditures such as interface fees, new features, expanding the number of backend users, and POS (Point of Sale) to grow the eCommerce system.
Disadvantages of SaaS eCommerce Platform
Having no control over the source code and data
Because the enterprise’s whole website system is housed on the provider’s server, ownership and control of the website source code will belong to that platform, not the firm. Businesses who transfer platforms can no longer utilize the previous site source code and must rebuild from scratch on the new platform. Moreover, data loss or misalignment is usually unavoidable.
The enterprise’s data, like the source code, is likewise kept on the provider’s server, thus ownership and control over the data remains constrained. There are many difficulties for not owning and controlling data, such as linking data between departments, customizing users, and so on.
Poor scalability and flexibility
Because the website system depends on the SaaS platform, customization and expansion are currently limited. When it comes to upgrading existing features, developing new functions for the company’s development, in line with the particular requirements of the product and industry, and optimizing the user experience, SaaS platforms are frequently unable to adapt. As a result, switching platforms after a period of usage is unavoidable, and of course, this change will take significant time and money for the company.
Usage costs increase over time
Because you must pay monthly or yearly license fees, the longer you use the higher the overall cost of use. Furthermore, the SaaS eCommerce Platform charges on the revenue online sales.
For example, various Shopify apps, such as DCart (Create Discount Codes on Cart), OctaneAI (Similar Product Suggestions), Ali Reviews (Product Reviews), and others, would charge a monthly fee, average $10 /month/features. The more applications that are installed, the more the monthly or yearly expenses will be.

Businesses can use the SaaS platform if they wish to enter the e-commerce industry rapidly, have minimal need for customization, and do not need to enhance the system. As a result, SaaS systems are frequently selected by startups, SMEs (small and medium enterprises), and businesses just getting started in the e-commerce industry.
Open Source eCommerce Platform
Open Source is software whose source code is publicly available and freely used by anyone.
Because the data and source code will be housed on a separate server system, Open Source eCommerce Platforms have the opposite aspects of SaaS platforms. Businesses that use open source platforms must collaborate with professional website developers or build a highly specialized in-house team for the website system to achieve maximum efficiency.
Advantages of Open Source eCommerce Platform
Control the data and own the source code.
Businesses have complete ownership and control over the source code and data on the system due to the characteristic of being housed on a separate server system. As a consequence, while deploying an eCommerce website, companies only need to pay development expenses in order to utilize the source code, rather than monthly/yearly license fees just like SaaS platforms. At this point, you could reuse the previous source code if you change developers or platforms. Furthermore, security is improved, reducing hacker attacks, server failures, and technical faults from staff and consumers.
Customize the interface to meet your requirements.
Businesses have more choices in developing their website’s interface to boost brand image and maximize revenue since they use Open Source eCommerce Platforms.
Currently, there are three methods for designing interfaces:
- Use pre-existing themes: Like SaaS platforms, organizations can select and use pre-existing themes from the market, development community, or cooperation unit. This method will help businesses save the most money since a standard UX/UI theme costs between $50 and $200 on average.
- Customize the interface based on an existing theme: Similar to the preceding method, but instead of purchasing and using the same theme, firms may design their own traits by rewriting the website’s code at the front-end. Since then, organizations have cut expenses while also expressing their own distinct characteristics.
- Create your own user interface: To effectively position the brand on the website, the interface should be created individually. This is typically more expensive than utilizing a theme, but it addresses the most particular and specific requirements of the company.
Full of features and add-ons
In terms of website system features, Open Source eCommerce Platforms are quite superior to SaaS platforms. Not only have basic functions, but Open Source eCommerce Platforms also have many advanced features such as quick search, similar product suggestions, abandoned cart notifications, real-time products, and so on.
In addition, the Open Source eCommerce Platforms also has many add-ons that are improved, provided, and shared by the developer community.
Great flexibility
Because organizations control their own source code, they can simply update the functional system, build new features, or expand the system to suit business demands and meet consumer needs. At the same time, the open-source code’s flexibility allows businesses to easily link with third-party utilities in order to run the system.
Disadvantages of Open Source eCommerce Platform
Require a professional team or experienced developer
It is hard to build “tailor-made” systems for each firm with a system of various e-commerce features ranging from basic to complex, therefore systems developed on open source e-commerce platforms frequently have high accuracy. As a result, in order to build and function efficiently, a specialized team or development organization must have strong knowledge and several years of experience.
Prolonged setup time
Deployment times for open source e-commerce platforms are frequently lengthier than those for SaaS platforms. Depending on the complexity of the functional system, the average amount of time for the IT team to build a website varies from 3 months to 1 year.
Expensive development
Using an open-source platform is basically free, but having a full e-commerce system from website to mobile app needs a significant commitment of your own labor. The in-house IT team will design interfaces and functions. As a result, the initial cost of developing an e-commerce website using an open-source platform is pretty expensive, an average of $10,000 per project.
The Open Source eCommerce Platform is suited for all sorts of enterprises due to its numerous features. However, budget and implementation time restrictions have kept many small and medium-sized businesses from utilizing it. Large firms frequently engage in these platforms to construct specialized and specialized eCommerce systems.
In general, the decision of which eCommerce platform to select will be determined by each firm’s business plan, budget, and time of eCommerce development.
 2
2

 4,176
4,176

 0
0

 1
1